444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The US LNG bunkering market represents a transformative segment within the maritime fuel industry, driven by stringent environmental regulations and the shipping sector’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions. Liquefied natural gas bunkering has emerged as a critical solution for vessel operators seeking cleaner alternatives to traditional marine fuels, particularly heavy fuel oil and marine gas oil. The market encompasses infrastructure development, fuel supply chains, and specialized equipment required for safe and efficient LNG transfer to marine vessels.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth potential, with the sector experiencing a compound annual growth rate of 12.5% as shipping companies increasingly adopt LNG as a marine fuel. The United States, with its abundant natural gas resources and expanding LNG export capabilities, is positioning itself as a key player in the global LNG bunkering ecosystem. Port authorities across major US maritime hubs are investing heavily in LNG bunkering infrastructure, creating a comprehensive network to support the growing fleet of LNG-powered vessels.
Regulatory frameworks established by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) have accelerated market adoption, particularly the implementation of sulfur emission limits that favor cleaner burning fuels like LNG. The US maritime industry is witnessing significant transformation as vessel operators, port authorities, and fuel suppliers collaborate to establish efficient LNG bunkering operations that meet both environmental standards and operational requirements.
The US LNG bunkering market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing the supply, storage, handling, and transfer of liquefied natural gas as a marine fuel for vessels operating in US waters and ports. LNG bunkering involves the specialized process of delivering LNG from shore-based facilities or bunker vessels to ships equipped with LNG fuel systems, requiring sophisticated infrastructure and safety protocols.
Bunkering operations include various delivery methods such as truck-to-ship transfers, shore-to-ship pipeline connections, and ship-to-ship transfers using dedicated LNG bunker vessels. The market encompasses the entire value chain from LNG production and liquefaction facilities to specialized storage terminals, transportation equipment, and the actual fuel transfer operations. Safety considerations are paramount in LNG bunkering, requiring specialized training, equipment certification, and adherence to strict operational procedures.
Market participants include LNG suppliers, terminal operators, shipping companies, port authorities, equipment manufacturers, and service providers who collectively enable the safe and efficient delivery of LNG as a marine fuel. The sector represents a critical component of the broader energy transition in maritime transportation, supporting the industry’s decarbonization objectives while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Strategic positioning of the US LNG bunkering market reflects the nation’s commitment to maritime decarbonization and energy security through domestic natural gas resources. The market is experiencing unprecedented growth driven by environmental regulations, technological advancements, and increasing adoption of LNG-powered vessels across various maritime segments including container ships, cruise vessels, and offshore support vessels.
Infrastructure development represents a key market driver, with major US ports investing in LNG bunkering facilities to accommodate the growing demand for cleaner marine fuels. The market benefits from 65% of new vessel orders incorporating LNG fuel systems, indicating strong future demand for bunkering services. Port authorities in Houston, Los Angeles, New York, and other major maritime hubs are establishing comprehensive LNG bunkering capabilities to serve both domestic and international vessel traffic.
Competitive dynamics are shaped by established energy companies, specialized marine fuel suppliers, and emerging technology providers who are developing innovative solutions for LNG storage, handling, and transfer operations. The market’s growth trajectory is supported by favorable regulatory frameworks, abundant domestic LNG supply, and increasing recognition of LNG as a transitional fuel toward zero-emission maritime transportation.
Market intelligence reveals several critical insights that define the US LNG bunkering landscape and its future development trajectory:
Environmental regulations serve as the primary catalyst for US LNG bunkering market growth, with the International Maritime Organization’s sulfur emission limits creating immediate demand for cleaner marine fuels. The IMO 2020 sulfur regulations have fundamentally altered the marine fuel landscape, making LNG an attractive compliance solution that offers significant environmental benefits while maintaining operational efficiency.
Economic advantages of LNG as a marine fuel continue to drive market adoption, particularly as natural gas prices remain competitive relative to traditional marine fuels. The price stability offered by long-term LNG supply contracts provides vessel operators with predictable fuel costs, enabling better operational planning and financial management. Additionally, the potential for carbon credit revenues and environmental incentives enhances the economic proposition of LNG adoption.
Infrastructure development initiatives by port authorities and private investors are creating the foundation for sustained market growth. Major US ports are recognizing LNG bunkering as a strategic capability that attracts environmentally conscious shipping lines and supports their sustainability objectives. The availability of domestic LNG supply provides the United States with a competitive advantage in developing cost-effective bunkering operations compared to regions dependent on LNG imports.
Technological advancements in LNG handling and transfer systems are improving operational efficiency and safety, making LNG bunkering more attractive to vessel operators and port authorities. Enhanced automation, improved safety systems, and more efficient transfer equipment are reducing operational complexity and costs associated with LNG bunkering operations.
High capital investment requirements for LNG bunkering infrastructure represent a significant barrier to market entry and expansion. The specialized equipment, storage facilities, and safety systems required for LNG bunkering operations demand substantial upfront investments that may deter smaller operators and limit the pace of infrastructure development in secondary ports.
Technical complexity associated with LNG handling and transfer operations creates operational challenges that require specialized expertise and training. The cryogenic nature of LNG demands sophisticated equipment and strict safety protocols, increasing operational complexity compared to conventional marine fuel bunkering. This technical complexity can result in longer transfer times and higher operational costs, particularly during the initial implementation phase.
Limited vessel availability equipped with LNG fuel systems constrains immediate market demand, as the majority of the existing global fleet operates on conventional marine fuels. The retrofit costs for converting existing vessels to LNG fuel systems are often prohibitive, limiting market growth to new vessel construction and specific vessel segments where conversion economics are favorable.
Regulatory uncertainties regarding future maritime fuel standards and potential shifts toward alternative zero-emission fuels create investment hesitation among market participants. The transitional nature of LNG as a marine fuel, while cleaner than conventional options, may face future regulatory challenges as the industry moves toward carbon-neutral objectives, potentially affecting long-term investment returns in LNG bunkering infrastructure.
Emerging vessel segments present significant growth opportunities for LNG bunkering services, particularly in the cruise ship industry, offshore support vessels, and specialized cargo carriers. The cruise industry’s commitment to environmental sustainability is driving adoption of LNG-powered vessels, creating consistent demand for bunkering services at major cruise ports throughout the United States.
International trade routes connecting US ports with global destinations offer opportunities for establishing the United States as a strategic LNG bunkering hub for international shipping. The geographic positioning of US ports along major shipping lanes, combined with abundant domestic LNG supply, creates competitive advantages for attracting international vessel traffic seeking cleaner fuel alternatives.
Technology integration opportunities exist in developing advanced bunkering systems that improve efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Digital solutions including automated transfer systems, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities can enhance operational performance and create differentiated service offerings in the competitive bunkering market.
Strategic partnerships between LNG producers, shipping companies, and port authorities can create integrated value chains that optimize costs and improve service reliability. Vertical integration opportunities allow market participants to capture value across multiple segments of the LNG bunkering ecosystem while providing customers with comprehensive fuel solutions and supply chain security.
Supply and demand dynamics in the US LNG bunkering market are characterized by rapidly growing demand from environmentally conscious vessel operators and expanding supply capabilities driven by infrastructure investments. The demand growth rate of 18% annually reflects the accelerating adoption of LNG-powered vessels and increasing recognition of LNG as a viable marine fuel alternative.
Competitive dynamics are evolving as traditional marine fuel suppliers, energy companies, and specialized LNG providers compete for market share in this emerging sector. Market consolidation trends are evident as larger players acquire smaller operators to build comprehensive service networks and achieve economies of scale in operations and infrastructure development.
Price dynamics reflect the underlying natural gas market fundamentals, with LNG bunkering prices generally tracking natural gas commodity prices while incorporating premiums for liquefaction, transportation, and specialized handling services. The price competitiveness of LNG relative to traditional marine fuels varies with crude oil prices and regional supply-demand balances, influencing adoption rates and market growth patterns.
Regulatory dynamics continue to shape market development as environmental standards become more stringent and new regulations emerge to address maritime emissions. The regulatory environment creates both opportunities through mandated adoption of cleaner fuels and challenges through compliance costs and operational complexity requirements.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to provide accurate and reliable insights into the US LNG bunkering market landscape. Primary research includes extensive interviews with industry executives, port authorities, vessel operators, and LNG suppliers to gather firsthand insights into market trends, challenges, and opportunities.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of industry reports, regulatory filings, company financial statements, and trade publications to validate primary research findings and provide comprehensive market context. Data triangulation methods ensure accuracy and reliability of market insights by cross-referencing multiple information sources and analytical approaches.
Market modeling techniques incorporate quantitative analysis of market drivers, historical trends, and forward-looking indicators to develop realistic growth projections and market scenarios. Scenario analysis considers various regulatory, economic, and technological factors that could influence market development trajectories and competitive dynamics.
Industry expert validation ensures research findings align with practical market realities and industry best practices. Continuous monitoring of market developments, regulatory changes, and technological innovations provides ongoing validation and refinement of research conclusions and market projections.
Gulf Coast region dominates the US LNG bunkering market, accounting for approximately 45% of current infrastructure capacity due to proximity to major LNG production and export facilities. Houston serves as the primary hub for LNG bunkering operations, leveraging its established energy infrastructure and strategic location for both domestic and international shipping routes. The region benefits from integrated supply chains connecting upstream LNG production with downstream bunkering operations.
West Coast markets represent 25% of bunkering capacity, with Los Angeles and Long Beach ports leading infrastructure development to serve the significant container shipping traffic and cruise operations. The region’s commitment to environmental sustainability and air quality improvement creates strong regulatory support for LNG adoption in maritime transportation. Pacific trade routes connecting to Asia provide substantial opportunities for LNG bunkering services.
East Coast facilities account for 20% of market capacity, with New York-New Jersey and Savannah ports developing LNG bunkering capabilities to serve Atlantic shipping routes and growing cruise operations. The region’s dense population centers and environmental regulations create favorable conditions for LNG adoption in maritime transportation.
Great Lakes region represents an emerging market segment with 10% of current capacity, focusing primarily on domestic shipping and specialized vessel operations. The region’s unique operational requirements and seasonal shipping patterns create specific opportunities for LNG bunkering services tailored to inland waterway transportation needs.
Market leadership in the US LNG bunkering sector is distributed among established energy companies, specialized marine fuel suppliers, and emerging technology providers who are developing comprehensive service offerings:
Strategic positioning among competitors varies from vertically integrated energy companies leveraging upstream LNG assets to specialized marine service providers focusing on operational excellence and customer service. Competitive advantages are built through infrastructure investments, supply chain integration, technological innovation, and strategic partnerships with port authorities and shipping companies.
By Vessel Type: The US LNG bunkering market serves diverse vessel segments with varying fuel requirements and operational characteristics. Container ships represent the largest segment, driven by major shipping lines’ commitments to environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance. Cruise vessels constitute a growing segment as the cruise industry adopts LNG propulsion for new ship construction and environmental positioning.
By Bunkering Method: Market segmentation includes truck-to-ship transfers for smaller vessels and ports with limited infrastructure, shore-to-ship pipeline connections for high-volume operations at major terminals, and ship-to-ship transfers using dedicated LNG bunker vessels for flexibility and operational efficiency.
By End-User: Segmentation encompasses commercial shipping companies operating container vessels, bulk carriers, and tankers, cruise operators seeking environmental differentiation, offshore energy companies using LNG-powered support vessels, and government agencies operating naval and coast guard vessels with environmental mandates.
By Infrastructure Type: Market segments include fixed terminal facilities with permanent LNG storage and transfer equipment, mobile bunkering units providing flexible service delivery, and integrated port facilities combining LNG import/export operations with bunkering services for operational synergies.
Container Shipping Category: This segment drives 40% of LNG bunkering demand as major container lines implement fleet-wide environmental strategies. Maersk, CMA CGM, and COSCO are leading adoption with significant orders for LNG-powered container vessels. The category benefits from regular sailing schedules that enable predictable bunkering operations and long-term supply contracts.
Cruise Industry Category: Representing 25% of market demand, cruise operators are adopting LNG propulsion for new vessel construction and environmental marketing advantages. Royal Caribbean, Carnival, and Norwegian Cruise Line are investing in LNG-powered ships that require specialized bunkering services at major cruise ports throughout the United States.
Offshore Support Category: This specialized segment accounts for 20% of bunkering demand, serving vessels supporting offshore oil and gas operations. LNG-powered offshore support vessels offer environmental benefits and operational efficiency for companies operating in environmentally sensitive areas and under strict regulatory oversight.
Bulk and Tanker Category: Representing 15% of current demand, this segment is experiencing gradual adoption as operators evaluate LNG economics for long-haul operations. Dry bulk carriers and chemical tankers are beginning to adopt LNG propulsion for specific trade routes where environmental regulations and port incentives support the business case for cleaner fuels.
Vessel Operators benefit from significant environmental compliance advantages, with LNG offering 20% reduction in CO2 emissions and virtually eliminating sulfur and particulate emissions compared to traditional marine fuels. Operational benefits include reduced maintenance costs due to cleaner combustion, potential for preferential port treatment, and enhanced corporate sustainability profiles that attract environmentally conscious customers and investors.
Port Authorities gain competitive advantages by offering LNG bunkering services that attract environmentally focused shipping lines and support local air quality objectives. Economic benefits include increased port revenues, job creation in specialized marine services, and positioning as preferred destinations for next-generation vessel operations.
LNG Suppliers access new market opportunities that diversify revenue streams beyond traditional power generation and industrial applications. Market expansion into marine bunkering provides stable, long-term demand that supports infrastructure investments and creates additional value from existing LNG production and distribution assets.
Equipment Manufacturers benefit from growing demand for specialized LNG handling and transfer equipment, including cryogenic storage systems, transfer arms, and safety equipment. Innovation opportunities exist in developing more efficient, safer, and cost-effective bunkering technologies that improve operational performance and reduce infrastructure requirements.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Infrastructure Consolidation is emerging as a key trend, with major energy companies and port authorities forming strategic partnerships to develop comprehensive LNG bunkering networks. Integrated facilities that combine LNG import/export operations with bunkering services are becoming more common, creating operational synergies and cost efficiencies that benefit all stakeholders.
Technology Integration trends include adoption of automated transfer systems, real-time monitoring capabilities, and predictive maintenance technologies that improve operational efficiency and safety. Digital solutions are enabling remote monitoring, automated documentation, and optimized scheduling that reduce operational costs and improve customer service levels.
Sustainability Focus is driving development of carbon-neutral LNG and bio-LNG options that further reduce the environmental impact of marine transportation. Green LNG initiatives incorporating renewable energy in production and carbon capture technologies are positioning LNG as a longer-term solution in maritime decarbonization strategies.
Market Standardization efforts are establishing common safety protocols, equipment specifications, and operational procedures that facilitate industry growth and improve interoperability between different bunkering systems and vessel types. Industry collaboration on standards development is reducing barriers to entry and improving operational efficiency across the market.
Major infrastructure projects are transforming the US LNG bunkering landscape, with Houston Ship Channel completing construction of the largest LNG bunkering facility in North America, capable of serving multiple vessels simultaneously. Port of Los Angeles has announced plans for a comprehensive LNG bunkering terminal that will serve the growing Pacific trade routes and support the port’s sustainability objectives.
Fleet expansion announcements from major shipping companies continue to drive market growth, with CMA CGM ordering additional LNG-powered container vessels for US trade routes and Carnival Corporation expanding its LNG-powered cruise ship fleet with vessels designed specifically for North American operations.
Regulatory developments include new safety standards for LNG bunkering operations and environmental incentives that support adoption of cleaner marine fuels. US Coast Guard has published updated guidelines for LNG bunkering operations that streamline approval processes while maintaining strict safety requirements.
Technology partnerships are accelerating innovation in LNG bunkering equipment and systems, with equipment manufacturers collaborating with port authorities and vessel operators to develop more efficient and cost-effective bunkering solutions tailored to specific operational requirements and market conditions.
MarkWide Research recommends that industry participants focus on strategic partnerships and infrastructure sharing to optimize capital investments and accelerate market development. Collaborative approaches between LNG suppliers, port authorities, and shipping companies can create more efficient operations and shared risk profiles that support sustainable market growth.
Investment priorities should emphasize flexible infrastructure designs that can accommodate future fuel alternatives and evolving vessel requirements. Modular bunkering systems that can be upgraded or reconfigured as market conditions change provide better long-term value and reduced obsolescence risk compared to fixed, single-purpose facilities.
Market entry strategies should consider regional specialization and niche market segments where competitive advantages can be established and defended. Specialized service offerings for specific vessel types or operational requirements can create differentiated market positions and premium pricing opportunities.
Risk management approaches should address both operational safety and market volatility through comprehensive insurance coverage, diversified supply sources, and flexible contract structures that adapt to changing market conditions and regulatory requirements.
Market expansion is projected to accelerate significantly over the next decade, with MWR analysis indicating potential growth rates exceeding 15% annually as LNG-powered vessel adoption reaches critical mass and infrastructure development reaches maturity. Geographic expansion beyond current hub ports will create new market opportunities and improve service accessibility for vessel operators.
Technology evolution will continue to improve operational efficiency and safety, with next-generation bunkering systems offering faster transfer rates, enhanced safety features, and reduced operational complexity. Automation and digitalization will become standard features that improve operational efficiency and reduce labor requirements.
Regulatory environment is expected to become more supportive of LNG adoption through environmental incentives and streamlined approval processes, while maintaining strict safety standards. International harmonization of LNG bunkering standards will facilitate global market development and improve operational efficiency for international shipping operations.
Market maturation will bring increased competition, operational standardization, and cost optimization that benefit end users while creating consolidation opportunities for market participants. Long-term sustainability will depend on successful integration with emerging zero-emission fuel alternatives and continued environmental performance advantages over conventional marine fuels.
The US LNG bunkering market represents a critical component of the maritime industry’s transition toward cleaner, more sustainable fuel alternatives. Strong market fundamentals including abundant domestic LNG supply, supportive regulatory frameworks, and growing environmental awareness create favorable conditions for sustained market growth and development.
Strategic opportunities exist for industry participants who can effectively navigate the complex requirements of LNG bunkering operations while building scalable, efficient service networks. Success factors include strategic partnerships, technology integration, operational excellence, and adaptive business models that respond to evolving market conditions and customer requirements.
Market challenges related to high capital requirements, technical complexity, and competitive pressures require careful planning and risk management, but the long-term outlook remains positive as environmental regulations and industry sustainability commitments drive continued adoption of LNG as a marine fuel. The foundation for a robust, competitive US LNG bunkering market is being established through current infrastructure investments and industry collaboration initiatives that will support future growth and market expansion.
What is LNG Bunkering?
LNG Bunkering refers to the process of supplying liquefied natural gas (LNG) as fuel to ships and vessels. This method is gaining traction due to its environmental benefits and efficiency compared to traditional marine fuels.
What are the key players in the US LNG Bunkering Market?
Key players in the US LNG Bunkering Market include companies like Shell, TotalEnergies, and Clean Marine Energy, which are actively involved in developing LNG infrastructure and services for maritime applications, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the US LNG Bunkering Market?
The US LNG Bunkering Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for cleaner marine fuels, regulatory pressures to reduce emissions, and the expansion of LNG infrastructure at ports.
What challenges does the US LNG Bunkering Market face?
Challenges in the US LNG Bunkering Market include the high initial investment for infrastructure development, regulatory uncertainties, and competition from alternative fuels like hydrogen and ammonia.
What opportunities exist in the US LNG Bunkering Market?
Opportunities in the US LNG Bunkering Market include the potential for technological advancements in LNG storage and delivery systems, as well as the growing interest in LNG as a transitional fuel for decarbonizing the shipping industry.
What trends are shaping the US LNG Bunkering Market?
Trends in the US LNG Bunkering Market include the increasing adoption of dual-fuel engines, the development of small-scale LNG bunkering solutions, and collaborations between shipping companies and LNG suppliers to enhance fuel availability.
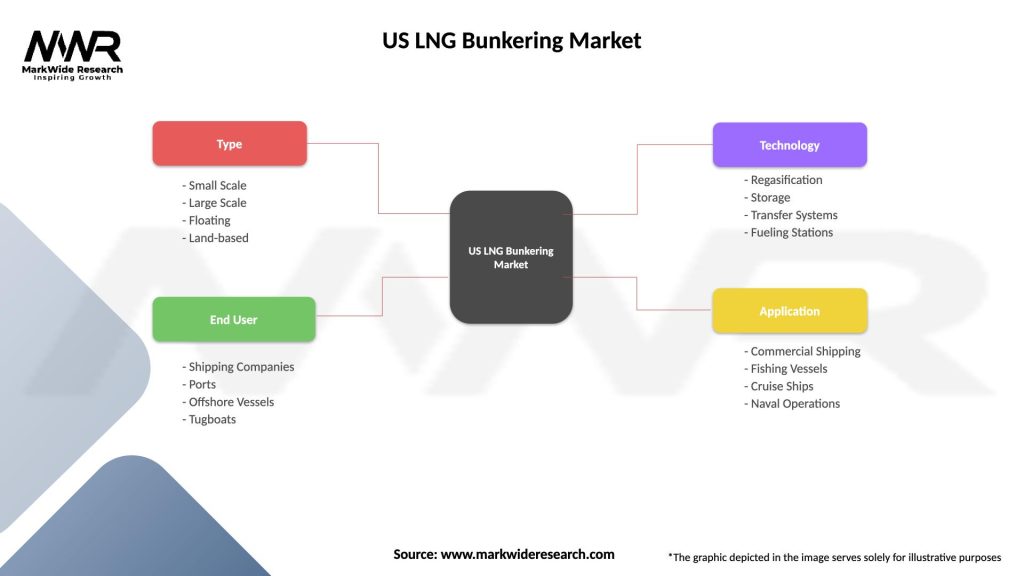
US LNG Bunkering Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Small Scale, Large Scale, Floating, Land-based |
| End User | Shipping Companies, Ports, Offshore Vessels, Tugboats |
| Technology | Regasification, Storage, Transfer Systems, Fueling Stations |
| Application | Commercial Shipping, Fishing Vessels, Cruise Ships, Naval Operations |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the US LNG Bunkering Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at