444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The US electricity transmission and distribution market is a critical component of the nation’s energy infrastructure, responsible for delivering electricity from power generation facilities to end-users across various sectors. This market encompasses the transmission of high-voltage electricity over long distances through an interconnected grid system, as well as the distribution of electricity to homes, businesses, and industries through local distribution networks. With the increasing demand for reliable and resilient electricity supply, coupled with the need for modernization and grid optimization, the US electricity transmission and distribution market play a vital role in ensuring the efficient and secure delivery of electricity to meet the nation’s growing energy needs.
Meaning
Electricity transmission and distribution involve the transport and delivery of electricity from power plants to consumers. Transmission refers to the bulk movement of electricity over long distances at high voltages, typically through overhead power lines or underground cables. Distribution involves the local delivery of electricity to homes, businesses, and industrial facilities through lower voltage distribution networks, including substations, transformers, and power lines. Together, transmission and distribution form the backbone of the electric grid, ensuring the reliable and safe delivery of electricity to meet the needs of consumers.
Executive Summary
The US electricity transmission and distribution market are undergoing significant transformations driven by factors such as increasing electricity demand, aging infrastructure, renewable energy integration, grid modernization initiatives, and technological advancements. These trends are reshaping the landscape of the electricity sector, presenting opportunities for investment, innovation, and infrastructure development. However, challenges such as regulatory hurdles, cybersecurity risks, funding constraints, and environmental concerns must be addressed to ensure the resilience, reliability, and sustainability of the electricity transmission and distribution system.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The US electricity transmission and distribution market operates in a dynamic environment shaped by technological advancements, regulatory changes, market trends, and stakeholder dynamics. These dynamics influence investment decisions, infrastructure development, policy initiatives, and market competitiveness, requiring stakeholders to adapt to changing market conditions, anticipate future trends, and leverage opportunities for growth and innovation.
Regional Analysis
The US electricity transmission and distribution market exhibits regional variations in electricity demand, generation mix, grid infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and energy policies across different geographic regions. Variability in population density, industrial activity, renewable energy resources, and environmental factors contributes to differences in transmission and distribution challenges, investment priorities, and grid modernization efforts among states, regions, and utility service territories.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The US electricity transmission and distribution market can be segmented based on various factors such as:
Segmentation provides insights into market dynamics, customer preferences, investment priorities, and infrastructure requirements, enabling stakeholders to tailor their strategies, products, and services to meet the specific needs of different market segments.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The US electricity transmission and distribution market offer several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the US electricity transmission and distribution market:
Understanding these factors through a SWOT analysis helps stakeholders identify strategic priorities, mitigate risks, capitalize on opportunities, and navigate market challenges in the US electricity transmission and distribution sector.
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had several impacts on the US electricity transmission and distribution market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The US electricity transmission and distribution market are poised for continued growth and transformation, driven by factors such as renewable energy expansion, grid modernization, electrification of transportation, and digitalization of the grid. However, challenges such as regulatory hurdles, funding constraints, cybersecurity risks, and environmental concerns must be addressed to ensure the resilience, reliability, and sustainability of the electricity transmission and distribution system. The industry’s future will be shaped by advancements in technology, regulatory reforms, market dynamics, and stakeholder collaboration, paving the way for a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
The US electricity transmission and distribution market play a critical role in delivering reliable, affordable, and sustainable electricity to meet the nation’s energy needs. With increasing electricity demand, renewable energy integration, grid modernization, and technological advancements, the electricity transmission and distribution sector are undergoing significant transformations. While challenges such as regulatory hurdles, cybersecurity risks, and aging infrastructure persist, opportunities for investment, innovation, and infrastructure development abound. By prioritizing grid resilience, renewable energy integration, and customer-centric solutions, stakeholders can navigate market uncertainties, capitalize on emerging trends, and build a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable electricity transmission and distribution system for the future.
What is Electricity Transmission and Distribution?
Electricity Transmission and Distribution refers to the systems and processes involved in transporting electricity from power plants to consumers. This includes high-voltage transmission lines and local distribution networks that deliver electricity to homes and businesses.
What are the key players in the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market?
Key players in the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market include companies like Duke Energy, Consolidated Edison, and Pacific Gas and Electric. These companies are involved in various aspects of electricity transmission and distribution, including infrastructure development and maintenance, among others.
What are the main drivers of the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market?
The main drivers of the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market include the increasing demand for electricity, the need for infrastructure upgrades, and the integration of renewable energy sources. These factors are pushing utilities to enhance their transmission and distribution capabilities.
What challenges does the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market face?
Challenges in the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market include aging infrastructure, regulatory hurdles, and the high costs associated with upgrading systems. These issues can hinder the efficiency and reliability of electricity delivery.
What opportunities exist in the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market?
Opportunities in the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market include advancements in smart grid technology, increased investment in renewable energy integration, and the potential for energy storage solutions. These developments can enhance grid reliability and efficiency.
What trends are shaping the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market?
Trends shaping the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market include the shift towards decentralized energy systems, the adoption of smart grid technologies, and a growing focus on sustainability. These trends are influencing how electricity is generated, transmitted, and consumed.
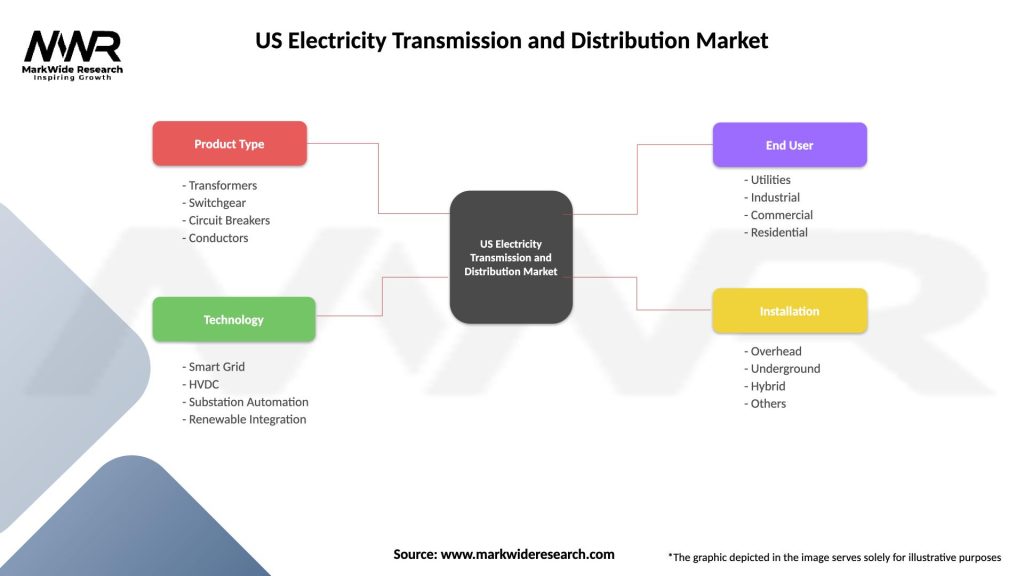
US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Transformers, Switchgear, Circuit Breakers, Conductors |
| Technology | Smart Grid, HVDC, Substation Automation, Renewable Integration |
| End User | Utilities, Industrial, Commercial, Residential |
| Installation | Overhead, Underground, Hybrid, Others |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the US Electricity Transmission and Distribution Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at