444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview:
The US Distributed Energy Resource Management System (DERMS) Market represents a transformative shift in the energy landscape, leveraging advanced technologies to manage and optimize the integration of distributed energy resources. DERMS plays a pivotal role in enhancing grid reliability, flexibility, and efficiency while facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources.
Meaning:
Distributed Energy Resource Management Systems (DERMS) encompass a suite of technologies and software solutions designed to monitor, control, and optimize the diverse array of distributed energy resources connected to the electrical grid. These resources include solar photovoltaics, energy storage systems, electric vehicles, and demand response technologies.
Executive Summary:
The US DERMS Market is undergoing significant growth driven by the increasing adoption of renewable energy, regulatory support for grid modernization, and the need for resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure. DERMS enables utilities, grid operators, and energy service providers to effectively manage the complexities of a decentralized energy ecosystem.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics:
The US DERMS Market operates within a dynamic landscape influenced by factors such as technological advancements, policy developments, market structures, and the evolving energy mix. Understanding and adapting to these dynamics are essential for stakeholders to harness the full potential of distributed energy resources.
Regional Analysis:
Regionally, the US DERMS Market exhibits variations based on factors such as renewable energy potential, grid infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and local energy policies. Key regions include:
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
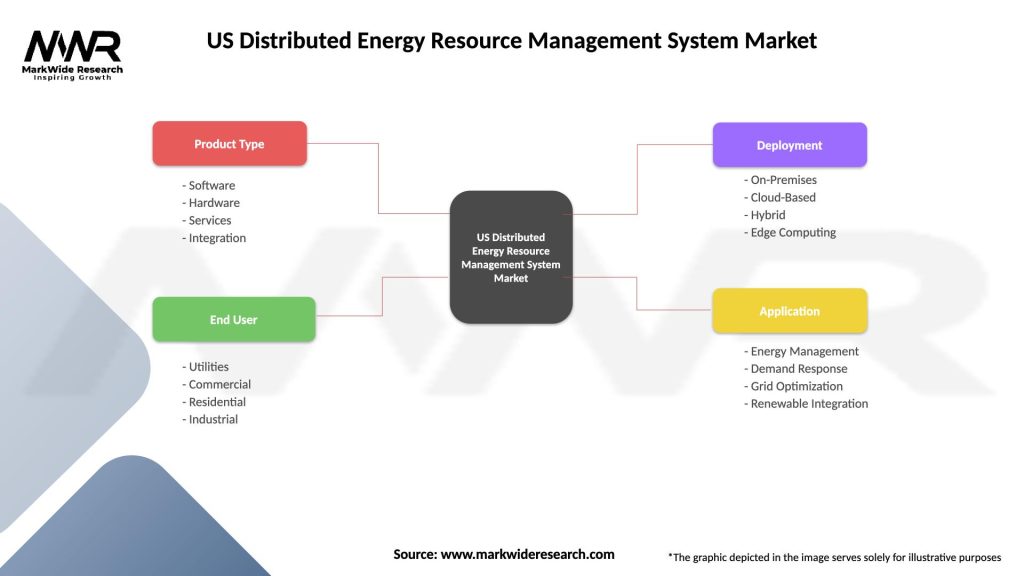
Segmentation:
The US DERMS Market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
A SWOT analysis provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats within the US DERMS Market:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact:
The Covid-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of resilient and adaptive energy systems. While the initial impact on DERMS projects may have included delays and resource constraints, the long-term outlook emphasizes the role of DERMS in enhancing grid flexibility and sustainability.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook:
The future outlook for the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System (DERMS) Market is optimistic, with sustained growth anticipated. As the energy landscape evolves, DERMS will continue to play a crucial role in shaping a resilient, flexible, and sustainable energy infrastructure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the US DERMS Market represents a pivotal element in the transformation of the energy sector, facilitating the integration of distributed energy resources and supporting the transition to a more sustainable and resilient grid. Industry participants, driven by technological innovation, regulatory support, and a commitment to environmental sustainability, are poised to contribute significantly to the advancement of DERMS solutions. As the market evolves, collaboration, education, and ongoing technological advancements will be key drivers of success in ensuring a reliable and efficient energy future for the United States.
What is Distributed Energy Resource Management System?
Distributed Energy Resource Management System refers to the technologies and processes used to manage distributed energy resources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems. These systems optimize the generation, distribution, and consumption of energy at a local level.
What are the key players in the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market?
Key players in the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market include companies like Siemens, Schneider Electric, and Enphase Energy, which provide innovative solutions for energy management and integration of renewable resources, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market?
The main drivers of growth in the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market include the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, the need for grid reliability, and advancements in energy storage technologies. These factors are pushing utilities and consumers towards more efficient energy management solutions.
What challenges does the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market face?
Challenges in the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market include regulatory hurdles, the complexity of integrating diverse energy sources, and the need for significant investment in infrastructure. These factors can slow down the deployment of effective management systems.
What opportunities exist in the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market?
Opportunities in the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market include the growing demand for smart grid technologies, increased investment in renewable energy projects, and the potential for enhanced energy efficiency in residential and commercial sectors. These trends are likely to drive innovation and market expansion.
What trends are shaping the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market?
Trends shaping the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market include the rise of decentralized energy systems, the integration of artificial intelligence for predictive analytics, and the increasing focus on sustainability and carbon reduction. These trends are influencing how energy is managed and consumed.
US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Software, Hardware, Services, Integration |
| End User | Utilities, Commercial, Residential, Industrial |
| Deployment | On-Premises, Cloud-Based, Hybrid, Edge Computing |
| Application | Energy Management, Demand Response, Grid Optimization, Renewable Integration |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the US Distributed Energy Resource Management System Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at