444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The Vietnam seed market is a thriving and rapidly growing sector within the country’s agricultural industry. Seeds play a crucial role in ensuring sustainable food production and meeting the increasing demand for agricultural products. The market encompasses a wide range of seeds, including cereals, oilseeds, vegetables, fruits, and forage crops. These seeds are developed and produced by both domestic and international seed companies, serving the needs of farmers across the country.
Meaning
The seed market refers to the trade and distribution of seeds used for agricultural purposes. Seeds are the foundation of agriculture as they determine the quality, productivity, and resilience of crops. In the context of the Vietnam seed market, it involves the buying and selling of various types of seeds, including hybrid seeds, genetically modified seeds, and traditional open-pollinated seeds.
Executive Summary
The Vietnam seed market is experiencing significant growth due to several factors, including increasing population, rising disposable income, and the government’s focus on agricultural development. The market offers a wide range of seed varieties tailored to meet the specific needs of farmers and agribusinesses. Both domestic and international seed companies are actively participating in the market, driving competition and innovation.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Vietnam seed market is highly dynamic, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and government support. The market is characterized by intense competition among both domestic and international seed companies. Continuous research and development efforts are essential to stay ahead in the market and meet the evolving needs of farmers.
Regional Analysis
The Vietnam seed market is spread across various regions, each with its unique agricultural characteristics and crop preferences. The northern regions are known for rice cultivation, while the southern regions focus on high-value crops such as fruits and vegetables. Central regions have a diverse agricultural landscape, with a mix of cash crops and staple crops. Understanding the regional dynamics and tailoring seed varieties to suit specific regions can enhance market penetration and growth.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Vietnam Seed Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
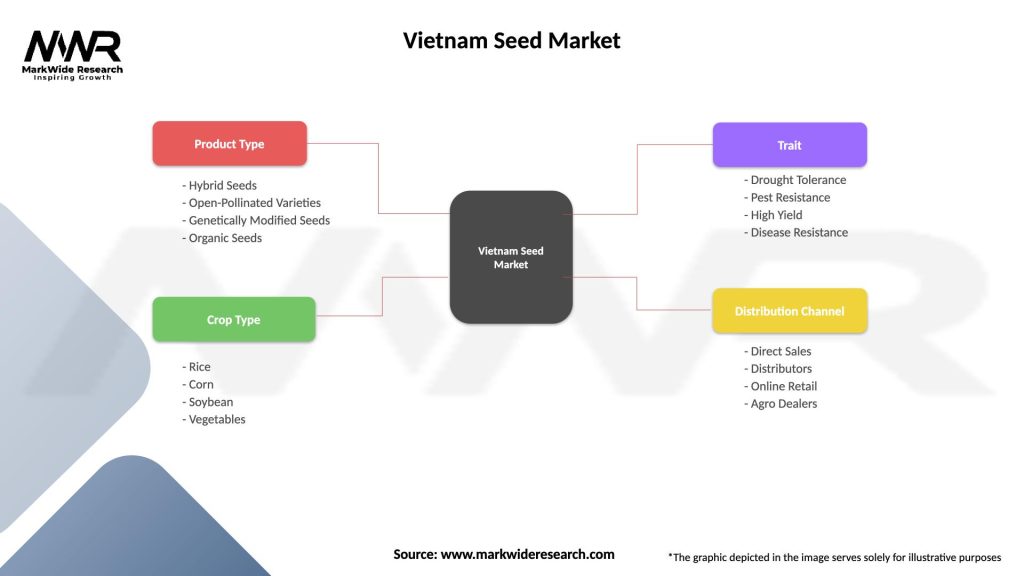
The Vietnam seed market can be segmented based on crop type, seed type, and distribution channel.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had both positive and negative impacts on the Vietnam seed market. While the initial disruption in supply chains and logistics affected the availability of seeds, the pandemic also highlighted the importance of food security. This led to increased interest in agriculture and a surge in demand for seeds as more individuals started home gardening and small-scale farming. The pandemic also accelerated the adoption of digital technologies in the seed industry, facilitating remote collaboration, and online seed sales.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Vietnam seed market is poised for significant growth in the coming years. Factors such as increasing population, rising food demand, government support, and technological advancements will continue to drive market expansion. The adoption of genetically modified seeds, focus on sustainability, and digitalization will shape the future of the seed industry. Collaboration among stakeholders and investment in research and development will play a vital role in ensuring the availability of high-quality seeds and sustainable agricultural practices.
Conclusion
The Vietnam seed market presents lucrative opportunities for both domestic and international seed companies. With a focus on research and development, innovation, and collaboration, the market can address challenges related to seed quality, distribution, and awareness. The future of the seed industry in Vietnam looks promising, driven by the increasing demand for food, sustainable agricultural practices, and the government’s support. By leveraging technological advancements and addressing market dynamics, the seed industry can contribute significantly to the country’s agricultural growth and food security.
What is Seed?
Seed refers to the reproductive part of flowering plants, which can be used for planting to grow new plants. In the context of agriculture, seeds are crucial for crop production and can vary widely in type, including cereals, legumes, and vegetables.
What are the key players in the Vietnam Seed Market?
Key players in the Vietnam Seed Market include companies like Syngenta, Bayer Crop Science, and Vietseed, which are involved in the development and distribution of various seed types for agriculture, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Vietnam Seed Market?
The Vietnam Seed Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for high-yield and disease-resistant crops, advancements in seed technology, and the government’s support for agricultural modernization.
What challenges does the Vietnam Seed Market face?
Challenges in the Vietnam Seed Market include issues related to seed quality, the prevalence of counterfeit seeds, and the need for better regulatory frameworks to ensure seed safety and efficacy.
What opportunities exist in the Vietnam Seed Market?
Opportunities in the Vietnam Seed Market include the potential for organic seed production, the expansion of export markets for high-quality seeds, and the increasing adoption of precision agriculture techniques.
What trends are shaping the Vietnam Seed Market?
Trends in the Vietnam Seed Market include the growing interest in genetically modified organisms (GMOs), the rise of sustainable farming practices, and the integration of digital technologies in seed production and distribution.
Vietnam Seed Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Hybrid Seeds, Open-Pollinated Varieties, Genetically Modified Seeds, Organic Seeds |
| Crop Type | Rice, Corn, Soybean, Vegetables |
| Trait | Drought Tolerance, Pest Resistance, High Yield, Disease Resistance |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Distributors, Online Retail, Agro Dealers |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Vietnam Seed Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at