444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Japan MCU market represents a cornerstone of the nation’s advanced semiconductor industry, driving innovation across automotive, industrial automation, consumer electronics, and IoT applications. Microcontroller units (MCUs) serve as the intelligent backbone of countless electronic devices, from smart home appliances to sophisticated automotive systems. Japan’s position as a global technology leader has fostered a robust ecosystem for MCU development and manufacturing, with domestic companies like Renesas Electronics, Toshiba, and Rohm Semiconductor maintaining significant market presence alongside international players.
Market dynamics in Japan reflect the country’s commitment to technological advancement and digital transformation initiatives. The automotive sector, particularly the electric vehicle segment, has emerged as a primary growth driver, with MCUs enabling advanced driver assistance systems, battery management, and autonomous driving capabilities. Industrial automation applications continue expanding as Japanese manufacturers embrace Industry 4.0 principles, requiring sophisticated microcontrollers for robotics, process control, and smart manufacturing systems.
Growth projections indicate the market will experience steady expansion at a CAGR of 6.2% through the forecast period, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions and the proliferation of connected devices. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities into MCU architectures represents a significant technological evolution, positioning Japan at the forefront of next-generation semiconductor innovation.
The Japan MCU market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing the design, manufacturing, distribution, and application of microcontroller units within Japan’s domestic and export-oriented technology sectors. Microcontroller units are integrated circuits that combine a processor core, memory, and programmable input/output peripherals on a single chip, serving as the control center for electronic systems across diverse industries.
MCU functionality extends beyond basic processing to include real-time control, sensor interfacing, communication protocols, and power management capabilities. These sophisticated semiconductors enable intelligent decision-making in embedded systems, from simple household appliances to complex industrial machinery. Japan’s MCU market encompasses various architectures including 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit processors, with increasing emphasis on ARM-based solutions and specialized automotive-grade components.
Market significance lies in the critical role MCUs play in Japan’s digital transformation strategy, supporting the country’s leadership in robotics, automotive innovation, and smart manufacturing. The market includes both domestic consumption for Japanese manufacturers and export activities that supply global technology companies with advanced microcontroller solutions.
Japan’s MCU market demonstrates remarkable resilience and innovation capacity, positioning the nation as a key player in the global semiconductor landscape. The market benefits from strong domestic demand across automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics sectors, while simultaneously serving as a crucial supplier to international technology companies. Automotive applications represent the largest segment, accounting for approximately 42% of total MCU consumption, driven by the rapid adoption of electric vehicles and advanced safety systems.
Technological advancement remains a defining characteristic of Japan’s MCU ecosystem, with companies investing heavily in research and development to maintain competitive advantages. The integration of AI acceleration capabilities, enhanced security features, and ultra-low power consumption technologies represents key innovation areas. Industrial automation applications continue expanding, supported by government initiatives promoting smart manufacturing and digital factory concepts.
Market challenges include intense global competition, supply chain complexities, and the need for continuous technological evolution. However, Japan’s strong engineering expertise, established manufacturing infrastructure, and collaborative industry-academia partnerships provide substantial competitive advantages. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that the market’s focus on high-value, specialized MCU solutions positions Japanese companies favorably in premium market segments.

Strategic insights reveal several critical factors shaping Japan’s MCU market trajectory and competitive positioning:
Primary growth drivers propelling Japan’s MCU market reflect the nation’s technological leadership and industrial transformation initiatives. The automotive sector stands as the most significant driver, with electric vehicle adoption creating unprecedented demand for sophisticated microcontrollers. Battery management systems require specialized MCUs capable of precise monitoring, thermal management, and safety control functions, while autonomous driving technologies demand high-performance processors with real-time processing capabilities.
Industrial automation represents another crucial driver, supported by Japan’s commitment to maintaining manufacturing competitiveness through digital transformation. Smart factories require extensive MCU deployment for robotics control, sensor networks, predictive maintenance systems, and quality assurance processes. The Industry 4.0 adoption rate of approximately 38% among Japanese manufacturers indicates substantial growth potential for industrial MCU applications.
Consumer electronics innovation continues driving MCU demand, particularly in smart home devices, wearable technology, and connected appliances. Japanese companies’ focus on user experience and product reliability creates opportunities for advanced microcontrollers with enhanced processing power, connectivity options, and energy efficiency. IoT device proliferation across residential and commercial applications further amplifies MCU requirements, with edge computing capabilities becoming increasingly important for real-time data processing and decision-making.
Significant challenges constrain Japan’s MCU market growth and competitive positioning despite strong fundamental drivers. Supply chain vulnerabilities have become increasingly apparent, with global semiconductor shortages highlighting dependencies on international manufacturing and raw material sources. Production capacity constraints limit the ability to meet surging demand, particularly for automotive-grade MCUs that require specialized manufacturing processes and extended qualification periods.
Intense global competition from established players and emerging market entrants pressures pricing and market share dynamics. Companies from Taiwan, South Korea, and China have invested heavily in MCU development and manufacturing capabilities, creating competitive pressure on Japanese firms. The need for continuous innovation and substantial R&D investments strains resources, particularly for smaller companies attempting to compete in specialized market segments.
Technical complexity and evolving customer requirements present ongoing challenges for MCU developers. The integration of AI capabilities, advanced security features, and multiple communication protocols increases design complexity and development costs. Time-to-market pressures require companies to balance innovation with reliability, while maintaining compatibility with existing systems and industry standards. Additionally, the shortage of skilled semiconductor engineers and the aging workforce in Japan’s technology sector pose long-term sustainability concerns for the industry.
Emerging opportunities in Japan’s MCU market reflect evolving technology trends and expanding application domains. The transition to electric vehicles creates substantial growth potential, with each electric vehicle requiring significantly more MCUs than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Autonomous driving development represents a particularly lucrative opportunity, as self-driving systems demand high-performance microcontrollers capable of processing sensor data, executing complex algorithms, and ensuring functional safety compliance.
Smart city initiatives across Japan present extensive MCU deployment opportunities in infrastructure monitoring, traffic management, environmental sensing, and public safety systems. Government investments in digital infrastructure and sustainability projects create demand for specialized microcontrollers designed for outdoor applications, long-term reliability, and energy efficiency. Healthcare technology advancement offers another promising avenue, with aging population demographics driving demand for medical devices, remote monitoring systems, and assistive technologies.
Edge computing proliferation creates opportunities for MCUs with integrated AI acceleration capabilities, enabling real-time processing and decision-making at the device level. The growing emphasis on data privacy and security favors edge processing solutions that minimize cloud dependency. Renewable energy systems require sophisticated MCUs for power conversion, grid integration, and energy management applications, aligning with Japan’s carbon neutrality goals and creating sustainable market growth opportunities.
Complex market dynamics shape Japan’s MCU landscape through the interplay of technological innovation, competitive pressures, and evolving customer requirements. The automotive sector’s transformation toward electrification and automation creates both opportunities and challenges, with traditional automotive suppliers adapting to new technology requirements while semiconductor companies develop specialized solutions for mobility applications. Collaboration patterns between MCU manufacturers and automotive OEMs have intensified, with joint development programs becoming essential for meeting specific performance and safety requirements.
Supply and demand imbalances continue influencing market dynamics, with strong demand growth outpacing production capacity expansion in certain segments. The lead time extension for automotive MCUs has reached an average of 26 weeks, reflecting both capacity constraints and the complex qualification processes required for safety-critical applications. This situation has prompted customers to adopt longer-term supply agreements and encouraged MCU manufacturers to invest in capacity expansion and supply chain diversification.
Technology convergence trends are reshaping competitive dynamics, with traditional MCU boundaries blurring as processors integrate more functionality and intelligence. The emergence of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and system-on-chip (SoC) solutions creates both competitive threats and collaboration opportunities for MCU companies. MWR analysis suggests that successful companies will need to balance standardization for cost efficiency with customization for competitive differentiation.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for analyzing Japan’s MCU market combines quantitative data analysis with qualitative insights from industry experts, technology leaders, and market participants. Primary research activities include structured interviews with MCU manufacturers, system integrators, automotive suppliers, and end-user companies across key application segments. Survey data collection encompasses market sizing, competitive positioning, technology trends, and customer requirements analysis.
Secondary research incorporates analysis of financial reports, patent filings, industry publications, and government statistics to validate primary findings and identify market trends. Technology roadmap analysis examines MCU architecture evolution, performance improvements, and feature integration patterns. Supply chain analysis evaluates manufacturing capacity, raw material availability, and distribution channel dynamics affecting market development.
Data validation processes ensure accuracy and reliability through triangulation of multiple information sources, expert review panels, and statistical analysis techniques. Market modeling incorporates historical trends, current market conditions, and forward-looking indicators to develop realistic growth projections and scenario analyses. Continuous monitoring of market developments, competitive activities, and technology announcements maintains research currency and relevance for strategic decision-making.
Regional distribution within Japan’s MCU market reflects the concentration of key industries and manufacturing capabilities across different prefectures. The Kanto region, encompassing Tokyo and surrounding areas, represents approximately 35% of total MCU consumption, driven by the presence of major electronics manufacturers, automotive companies, and technology development centers. This region serves as the primary hub for MCU design activities, with companies like Renesas Electronics maintaining significant R&D and corporate functions.
Chubu region accounts for roughly 28% of market activity, primarily due to the concentration of automotive manufacturing facilities and industrial automation companies. Toyota’s headquarters and extensive supplier network create substantial demand for automotive MCUs, while the region’s precision machinery and robotics industries drive industrial automation applications. Manufacturing excellence in this region supports both domestic consumption and export activities.
Kansai region contributes approximately 22% of market share, with strong representation in consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and semiconductor manufacturing. Companies like Panasonic and Sharp maintain significant operations in this region, creating demand for MCUs across diverse application areas. The remaining 15% of market activity is distributed across other regions, including Kyushu’s semiconductor manufacturing cluster and Tohoku’s emerging technology centers, reflecting Japan’s distributed industrial base and regional specialization patterns.
Japan’s MCU market features a dynamic competitive landscape with both domestic leaders and international players vying for market share across diverse application segments. The competitive environment reflects the market’s maturity and technological sophistication, with companies differentiating through innovation, customer relationships, and specialized solutions.
Market segmentation analysis reveals the diverse application areas and technology categories driving Japan’s MCU market growth and development patterns.
By Application:
By Architecture:
Automotive MCU category demonstrates the highest growth potential and technological complexity within Japan’s market landscape. Electric vehicle adoption drives demand for specialized microcontrollers capable of managing battery systems, motor control, and charging infrastructure. Advanced driver assistance systems require high-performance MCUs with real-time processing capabilities, functional safety compliance, and extensive sensor interfacing. The automotive segment’s quality requirements exceed those of other categories, with AEC-Q100 qualification standards and extended temperature ranges necessitating specialized manufacturing processes.
Industrial automation MCUs focus on reliability, real-time performance, and communication capabilities essential for smart manufacturing applications. These microcontrollers must support various industrial protocols, provide deterministic response times, and operate in harsh environmental conditions. Predictive maintenance applications drive demand for MCUs with integrated sensor interfaces and edge computing capabilities, enabling real-time analysis and decision-making at the equipment level.
Consumer electronics MCUs emphasize energy efficiency, connectivity, and user interface capabilities while maintaining cost competitiveness. Smart home devices require MCUs with wireless communication support, security features, and low-power operation for battery-powered applications. Wearable technology creates demand for ultra-low-power MCUs with integrated sensors and wireless connectivity, while gaming and entertainment applications require high-performance processors with graphics acceleration capabilities.
MCU manufacturers benefit from Japan’s strong domestic demand and export opportunities, with the market providing stable revenue streams and opportunities for technology leadership. The country’s emphasis on quality and innovation creates premium market segments where companies can achieve higher margins through differentiated products. Research and development collaboration with Japanese universities and research institutions provides access to cutting-edge technologies and skilled engineering talent.
System integrators and OEMs gain access to advanced MCU technologies that enable product differentiation and competitive advantages in global markets. Japanese MCU suppliers’ focus on customer support, technical documentation, and development tools reduces time-to-market and development costs. Long-term partnerships with MCU manufacturers provide supply security and access to roadmap information essential for strategic planning.
End-users and consumers benefit from improved product performance, energy efficiency, and functionality enabled by advanced MCU technologies. Automotive applications deliver enhanced safety, comfort, and environmental performance, while industrial systems provide improved productivity and operational efficiency. Smart device proliferation enhances quality of life through home automation, health monitoring, and entertainment applications powered by sophisticated microcontrollers.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Artificial intelligence integration represents the most significant trend reshaping Japan’s MCU market, with manufacturers developing microcontrollers capable of running machine learning algorithms at the edge. This trend enables real-time decision-making without cloud connectivity, addressing privacy concerns and reducing latency in critical applications. AI acceleration capabilities are becoming standard features in high-end MCUs, with dedicated neural processing units and optimized software frameworks supporting diverse AI workloads.
Security enhancement has emerged as a critical trend driven by increasing cybersecurity threats and regulatory requirements. Modern MCUs incorporate hardware-based security features including secure boot, encryption engines, and tamper detection mechanisms. Zero-trust architecture principles are being embedded at the hardware level, with MCUs providing root-of-trust functionality for connected devices and systems.
Ultra-low power design continues advancing to support battery-powered IoT devices and energy-efficient systems. New MCU architectures achieve power consumption reductions of up to 60% compared to previous generations through advanced process technologies, intelligent power management, and optimized instruction sets. Energy harvesting compatibility enables MCUs to operate from ambient energy sources, eliminating battery replacement requirements for certain applications.
Recent industry developments highlight the dynamic nature of Japan’s MCU market and the continuous innovation driving competitive positioning. Renesas Electronics has expanded its automotive MCU portfolio with new R-Car generation processors featuring enhanced AI processing capabilities and functional safety compliance for autonomous driving applications. The company’s strategic focus on software-defined vehicles positions it advantageously for the automotive industry’s digital transformation.
Partnership announcements between Japanese MCU manufacturers and international technology companies demonstrate the collaborative approach to market development. Toshiba’s collaboration with Microsoft on IoT solutions integrates Azure cloud services with MCU hardware, providing end-to-end solutions for industrial customers. These partnerships combine hardware expertise with software platforms and cloud services to address complex customer requirements.
Manufacturing capacity expansion initiatives reflect strong market confidence and demand projections. Several Japanese semiconductor companies have announced facility upgrades and new production lines dedicated to automotive-grade MCUs. Government support for domestic semiconductor manufacturing through subsidies and policy initiatives strengthens Japan’s position in strategic technology areas while reducing supply chain dependencies.
Strategic recommendations for MCU market participants emphasize the importance of balancing innovation with operational excellence while addressing evolving customer requirements. Companies should prioritize development of AI-enabled MCUs with edge computing capabilities, as this technology trend will define competitive positioning in premium market segments. Investment in software ecosystems and development tools becomes increasingly critical for customer adoption and differentiation from commodity competitors.
Supply chain resilience requires immediate attention through diversification strategies, strategic inventory management, and alternative supplier development. MarkWide Research recommends establishing regional supply partnerships and investing in domestic manufacturing capabilities to reduce dependency on single-source suppliers. Long-term supply agreements with key customers can provide demand visibility and support capacity planning decisions.
Market expansion strategies should focus on emerging application areas including healthcare technology, renewable energy systems, and smart infrastructure. These sectors offer growth opportunities with less intense competition than traditional automotive and industrial markets. Vertical integration through software and solution development can create higher-value propositions and stronger customer relationships while improving profit margins.
Long-term market prospects for Japan’s MCU industry remain positive despite near-term challenges and competitive pressures. The automotive sector’s transformation toward electrification and automation will continue driving substantial MCU demand growth, with electric vehicle penetration expected to reach 55% of new car sales by 2030. This transition creates opportunities for specialized microcontrollers designed for battery management, motor control, and autonomous driving applications.
Industrial digitalization initiatives will expand MCU applications across manufacturing, infrastructure, and service sectors as companies adopt IoT technologies and smart systems. The integration of 5G connectivity and edge computing capabilities will enable new application categories requiring high-performance microcontrollers with advanced communication features. Smart city development projects across Japan will create sustained demand for MCUs in traffic management, environmental monitoring, and public safety systems.
Technology evolution toward more intelligent and autonomous systems will drive MCU architecture advancement, with AI acceleration becoming standard rather than optional. The convergence of MCUs with other semiconductor technologies including sensors, power management, and wireless communication will create system-on-chip solutions addressing complex application requirements. Sustainability considerations will influence product development, with energy efficiency and environmental impact becoming key competitive factors in customer selection processes.
Japan’s MCU market stands at a pivotal juncture, with strong fundamental drivers supporting continued growth while technological disruption creates both opportunities and challenges for market participants. The automotive sector’s transformation toward electrification and automation provides substantial growth momentum, while industrial digitalization and IoT proliferation expand application opportunities across diverse sectors. Japanese companies maintain competitive advantages through technology leadership, quality reputation, and strong customer relationships, particularly in premium market segments requiring specialized solutions.
Success factors for the future include continuous innovation in AI integration, security enhancement, and energy efficiency while maintaining operational excellence and supply chain resilience. The market’s evolution toward more intelligent and connected systems creates opportunities for companies that can effectively combine hardware capabilities with software solutions and customer support services. Strategic partnerships and collaborative development approaches will become increasingly important for addressing complex customer requirements and accelerating time-to-market for new technologies.
Market outlook remains optimistic with projected growth driven by automotive electrification, industrial automation, and emerging applications in healthcare, smart cities, and renewable energy systems. Companies that successfully navigate current supply chain challenges while investing in next-generation technologies will be well-positioned to capitalize on Japan’s continued leadership in advanced semiconductor solutions and maintain competitive advantages in the global MCU market.
What is MCU?
MCU stands for Microcontroller Unit, which is a compact integrated circuit designed to govern a specific operation in an embedded system. MCUs are widely used in various applications, including automotive systems, consumer electronics, and industrial automation.
What are the key players in the Japan MCU Market?
Key players in the Japan MCU Market include Renesas Electronics Corporation, NXP Semiconductors, and Microchip Technology. These companies are known for their innovative microcontroller solutions that cater to various industries, including automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Japan MCU Market?
The Japan MCU Market is driven by the increasing demand for automation in industries, the rise of IoT applications, and the growing need for energy-efficient solutions. Additionally, advancements in technology and the expansion of smart devices contribute to market growth.
What challenges does the Japan MCU Market face?
The Japan MCU Market faces challenges such as supply chain disruptions, high competition among manufacturers, and the rapid pace of technological change. These factors can impact production costs and the ability to meet market demands effectively.
What opportunities exist in the Japan MCU Market?
Opportunities in the Japan MCU Market include the growing adoption of electric vehicles, the expansion of smart home technologies, and the increasing integration of AI in microcontroller applications. These trends present avenues for innovation and market expansion.
What trends are shaping the Japan MCU Market?
Trends shaping the Japan MCU Market include the shift towards low-power microcontrollers, the integration of wireless communication capabilities, and the development of advanced security features. These trends are essential for meeting the evolving needs of various applications.
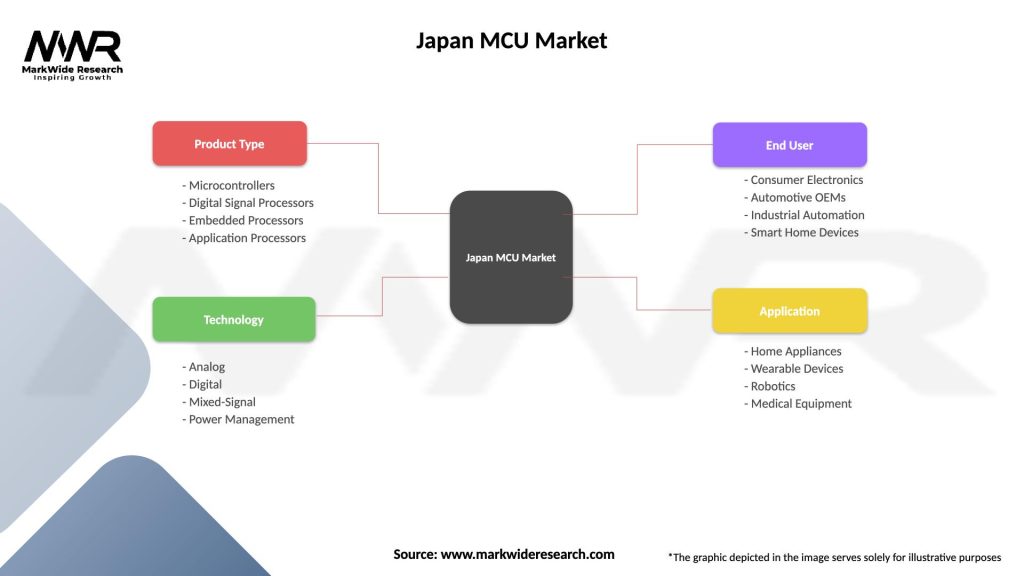
Japan MCU Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Microcontrollers, Digital Signal Processors, Embedded Processors, Application Processors |
| Technology | Analog, Digital, Mixed-Signal, Power Management |
| End User | Consumer Electronics, Automotive OEMs, Industrial Automation, Smart Home Devices |
| Application | Home Appliances, Wearable Devices, Robotics, Medical Equipment |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Japan MCU Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at