444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The US electric bus battery pack market represents a transformative segment within the broader electric vehicle ecosystem, driving the nationwide transition toward sustainable public transportation. Electric bus battery packs serve as the critical energy storage systems that power municipal transit fleets, school buses, and intercity transportation networks across America. This rapidly expanding market encompasses lithium-ion battery technologies, advanced battery management systems, and innovative charging infrastructure solutions designed specifically for heavy-duty electric buses.
Market dynamics indicate substantial growth momentum, with the sector experiencing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.5% as cities nationwide prioritize clean transportation initiatives. The integration of advanced battery technologies has revolutionized public transit operations, offering enhanced range capabilities, reduced operational costs, and significant environmental benefits. Federal funding programs and state-level incentives continue to accelerate adoption rates, with transit authorities increasingly recognizing the long-term economic advantages of electric bus fleets.
Technological advancements in battery chemistry, energy density improvements, and thermal management systems have positioned the US market as a global leader in electric bus battery innovation. The market encompasses various battery configurations, including depot charging systems, opportunity charging solutions, and emerging wireless charging technologies that support diverse operational requirements across different transit environments.
The US electric bus battery pack market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of energy storage solutions specifically designed and manufactured for electric buses operating within the United States transportation network. This market encompasses the design, production, distribution, and maintenance of high-capacity battery systems that power electric buses across various applications including urban transit, school transportation, and intercity services.
Battery pack systems typically consist of multiple lithium-ion cells configured in series and parallel arrangements to deliver the high voltage and energy capacity required for heavy-duty bus operations. These systems integrate sophisticated battery management systems (BMS) that monitor cell performance, ensure safety protocols, and optimize charging cycles to maximize battery life and operational efficiency.
The market definition extends beyond the physical battery components to include charging infrastructure, software management platforms, and comprehensive service networks that support the entire lifecycle of electric bus battery systems. This holistic approach ensures reliable performance, predictable maintenance schedules, and optimal total cost of ownership for transit operators nationwide.
Strategic market positioning reveals the US electric bus battery pack market as a cornerstone of the nation’s clean transportation transformation. The sector demonstrates remarkable resilience and growth potential, driven by unprecedented federal investment in infrastructure modernization and growing environmental consciousness among municipal decision-makers. Transit authorities across major metropolitan areas are implementing comprehensive electrification strategies, creating sustained demand for advanced battery solutions.
Technology leadership from domestic manufacturers has established competitive advantages in battery chemistry optimization, with energy density improvements of 35% achieved over the past three years. The market benefits from strong supply chain localization efforts, reducing dependence on international suppliers while supporting domestic job creation and technological innovation. Partnership ecosystems between battery manufacturers, bus OEMs, and charging infrastructure providers have created integrated solutions that address the complete spectrum of transit electrification requirements.
Market penetration rates continue accelerating, with electric buses representing 12% of new transit bus purchases in major urban markets. The convergence of declining battery costs, improved performance characteristics, and favorable regulatory environments positions the market for sustained expansion through the remainder of the decade.

Fundamental market drivers reveal several critical insights that shape the competitive landscape and growth trajectory of the US electric bus battery pack market:
Environmental regulations serve as the primary catalyst driving electric bus battery pack adoption across the United States. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) Innovative Clean Transit regulation requires transit agencies to gradually transition to zero-emission bus fleets, with full electrification mandated by 2040. Similar regulatory frameworks in states like New York, Washington, and Massachusetts create sustained demand for advanced battery solutions that meet stringent environmental standards.
Federal funding initiatives provide unprecedented financial support for transit electrification projects. The Federal Transit Administration (FTA) Low or No Emission Vehicle Program offers competitive grants that cover up to 80% of incremental costs associated with electric bus procurement. These funding mechanisms reduce financial barriers and accelerate adoption timelines for transit authorities evaluating electrification strategies.
Operational cost advantages increasingly favor electric bus deployments, particularly in high-mileage applications where fuel savings and reduced maintenance requirements generate substantial long-term value. Energy costs for electric buses typically represent 60-70% savings compared to diesel alternatives, while simplified drivetrain configurations reduce maintenance complexity and associated labor costs.
Technological maturation has eliminated many early adoption concerns related to battery performance, charging infrastructure, and operational reliability. Modern lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) battery chemistries deliver consistent performance across extreme temperature ranges while maintaining safety standards that exceed traditional vehicle requirements.
Capital investment requirements represent the most significant barrier to widespread electric bus battery pack adoption. The upfront cost premium for electric buses, including battery systems, typically ranges from 40-60% above comparable diesel vehicles. This financial challenge particularly impacts smaller transit agencies with limited capital budgets and restricted access to federal funding programs.
Infrastructure development costs create additional financial burdens for transit operators considering electrification. Depot charging installations require substantial electrical infrastructure upgrades, including high-voltage electrical service, charging equipment, and facility modifications that can represent significant capital expenditures beyond vehicle procurement costs.
Range limitations in extreme weather conditions continue to challenge operational planning for certain route configurations. Cold weather performance degradation can reduce battery capacity by 20-30% in severe winter conditions, requiring careful route planning and potentially limiting service flexibility during peak demand periods.
Supply chain constraints periodically impact battery pack availability and pricing stability. Global semiconductor shortages, raw material price volatility, and manufacturing capacity limitations can create delivery delays and cost uncertainties that complicate fleet planning and procurement processes for transit authorities.
Technical workforce requirements demand specialized training and certification programs for maintenance personnel. The transition from mechanical to electrical systems requires significant investment in staff development and specialized diagnostic equipment that many transit agencies must acquire to support in-house maintenance capabilities.
School bus electrification presents an enormous untapped opportunity within the US electric bus battery pack market. With approximately 480,000 school buses in operation nationwide, this segment offers substantial growth potential as school districts prioritize student health and environmental responsibility. Federal and state incentive programs specifically targeting school bus electrification create favorable economic conditions for widespread adoption.
Intercity and coach applications represent emerging opportunities as battery technology advances enable longer-range capabilities suitable for regional transportation services. The development of high-energy density battery packs and fast-charging infrastructure along major transportation corridors opens new market segments beyond traditional urban transit applications.
Second-life battery applications create additional revenue streams and sustainability benefits through repurposing electric bus batteries for stationary energy storage applications. Grid stabilization and renewable energy integration projects can utilize retired bus batteries that retain 70-80% of original capacity, extending overall battery lifecycle value.
Wireless charging technology development offers revolutionary operational advantages that could accelerate market adoption. Dynamic wireless charging systems embedded in roadways could eliminate range anxiety while reducing battery pack size requirements, creating new market opportunities for specialized battery configurations optimized for continuous charging scenarios.
Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS) business models provide alternative financing mechanisms that reduce upfront capital requirements for transit operators. These innovative approaches separate battery ownership from vehicle ownership, creating new market opportunities for financial services and battery lifecycle management companies.
Competitive dynamics within the US electric bus battery pack market reflect a complex interplay between established automotive battery manufacturers, emerging technology companies, and integrated bus manufacturers developing proprietary solutions. Market consolidation trends indicate strategic partnerships and vertical integration efforts as companies seek to control critical supply chain components and differentiate their offerings.
Technology evolution continues reshaping market dynamics through continuous improvements in energy density, charging speed, and battery lifecycle performance. The transition from nickel-based chemistries to more cost-effective lithium iron phosphate solutions demonstrates how technological advancement drives competitive positioning and market share distribution.
Regional market variations create diverse competitive landscapes across different geographic areas. California’s aggressive electrification mandates drive different market dynamics compared to regions with voluntary adoption approaches, influencing pricing strategies, product development priorities, and competitive positioning among market participants.
Supply chain dynamics increasingly emphasize domestic manufacturing capabilities and supply security. MarkWide Research analysis indicates growing preference for domestically produced battery solutions among transit authorities concerned about supply chain resilience and long-term parts availability.
Customer relationship dynamics evolve toward comprehensive service partnerships rather than traditional vendor relationships. Transit operators increasingly value integrated solutions that combine battery supply, charging infrastructure, maintenance services, and performance guarantees within single contractual frameworks.
Primary research methodologies employed in analyzing the US electric bus battery pack market encompass comprehensive stakeholder interviews, industry surveys, and direct engagement with key market participants across the value chain. Transit authority executives, battery manufacturers, charging infrastructure providers, and policy makers provided critical insights through structured interviews and questionnaire responses.
Secondary research approaches involved extensive analysis of industry publications, government reports, regulatory filings, and company financial statements to establish market sizing, competitive positioning, and trend identification. Federal Transit Administration data, state transportation department reports, and industry association publications provided foundational market intelligence.
Data validation processes included cross-referencing multiple information sources, conducting follow-up interviews with key stakeholders, and employing statistical analysis techniques to ensure accuracy and reliability of market projections. Triangulation methodologies confirmed key findings through multiple independent data sources and analytical approaches.
Market modeling techniques incorporated bottom-up and top-down analytical approaches to develop comprehensive market forecasts. Bottom-up analysis examined individual transit agency electrification plans and procurement schedules, while top-down modeling considered macroeconomic factors, regulatory timelines, and technology adoption curves.
Expert validation processes involved review and feedback from industry experts, academic researchers, and policy specialists to ensure analytical accuracy and market insight relevance. This collaborative approach enhanced the credibility and practical applicability of research findings and market projections.
California dominates the US electric bus battery pack market, representing approximately 35% of national demand driven by aggressive regulatory mandates and substantial state incentive programs. The California Air Resources Board Innovative Clean Transit regulation creates predictable demand patterns that support long-term market planning and investment decisions among battery manufacturers and transit operators.
Northeast corridor states including New York, Massachusetts, and Connecticut demonstrate strong market growth momentum, collectively accounting for 25% of market activity. These states benefit from dense urban populations, established public transit systems, and state-level policies that prioritize environmental sustainability and air quality improvement initiatives.
Pacific Northwest markets in Washington and Oregon show robust adoption rates supported by abundant renewable energy resources and environmentally conscious political leadership. The region’s commitment to carbon neutrality goals creates favorable conditions for electric bus deployment, with Seattle and Portland serving as early adoption leaders.
Texas and Florida represent emerging growth markets where large metropolitan areas are beginning to evaluate electric bus solutions. Houston, Dallas, Austin, Miami, and Tampa transit authorities are conducting pilot programs and feasibility studies that indicate substantial future market potential in these high-growth regions.
Midwest markets demonstrate selective adoption patterns, with Chicago, Detroit, and Minneapolis leading regional electrification efforts. Cold weather performance considerations influence battery pack specifications and charging infrastructure requirements in these markets, creating opportunities for specialized cold-weather battery solutions.
Market leadership within the US electric bus battery pack sector reflects a diverse ecosystem of established automotive suppliers, specialized battery manufacturers, and integrated transportation solution providers. The competitive landscape continues evolving as companies pursue different strategic approaches to capture market share and establish sustainable competitive advantages.
By Battery Chemistry:
By Application Segment:
By Charging Strategy:
Urban Transit Applications represent the most mature and established segment within the US electric bus battery pack market. These applications benefit from predictable route patterns, centralized maintenance facilities, and established charging infrastructure that optimize battery utilization and lifecycle management. Transit authorities in major cities demonstrate strong preference for lithium iron phosphate chemistry due to safety considerations and proven performance in high-utilization scenarios.
School Bus Electrification emerges as the highest growth potential segment, driven by unique value propositions including improved air quality for students, reduced noise pollution, and substantial operational cost savings. Federal funding programs specifically targeting school bus electrification create favorable economic conditions, while shorter route distances and predictable schedules align well with current battery technology capabilities.
Intercity Coach Applications present technical challenges that drive innovation in high-energy density battery solutions and fast-charging infrastructure. These applications require extended range capabilities and rapid charging systems that support long-distance travel patterns while maintaining passenger comfort and operational reliability standards.
Depot Charging Systems dominate current market installations due to infrastructure simplicity and operational predictability. These systems optimize overnight charging cycles that align with traditional bus maintenance schedules while minimizing electrical demand charges through off-peak energy consumption patterns.
Opportunity Charging Solutions gain traction in high-frequency route applications where smaller battery packs combined with strategic charging locations provide operational flexibility and reduced vehicle weight. This approach requires sophisticated route optimization and charging infrastructure coordination but offers advantages in capital cost reduction and operational efficiency.
Transit Operators realize substantial operational benefits through electric bus battery pack adoption, including 60-70% reduction in fuel costs, simplified maintenance requirements, and improved vehicle reliability. Predictable energy costs enable more accurate budget planning while reduced maintenance complexity decreases operational disruptions and associated costs.
Environmental Benefits extend beyond direct emission reductions to include noise pollution mitigation, improved air quality in urban environments, and contribution to broader sustainability goals. Zero tailpipe emissions particularly benefit communities with environmental justice concerns where traditional diesel bus operations disproportionately impact air quality.
Economic Development opportunities emerge through domestic battery manufacturing job creation, supply chain localization, and technology innovation leadership. Federal investment in electric vehicle infrastructure supports American manufacturing competitiveness while reducing dependence on international battery supply chains.
Grid Integration Benefits include potential vehicle-to-grid services where electric bus batteries provide grid stabilization and energy storage capabilities during non-operational periods. This bidirectional charging capability creates additional revenue opportunities for transit operators while supporting renewable energy integration.
Public Health Improvements result from reduced particulate matter emissions, decreased noise pollution, and improved air quality in urban environments. School bus applications particularly benefit student health through elimination of diesel exhaust exposure during transportation to and from educational facilities.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Battery Chemistry Evolution demonstrates clear market trends toward lithium iron phosphate solutions that prioritize safety, longevity, and cost-effectiveness over maximum energy density. This shift reflects transit operator preferences for proven reliability and predictable lifecycle costs rather than cutting-edge performance specifications that may introduce operational risks.
Charging Infrastructure Integration trends emphasize seamless integration between battery systems and charging equipment through standardized protocols and communication interfaces. Smart charging systems optimize energy consumption, manage electrical demand, and provide predictive maintenance capabilities that enhance overall system reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Modular Battery Design approaches gain popularity as manufacturers develop scalable solutions that accommodate diverse operational requirements and enable easier maintenance and replacement procedures. This modularity supports customization for specific route requirements while maintaining economies of scale in manufacturing and service operations.
Data Analytics Integration transforms battery management through predictive maintenance, performance optimization, and operational planning capabilities. Advanced telematics systems provide real-time monitoring of battery health, charging patterns, and performance metrics that enable proactive maintenance and operational optimization.
Sustainability Focus drives development of circular economy approaches including battery recycling, second-life applications, and sustainable manufacturing processes. MWR analysis indicates growing emphasis on lifecycle environmental impact assessment and sustainable supply chain practices among major market participants.
Manufacturing Capacity Expansion represents the most significant recent development, with multiple battery manufacturers announcing major US production facility investments. CATL’s Michigan facility and LG Energy Solution’s Ohio plant expansion demonstrate commitment to domestic supply chain development and reduced dependence on international manufacturing.
Technology Partnerships between battery manufacturers and bus OEMs create integrated solutions that optimize performance and reduce integration complexity. Strategic alliances focus on co-development of battery systems specifically designed for transit applications rather than adapting automotive solutions for commercial vehicle use.
Charging Standard Development through industry collaboration establishes common protocols that ensure interoperability between different battery and charging system manufacturers. The CharIN consortium and similar organizations drive standardization efforts that reduce operational complexity for transit operators.
Federal Policy Implementation includes specific guidelines for Buy America compliance in federal funding programs, encouraging domestic battery manufacturing and supply chain development. These requirements influence market dynamics by creating preferences for domestically produced battery solutions in federally funded projects.
Pilot Program Results from major transit agencies provide real-world performance data that validates battery technology capabilities and informs future procurement decisions. Successful deployments in challenging operational environments demonstrate technology maturity and support broader market adoption.
Strategic Investment Focus should prioritize domestic manufacturing capacity development and supply chain resilience to capture growing market opportunities while reducing geopolitical risks. Companies investing in US-based production facilities position themselves advantageously for federal funding program requirements and long-term market growth.
Technology Development Priorities should emphasize cold weather performance improvements, fast-charging capabilities, and battery lifecycle extension to address current market limitations. Research and development investments in these areas directly address operational concerns that limit broader market adoption.
Partnership Strategy Development becomes increasingly important as the market matures and customers seek integrated solutions rather than individual components. Collaborative approaches with charging infrastructure providers, bus manufacturers, and service organizations create competitive advantages and customer value.
Market Entry Timing favors companies that can establish market presence before widespread adoption accelerates. Early market positioning enables relationship development with key transit authorities and establishes track records that influence future procurement decisions.
Service Model Innovation offers differentiation opportunities through Battery-as-a-Service offerings, comprehensive maintenance programs, and performance guarantee structures that address customer financial and operational concerns while creating recurring revenue streams.
Market expansion trajectory indicates sustained growth momentum through the remainder of the decade, driven by regulatory mandates, federal funding availability, and improving technology cost-effectiveness. MarkWide Research projects continued market acceleration with compound annual growth rates exceeding 15% as adoption moves beyond early adopter transit agencies to mainstream market acceptance.
Technology evolution will focus on addressing current limitations through improved cold weather performance, enhanced energy density, and reduced charging times. Solid-state battery development and advanced thermal management systems promise to eliminate remaining operational constraints while maintaining safety and reliability standards.
Geographic expansion beyond current leading markets will drive substantial growth as smaller transit agencies and rural transportation providers evaluate electric bus solutions. Federal funding programs specifically targeting smaller agencies and disadvantaged communities will accelerate adoption in previously underserved markets.
Application diversification into school buses, intercity coaches, and specialized transportation services will multiply market opportunities and drive technology development for diverse operational requirements. School bus electrification alone represents potential market expansion of 400-500% beyond current transit bus applications.
Integration advancement will create seamless ecosystems connecting battery systems, charging infrastructure, grid services, and fleet management platforms. This holistic approach will optimize total system performance while creating new revenue opportunities and operational efficiencies for all market participants.
The US electric bus battery pack market stands at a transformative inflection point where technological maturity, policy support, and economic viability converge to create unprecedented growth opportunities. Federal infrastructure investment, state-level environmental mandates, and improving cost competitiveness establish favorable conditions for sustained market expansion across diverse geographic regions and application segments.
Technology advancement continues addressing historical limitations while opening new possibilities for enhanced performance, operational flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. The evolution from early adoption challenges to mainstream market acceptance reflects the successful development of reliable, safe, and economically viable battery solutions that meet the demanding requirements of public transportation operations.
Market dynamics favor companies that combine technological innovation with strategic partnerships, domestic manufacturing capabilities, and comprehensive service offerings. The transition from component suppliers to integrated solution providers creates competitive advantages while addressing customer preferences for simplified procurement and operational management.
Future market potential extends far beyond current applications, with school bus electrification, intercity transportation, and emerging service models representing substantial growth opportunities. The foundation established by urban transit adoption creates the technological and infrastructure platform necessary to support broader market expansion and continued innovation in electric bus battery pack solutions.
What is Electric Bus Battery Pack?
Electric Bus Battery Pack refers to the collection of batteries used to power electric buses, providing the necessary energy for propulsion and onboard systems. These battery packs are crucial for the performance, range, and efficiency of electric buses.
What are the key players in the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market?
Key players in the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market include Proterra, BYD, and New Flyer, among others. These companies are involved in the design, manufacturing, and supply of battery packs specifically for electric buses.
What are the main drivers of the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market?
The main drivers of the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market include the increasing demand for sustainable public transportation, government incentives for electric vehicles, and advancements in battery technology that enhance performance and reduce costs.
What challenges does the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market face?
Challenges in the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market include high initial costs of battery technology, limited charging infrastructure, and concerns regarding battery lifespan and recycling. These factors can hinder widespread adoption of electric buses.
What opportunities exist in the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market?
Opportunities in the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market include the potential for innovation in battery chemistry, the expansion of charging networks, and increasing investments in electric public transport systems. These factors can drive growth and adoption.
What trends are shaping the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market?
Trends shaping the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market include the shift towards higher energy density batteries, the integration of smart technologies for battery management, and a growing focus on sustainability and environmental impact in transportation solutions.
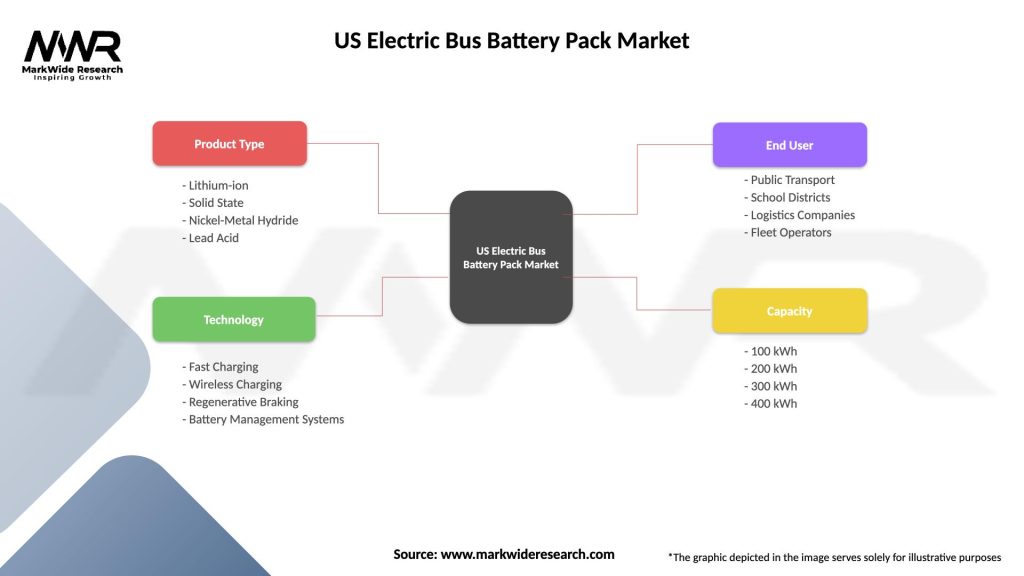
US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Lithium-ion, Solid State, Nickel-Metal Hydride, Lead Acid |
| Technology | Fast Charging, Wireless Charging, Regenerative Braking, Battery Management Systems |
| End User | Public Transport, School Districts, Logistics Companies, Fleet Operators |
| Capacity | 100 kWh, 200 kWh, 300 kWh, 400 kWh |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the US Electric Bus Battery Pack Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at