444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Vietnam insecticide market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector within the country’s agricultural landscape, driven by the nation’s commitment to enhancing crop productivity and food security. Vietnam’s agricultural sector heavily relies on effective pest management solutions to protect rice, coffee, rubber, and various cash crops that form the backbone of the country’s economy. The market encompasses a comprehensive range of chemical insecticides, biological control agents, and integrated pest management solutions designed to combat diverse insect threats across different agricultural zones.
Market dynamics in Vietnam reflect the country’s transition toward more sustainable agricultural practices while maintaining high productivity standards. The insecticide market experiences robust growth, with adoption rates increasing by approximately 8.5% annually as farmers seek more effective pest control solutions. Regional distribution shows the Mekong Delta accounting for nearly 35% of total insecticide consumption, followed by the Red River Delta and Central Highlands regions, each contributing significantly to overall market demand.
Government initiatives promoting modern agricultural practices and the increasing prevalence of invasive pest species have created substantial opportunities for market expansion. The market demonstrates strong resilience, with domestic production meeting approximately 60% of local demand while imports supplement specialized formulations and advanced active ingredients.
The Vietnam insecticide market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of pest control products, services, and technologies specifically designed to manage insect populations that threaten agricultural productivity across Vietnam’s diverse farming regions. This market encompasses various chemical formulations, biological control agents, and integrated pest management solutions that help farmers protect their crops from damaging insects while optimizing yield potential and maintaining sustainable agricultural practices.
Market scope includes organophosphates, pyrethroids, neonicotinoids, and emerging bio-based insecticides that address specific pest challenges prevalent in Vietnam’s tropical and subtropical agricultural zones. The market serves multiple stakeholders including smallholder farmers, commercial agricultural enterprises, distributors, and government agencies focused on agricultural development and food security initiatives.
Vietnam’s insecticide market demonstrates exceptional growth potential, driven by expanding agricultural activities, increasing crop diversification, and rising awareness of integrated pest management practices. The market benefits from strong government support for agricultural modernization and the country’s strategic position as a major agricultural exporter in Southeast Asia.
Key growth drivers include the expansion of cash crop cultivation, particularly coffee and rubber, which require specialized pest management solutions. The market shows increasing adoption of precision agriculture technologies, with smart application systems gaining 15% market penetration among commercial farms. Biological insecticides represent a rapidly growing segment, with adoption rates increasing by 12% annually as farmers embrace sustainable pest management approaches.
Market challenges include regulatory compliance requirements, environmental concerns, and the need for farmer education regarding proper application techniques. Despite these challenges, the market maintains strong momentum supported by continuous innovation in formulation technologies and delivery systems.
Strategic market insights reveal several critical trends shaping Vietnam’s insecticide landscape:
Agricultural expansion serves as the primary driver for Vietnam’s insecticide market growth, with the government’s commitment to increasing agricultural productivity and food security creating sustained demand for effective pest management solutions. The country’s strategic focus on becoming a major agricultural exporter necessitates high-quality crop protection to meet international standards and maintain competitive advantages in global markets.
Climate change impacts significantly influence market dynamics, as changing weather patterns create new pest challenges and alter traditional pest cycles. Rising temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns have led to increased pest pressure and the emergence of previously uncommon insect species, driving demand for specialized control solutions and adaptive pest management strategies.
Crop diversification initiatives contribute substantially to market growth, with farmers increasingly cultivating high-value crops such as fruits, vegetables, and specialty commodities that require intensive pest management programs. This diversification creates opportunities for specialized insecticide formulations and targeted application technologies.
Technology adoption accelerates market development through precision agriculture tools, drone applications, and smart monitoring systems that optimize insecticide use efficiency. These technological advances enable farmers to implement more targeted and effective pest control strategies while reducing overall chemical inputs and environmental impact.
Regulatory constraints present significant challenges for the Vietnam insecticide market, with increasingly stringent registration requirements and environmental safety standards affecting product availability and market entry for new formulations. These regulations, while necessary for environmental protection, create compliance costs and lengthy approval processes that can limit market growth and innovation.
Environmental concerns regarding pesticide residues and ecological impact create market resistance, particularly among environmentally conscious consumers and export markets with strict residue limits. These concerns drive demand for alternative solutions but simultaneously restrict the use of certain effective chemical insecticides.
Economic limitations affect market penetration, especially among smallholder farmers who may lack sufficient financial resources to invest in premium insecticide products or modern application equipment. Price sensitivity remains a significant factor influencing product selection and application frequency decisions.
Knowledge gaps regarding proper application techniques and integrated pest management practices limit market efficiency and effectiveness. Inadequate farmer education can lead to overuse, underuse, or misuse of insecticides, creating resistance issues and reducing overall market sustainability.
Biological insecticide development presents substantial growth opportunities as Vietnam embraces sustainable agriculture practices and seeks alternatives to synthetic chemicals. The increasing demand for organic and residue-free produce creates market space for bio-based pest control solutions that align with environmental sustainability goals.
Digital agriculture integration offers significant potential for market expansion through smart pest monitoring systems, precision application technologies, and data-driven pest management decisions. These technological solutions can improve insecticide effectiveness while reducing environmental impact and application costs.
Export market compliance creates opportunities for specialized formulations that meet international residue standards and quality requirements. As Vietnam expands its agricultural exports, demand increases for insecticides that enable farmers to meet stringent international market specifications.
Regional expansion into underserved agricultural areas presents growth potential, particularly in highland regions and emerging agricultural zones where modern pest management practices are still developing. These areas offer opportunities for market education and technology transfer initiatives.
Supply chain dynamics in Vietnam’s insecticide market reflect a complex network of international manufacturers, domestic producers, distributors, and retailers serving diverse agricultural communities. The market demonstrates strong seasonal fluctuations aligned with agricultural cycles, creating inventory management challenges and pricing pressures during peak demand periods.
Competitive dynamics show increasing consolidation among major players while maintaining space for specialized regional suppliers and niche product developers. Market competition intensifies around product efficacy, environmental safety, and cost-effectiveness, driving continuous innovation and formulation improvements.
Pricing dynamics reflect global commodity trends, regulatory compliance costs, and local economic conditions. The market shows price sensitivity among smallholder farmers while commercial operations demonstrate willingness to invest in premium solutions that deliver superior performance and compliance benefits.
Innovation dynamics focus on developing more targeted, environmentally friendly formulations that address specific pest challenges while minimizing non-target effects. Research and development investments concentrate on improving application efficiency and reducing environmental persistence.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into Vietnam’s insecticide market dynamics. Primary research involves extensive field surveys, farmer interviews, and stakeholder consultations across major agricultural regions to gather firsthand market intelligence and usage patterns.
Secondary research incorporates government agricultural statistics, trade data, regulatory filings, and industry reports to establish market baselines and trend analysis. This approach ensures comprehensive coverage of market segments, regional variations, and competitive landscapes.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing multiple sources, expert consultations, and statistical analysis to ensure accuracy and reliability of market findings. The methodology incorporates both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights to provide a complete market perspective.
Market modeling techniques utilize historical data, current trends, and forward-looking indicators to develop reliable market projections and scenario analyses. This approach enables stakeholders to make informed decisions based on comprehensive market intelligence.
Mekong Delta region dominates Vietnam’s insecticide market, accounting for approximately 35% of total consumption due to intensive rice cultivation and diverse agricultural activities. This region demonstrates the highest adoption rates for modern pest management technologies and shows strong demand for both chemical and biological insecticides.
Red River Delta represents the second-largest market segment, contributing roughly 25% of national consumption with focus on rice production and vegetable cultivation. The region shows increasing adoption of integrated pest management practices and precision application technologies.
Central Highlands accounts for approximately 20% of market share, driven primarily by coffee cultivation and specialty crop production. This region demonstrates strong demand for specialized insecticides designed for perennial crops and shows growing interest in sustainable pest management solutions.
Northern Mountains and South Central Coast regions collectively represent the remaining 20% of market consumption, with diverse agricultural activities including fruit production, aquaculture support, and emerging cash crop cultivation. These regions show potential for market expansion as agricultural development initiatives progress.
Market leadership in Vietnam’s insecticide sector reflects a combination of international corporations and domestic manufacturers serving different market segments and customer needs:
By Product Type:
By Application Method:
By Crop Type:
Chemical insecticides continue to dominate the Vietnam market, representing approximately 75% of total consumption due to their proven efficacy and cost-effectiveness. Within this category, organophosphates maintain strong market presence despite environmental concerns, particularly in rice production systems where their broad-spectrum activity addresses multiple pest species simultaneously.
Pyrethroid insecticides show steady growth in vegetable and fruit production segments, valued for their rapid knockdown effect and relatively favorable environmental profile. These products demonstrate particular strength in export-oriented agriculture where residue management is critical for market access.
Biological insecticides represent the fastest-growing category, with adoption rates increasing by 12% annually as farmers and regulators embrace sustainable pest management approaches. This segment benefits from government support for organic agriculture and increasing consumer demand for residue-free produce.
Specialty formulations including insect growth regulators and pheromone-based products show promising growth in integrated pest management programs. These products appeal to progressive farmers seeking to reduce chemical inputs while maintaining effective pest control.
Farmers benefit from access to diverse insecticide options that enable effective pest management while meeting economic and environmental objectives. Modern formulations provide improved efficacy, reduced application frequency, and better crop safety profiles that enhance overall farm productivity and profitability.
Manufacturers gain from Vietnam’s expanding agricultural sector and increasing demand for innovative pest management solutions. The market offers opportunities for product differentiation, premium pricing for advanced formulations, and long-term customer relationships built on technical support and service excellence.
Distributors enjoy stable demand patterns aligned with agricultural cycles and opportunities to provide value-added services including technical advice, application equipment, and farmer education programs. The market structure supports both large-scale distribution networks and specialized regional suppliers.
Government stakeholders benefit from improved agricultural productivity, enhanced food security, and reduced crop losses that support economic development goals. Effective pest management contributes to export competitiveness and rural income generation.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Sustainable pest management emerges as the dominant trend shaping Vietnam’s insecticide market, with increasing adoption of integrated pest management practices that combine chemical, biological, and cultural control methods. This trend reflects growing environmental awareness and regulatory pressure for reduced chemical inputs in agricultural systems.
Precision application technologies gain momentum as farmers seek to optimize insecticide use efficiency and minimize environmental impact. Drone applications and GPS-guided spraying systems show increasing adoption among commercial farms, improving coverage accuracy and reducing labor requirements.
Biological control integration represents a significant market trend, with farmers increasingly incorporating beneficial insects, microbial pesticides, and botanical extracts into their pest management programs. This trend aligns with organic certification requirements and export market demands for residue-free produce.
Resistance management becomes increasingly important as pest populations develop tolerance to commonly used insecticides. Farmers and advisors focus on rotation strategies, mode-of-action diversity, and threshold-based applications to preserve product effectiveness and extend useful life of active ingredients.
Regulatory framework evolution significantly impacts the Vietnam insecticide market, with new registration requirements emphasizing environmental safety and efficacy data. Recent policy changes require comprehensive residue studies and environmental impact assessments for product approvals, affecting market entry strategies for new formulations.
Technology partnerships between international manufacturers and local distributors accelerate market development through knowledge transfer and capacity building initiatives. These collaborations focus on farmer education, application technology improvement, and sustainable pest management practice adoption.
Research and development investments increase substantially, with companies developing Vietnam-specific formulations adapted to local pest species, climate conditions, and cropping systems. MarkWide Research indicates that R&D spending in the region has grown by 18% over the past two years, reflecting industry commitment to innovation.
Digital platform development transforms market dynamics through mobile applications providing pest identification, treatment recommendations, and application timing guidance. These platforms improve farmer decision-making and create new channels for product promotion and technical support.
Market participants should prioritize sustainable product development and integrated pest management solutions to align with evolving regulatory requirements and farmer preferences. Investment in biological insecticides and precision application technologies offers significant growth potential in Vietnam’s dynamic agricultural market.
Strategic partnerships with local distributors and agricultural cooperatives can enhance market penetration and provide valuable insights into regional pest management needs. These relationships enable better customer service and technical support delivery across Vietnam’s diverse agricultural regions.
Farmer education initiatives represent critical investments for long-term market success, helping to improve product effectiveness, reduce resistance development, and build customer loyalty. Companies should develop comprehensive training programs covering proper application techniques, safety procedures, and integrated pest management principles.
Digital transformation opportunities should be leveraged to improve customer engagement, provide real-time technical support, and gather market intelligence for product development decisions. Mobile platforms and precision agriculture tools can differentiate companies in an increasingly competitive market environment.
Vietnam’s insecticide market demonstrates strong growth prospects driven by agricultural expansion, crop diversification, and increasing adoption of modern farming practices. MWR projections indicate sustained market growth with CAGR of 7.2% over the next five years, supported by government agricultural development initiatives and rising food security concerns.
Biological insecticides are expected to capture increasing market share, with adoption rates projected to reach 25% of total market volume by 2029. This growth reflects environmental sustainability trends and regulatory support for reduced chemical inputs in agricultural systems.
Technology integration will accelerate market transformation, with precision agriculture tools and digital platforms becoming standard components of pest management programs. Smart application systems and data-driven decision support tools will improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Regional market expansion into underserved agricultural areas presents significant opportunities, particularly as infrastructure development improves access to remote farming communities. Highland regions and emerging agricultural zones show particular potential for market growth and technology adoption.
Vietnam’s insecticide market stands at a critical juncture, balancing traditional pest management needs with evolving sustainability requirements and technological innovations. The market demonstrates remarkable resilience and growth potential, supported by the country’s expanding agricultural sector and commitment to food security enhancement.
Key success factors for market participants include sustainable product development, strategic partnerships with local stakeholders, comprehensive farmer education programs, and investment in precision agriculture technologies. Companies that successfully navigate regulatory requirements while delivering effective, environmentally responsible solutions will capture the greatest market opportunities.
Future market dynamics will be shaped by increasing integration of biological control methods, precision application technologies, and data-driven pest management decisions. The market’s evolution toward sustainability and efficiency creates opportunities for innovation while maintaining the fundamental goal of protecting Vietnam’s vital agricultural production systems from destructive insect pests.
What is Insecticide?
Insecticide refers to substances used to kill or control insects that are harmful to crops, livestock, and human health. They are essential in agriculture for protecting plants from pests and ensuring food security.
What are the key companies in the Vietnam Insecticide Market?
Key companies in the Vietnam Insecticide Market include Syngenta, Bayer CropScience, and BASF, which are known for their innovative pest control solutions and extensive product portfolios, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Vietnam Insecticide Market?
The Vietnam Insecticide Market is driven by increasing agricultural production, the rising need for pest management, and the adoption of modern farming techniques. Additionally, the growing awareness of crop protection is contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the Vietnam Insecticide Market face?
The Vietnam Insecticide Market faces challenges such as regulatory compliance, the development of pest resistance, and environmental concerns regarding chemical usage. These factors can hinder market growth and innovation.
What opportunities exist in the Vietnam Insecticide Market?
Opportunities in the Vietnam Insecticide Market include the development of biopesticides, increasing demand for organic farming, and advancements in precision agriculture technologies. These trends are likely to shape the future of pest control.
What trends are currently influencing the Vietnam Insecticide Market?
Current trends in the Vietnam Insecticide Market include the shift towards sustainable pest management practices, the integration of digital technologies in agriculture, and the growing preference for environmentally friendly products. These trends are reshaping the industry landscape.
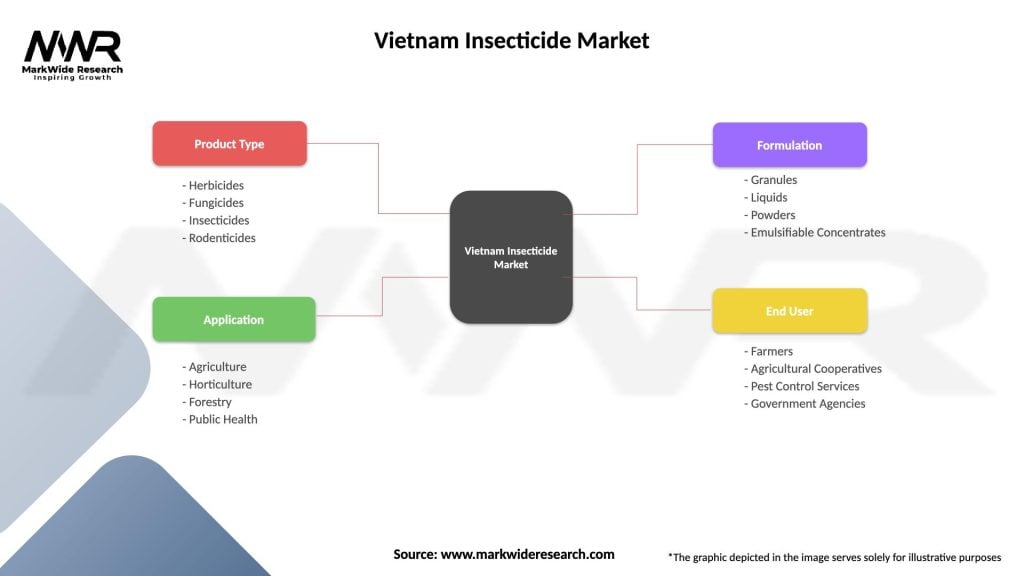
Vietnam Insecticide Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Herbicides, Fungicides, Insecticides, Rodenticides |
| Application | Agriculture, Horticulture, Forestry, Public Health |
| Formulation | Granules, Liquids, Powders, Emulsifiable Concentrates |
| End User | Farmers, Agricultural Cooperatives, Pest Control Services, Government Agencies |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Vietnam Insecticide Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at