444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The US propane market is a vital segment of the energy sector, characterized by a robust supply chain and diverse applications across residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural sectors. Propane, a byproduct of natural gas processing and crude oil refining, is used primarily as a fuel for heating, cooking, and powering vehicles. The market is driven by increasing demand for cleaner-burning fuels, advancements in propane technologies, and favorable government policies supporting its use as an alternative energy source.
Meaning
Propane is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature but is commonly stored as a liquid under pressure. It is part of the liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) family and is known for its efficiency and low emissions compared to other fossil fuels. Its versatility allows it to be used in various applications, including heating homes, powering appliances, fueling vehicles (autogas), and serving as a feedstock in petrochemical production.
Executive Summary
The US propane market is poised for continued growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions, the transition to cleaner energy sources, and the expansion of propane infrastructure. Key market drivers include rising residential and commercial demand, the growth of the agricultural sector, and the increasing adoption of propane-fueled vehicles. However, challenges such as price volatility, regulatory changes, and competition from alternative energy sources may hinder market growth. Opportunities exist in technological advancements, expanded distribution networks, and increasing export potential. The market is characterized by a competitive landscape, with key players focusing on supply chain efficiency, customer service, and sustainability to strengthen their market positions.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics
The interplay of various factors influences the dynamics of the US propane market:
Regional Analysis
The US propane market can be segmented regionally to provide insights into dynamics in different areas:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in US Propane Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
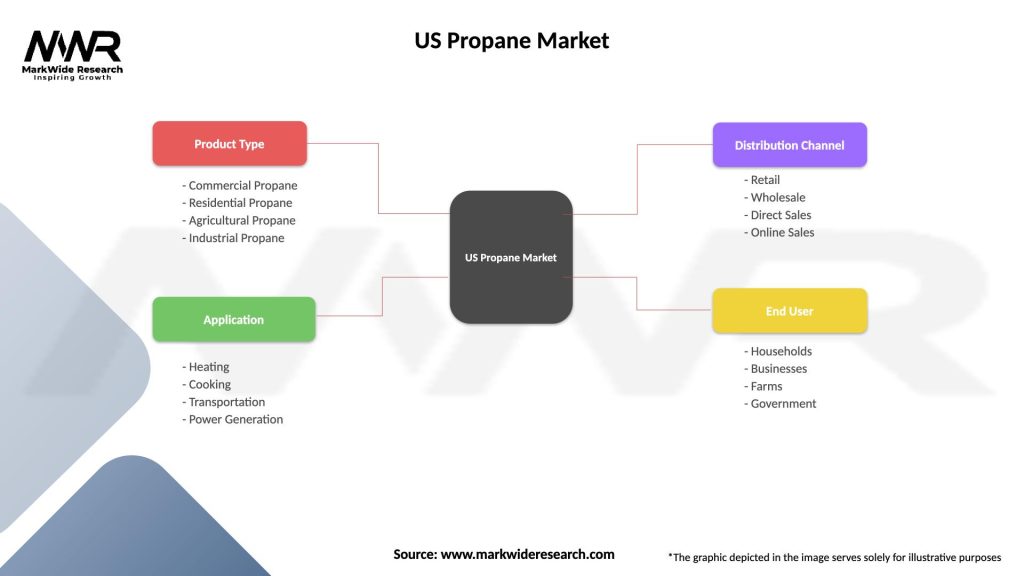
Segmentation
The US propane market can be segmented based on various criteria:
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact:
The Covid-19 pandemic had mixed effects on the US propane market. While certain sectors, such as residential heating, experienced increased demand as people spent more time at home, other sectors, including commercial and industrial usage, faced disruptions due to lockdowns and restrictions.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook:
The future outlook for the US propane market remains positive, driven by its versatility, cleaner-burning characteristics, and role in supporting energy transition initiatives. Continued innovation, investments in renewable propane, and strategic partnerships will shape the industry’s trajectory, ensuring its resilience and relevance in the evolving energy landscape.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the US propane market stands as a vital component of the nation’s energy portfolio, offering a versatile and clean-burning fuel source for various applications. The market’s resilience, adaptability to changing circumstances, and contributions to energy security position it favorably in a dynamic energy environment. As the industry navigates challenges, including price fluctuations and competition from alternative energy sources, strategic initiatives such as renewable propane development, infrastructure investments, and digitalization are key to ensuring sustained growth and meeting the evolving needs of consumers.
What is Propane?
Propane is a colorless, odorless gas that is commonly used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and vehicles. It is a byproduct of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, making it an important energy source in various applications.
What are the key companies in the US Propane Market?
Key companies in the US Propane Market include AmeriGas, Ferrellgas, and Suburban Propane, which provide propane distribution and services across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the US Propane Market?
The US Propane Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for clean energy sources, the growth of the agricultural sector for crop drying, and the rising use of propane in residential heating and cooking applications.
What challenges does the US Propane Market face?
Challenges in the US Propane Market include price volatility due to fluctuating crude oil prices, regulatory pressures regarding emissions, and competition from alternative energy sources like electricity and natural gas.
What opportunities exist in the US Propane Market?
Opportunities in the US Propane Market include the expansion of propane as a transportation fuel, increased adoption in off-grid applications, and the potential for growth in the export market as global demand rises.
What trends are shaping the US Propane Market?
Trends in the US Propane Market include the development of more efficient propane appliances, the integration of propane with renewable energy systems, and a growing focus on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints in energy consumption.
US Propane Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Commercial Propane, Residential Propane, Agricultural Propane, Industrial Propane |
| Application | Heating, Cooking, Transportation, Power Generation |
| Distribution Channel | Retail, Wholesale, Direct Sales, Online Sales |
| End User | Households, Businesses, Farms, Government |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in US Propane Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at