444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The US accommodation market represents one of the most dynamic and resilient sectors within the American hospitality industry, encompassing a diverse range of lodging options from luxury hotels to budget motels, vacation rentals, and extended-stay facilities. Market dynamics indicate substantial growth potential driven by recovering travel demand, evolving consumer preferences, and technological innovations transforming guest experiences. The sector has demonstrated remarkable adaptability, particularly following recent global challenges that reshaped travel patterns and accommodation preferences.
Industry transformation continues to accelerate as operators embrace digital technologies, sustainable practices, and personalized service offerings. The market encompasses traditional hotel chains, independent properties, alternative accommodations, and emerging hospitality concepts that cater to diverse traveler segments. Growth projections suggest the market will expand at a compound annual growth rate of 6.2% through the forecast period, supported by robust domestic tourism, business travel recovery, and increasing international visitor arrivals.
Regional distribution shows significant concentration in major metropolitan areas, tourist destinations, and business centers, with approximately 35% of accommodation capacity located in the top ten urban markets. The sector’s resilience stems from its ability to adapt to changing consumer behaviors, implement innovative revenue management strategies, and leverage technology to enhance operational efficiency and guest satisfaction.
The US accommodation market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of lodging facilities and services that provide temporary housing solutions for travelers, tourists, and business professionals across the United States. This market encompasses various property types including full-service hotels, limited-service hotels, extended-stay properties, motels, resorts, vacation rentals, and alternative accommodation platforms that facilitate short-term stays for diverse consumer segments.
Market scope extends beyond traditional hospitality services to include integrated experiences, technology-enabled booking platforms, property management systems, and ancillary services that enhance guest experiences. The accommodation sector serves as a critical component of the broader travel and tourism industry, supporting economic activity through direct employment, tax revenue generation, and multiplier effects across related industries including food service, transportation, and entertainment.
Operational framework involves complex revenue management strategies, distribution channel optimization, and service delivery models that adapt to seasonal demand fluctuations, market conditions, and evolving consumer expectations for personalized, technology-enhanced hospitality experiences.
Strategic analysis reveals the US accommodation market is experiencing a robust recovery phase characterized by strong demand fundamentals, operational innovation, and strategic repositioning across property segments. The market demonstrates resilience through diversified revenue streams, enhanced health and safety protocols, and accelerated digital transformation initiatives that improve guest engagement and operational efficiency.
Key performance indicators show occupancy rates have recovered to approximately 68% of pre-pandemic levels, with average daily rates experiencing upward pressure due to strong demand and constrained supply in key markets. The sector benefits from pent-up travel demand, corporate travel resumption, and leisure travel growth driven by domestic tourism preferences and flexible work arrangements enabling extended stays.
Competitive landscape features established hotel chains expanding their portfolio diversity, independent operators leveraging unique positioning strategies, and alternative accommodation platforms gaining market share through innovative service offerings. Technology adoption accelerates across property management, guest services, and revenue optimization, with 78% of properties implementing contactless check-in solutions and mobile-first guest experiences.
Future trajectory indicates sustained growth supported by infrastructure investments, tourism promotion initiatives, and evolving accommodation preferences that favor experiential stays, sustainable practices, and flexible booking options that accommodate changing travel patterns and consumer expectations.
Market intelligence reveals several transformative trends reshaping the accommodation landscape and creating new opportunities for growth and differentiation. Understanding these insights enables stakeholders to make informed strategic decisions and capitalize on emerging market dynamics.
Primary growth catalysts propelling the US accommodation market include recovering travel demand, evolving consumer preferences, and technological innovations that enhance operational efficiency and guest experiences. These drivers create sustainable momentum for market expansion across diverse property segments and geographic regions.
Travel demand recovery represents the most significant driver, with domestic leisure travel leading the resurgence followed by business travel normalization and international visitor growth. Corporate travel policies adapt to hybrid work models, creating opportunities for extended-stay properties and flexible accommodation arrangements that support remote work capabilities.
Consumer behavior evolution drives demand for personalized experiences, contactless services, and sustainable accommodation options. Travelers increasingly value authentic local experiences, wellness amenities, and technology-enabled convenience features that streamline the booking and stay experience while providing greater control over service interactions.
Economic factors including disposable income growth, employment recovery, and consumer confidence improvements support increased travel spending and accommodation demand. Government infrastructure investments and tourism promotion initiatives further stimulate market growth through improved accessibility and destination marketing efforts.
Technology advancement enables operational innovations, revenue optimization, and enhanced guest engagement through mobile applications, artificial intelligence, and integrated property management systems that improve efficiency while reducing operational costs and enhancing service quality.
Operational challenges continue to impact accommodation market growth, with labor shortages representing the most significant constraint affecting service delivery, operational efficiency, and expansion capabilities across property segments. The hospitality industry faces ongoing difficulties recruiting and retaining qualified staff, particularly in housekeeping, food service, and guest services roles.
Economic uncertainties including inflation pressures, interest rate fluctuations, and potential recession concerns create headwinds for both operators and consumers. Rising operational costs for utilities, supplies, and labor compress profit margins while potentially reducing consumer travel spending and accommodation demand.
Regulatory compliance requirements related to health and safety standards, accessibility regulations, and local zoning restrictions increase operational complexity and compliance costs. Alternative accommodation platforms face evolving regulatory frameworks that may limit growth opportunities in certain markets.
Supply chain disruptions affect property maintenance, renovation projects, and new construction timelines, potentially constraining capacity expansion and property improvement initiatives. Construction cost inflation and material availability issues impact development economics and project feasibility assessments.
Competition intensity from alternative accommodation options, including vacation rentals and home-sharing platforms, creates pricing pressure and market share challenges for traditional hotel operators, particularly in leisure travel segments and extended-stay categories.
Emerging opportunities within the US accommodation market create significant potential for growth, innovation, and market expansion across diverse segments and geographic regions. These opportunities align with evolving consumer preferences and technological capabilities that enable new service delivery models.
Sustainable tourism presents substantial opportunities as environmentally conscious travelers increasingly seek eco-friendly accommodation options. Properties implementing comprehensive sustainability programs, renewable energy systems, and waste reduction initiatives can command premium pricing while attracting environmentally aware guests and corporate clients with sustainability mandates.
Extended-stay accommodations benefit from remote work trends, corporate relocation needs, and temporary housing demand. This segment offers higher profit margins through longer average stays, reduced turnover costs, and opportunities for additional service revenue through laundry, grocery, and workspace amenities.
Technology integration creates opportunities for operational efficiency improvements, enhanced guest experiences, and new revenue streams through smart room features, mobile applications, and data analytics capabilities that optimize pricing and marketing strategies.
Niche market segments including wellness tourism, adventure travel, and cultural experiences offer differentiation opportunities for properties that can provide specialized amenities and services tailored to specific traveler interests and preferences.
Geographic expansion into underserved markets, emerging destinations, and secondary cities provides growth opportunities as travel patterns diversify and travelers seek authentic experiences beyond traditional tourist destinations.
Dynamic market forces continuously reshape the accommodation landscape through supply and demand interactions, competitive pressures, and external factors that influence operational strategies and investment decisions. According to MarkWide Research analysis, these dynamics create both challenges and opportunities for market participants.
Demand patterns exhibit seasonal variations, geographic concentration, and segment-specific characteristics that require sophisticated revenue management strategies. Leisure travel demand peaks during summer months and holiday periods, while business travel maintains more consistent patterns with weekday concentration in major metropolitan markets.
Supply dynamics reflect new property development, conversion projects, and capacity optimization initiatives that respond to market demand signals. Limited-service hotels and extended-stay properties represent the fastest-growing supply segments, with 42% of new hotel development focused on these categories due to favorable development economics and strong demand fundamentals.
Pricing mechanisms incorporate dynamic pricing strategies, competitive positioning, and value-based pricing models that optimize revenue per available room while maintaining market competitiveness. Advanced revenue management systems enable real-time pricing adjustments based on demand forecasts, competitor analysis, and market conditions.
Competitive dynamics intensify as traditional hotel operators compete with alternative accommodation platforms, independent properties, and new hospitality concepts that challenge conventional service delivery models and guest experience expectations.
Comprehensive research approach combines quantitative analysis, qualitative insights, and industry expertise to provide accurate market assessment and strategic recommendations. The methodology incorporates multiple data sources, validation techniques, and analytical frameworks that ensure research reliability and actionable insights.
Primary research includes structured interviews with industry executives, property managers, and hospitality professionals across diverse market segments and geographic regions. Survey data collection from accommodation operators provides insights into operational challenges, growth strategies, and market outlook perspectives.
Secondary research encompasses industry reports, government statistics, trade association data, and financial filings from publicly traded hospitality companies. Market data validation occurs through cross-referencing multiple sources and applying statistical analysis techniques to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Analytical framework utilizes market sizing methodologies, competitive analysis models, and trend identification techniques that provide comprehensive market understanding. Forecasting models incorporate historical performance data, leading indicators, and scenario analysis to project future market conditions.
Quality assurance processes include peer review, data verification, and expert validation to ensure research findings meet professional standards and provide reliable foundation for strategic decision-making by industry stakeholders and investors.
Geographic distribution of accommodation demand and supply reveals significant regional variations driven by economic activity, tourism attractions, and demographic factors that influence travel patterns and lodging preferences across different US markets.
Northeast region maintains strong market fundamentals supported by dense urban populations, established business centers, and cultural attractions that generate consistent accommodation demand. Major metropolitan areas including New York, Boston, and Washington DC account for approximately 28% of regional accommodation revenue, with luxury and business hotels commanding premium rates.
Southeast markets benefit from favorable climate conditions, tourism destinations, and population growth that drive accommodation demand across leisure and business segments. Florida leads regional performance with diverse tourism offerings, while Atlanta, Charlotte, and Nashville provide strong business travel foundations.
West Coast region demonstrates resilience through technology industry presence, international gateway airports, and diverse tourism attractions. California dominates regional accommodation capacity with 31% market share, while Pacific Northwest markets show strong growth potential driven by economic diversification and outdoor recreation tourism.
Central regions including the Midwest and Southwest exhibit steady growth supported by agricultural economies, energy industries, and emerging technology centers. Texas leads regional development with major metropolitan markets and diverse economic drivers supporting accommodation demand growth.
Mountain West represents the fastest-growing regional segment, benefiting from population migration, outdoor recreation tourism, and economic diversification that creates new accommodation demand in previously underserved markets.
Market structure features a diverse competitive environment with established hotel chains, independent operators, alternative accommodation platforms, and emerging hospitality concepts competing across multiple segments and price points.
Competitive strategies focus on brand differentiation, technology integration, loyalty program enhancement, and operational efficiency improvements that drive market share growth and profitability optimization across diverse property portfolios.
Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct accommodation categories serving different consumer needs, price points, and service expectations. Understanding these segments enables targeted marketing strategies and operational optimization approaches.
By Property Type:
By Guest Segment:
Luxury segment demonstrates strong performance recovery with affluent travelers prioritizing premium experiences, personalized service, and exclusive amenities. This category benefits from pent-up demand for high-end travel experiences and shows resilience to economic fluctuations through strong brand loyalty and pricing power.
Midscale properties represent the largest accommodation segment by room count, serving diverse traveler needs with balanced amenities and competitive pricing. This category adapts well to changing market conditions through operational flexibility and broad appeal across business and leisure segments.
Economy accommodations maintain steady demand from price-sensitive travelers, essential workers, and budget-conscious leisure guests. Operators focus on operational efficiency, technology integration, and strategic location selection to maintain profitability in this competitive segment.
Extended-stay category experiences the strongest growth trajectory, benefiting from remote work trends, corporate relocations, and temporary housing needs. Properties in this segment achieve higher profit margins through longer average stays and reduced operational costs per occupied room.
Alternative accommodations including vacation rentals and boutique properties gain market share through unique positioning, local experiences, and flexible booking options that appeal to experience-seeking travelers and groups requiring specialized accommodations.
Operational advantages for accommodation providers include revenue diversification opportunities, technology-enabled efficiency improvements, and enhanced guest engagement capabilities that drive customer loyalty and repeat business generation.
Investment benefits for stakeholders encompass stable cash flow generation, asset appreciation potential, and portfolio diversification advantages through real estate ownership and hospitality operations that provide inflation hedging characteristics.
Economic contributions extend beyond direct operations to include employment generation, tax revenue creation, and multiplier effects that support local economies through supply chain spending, employee wages, and ancillary business development.
Guest value propositions include convenient accommodation options, competitive pricing structures, and enhanced service offerings that meet diverse travel needs while providing memorable experiences and value-added amenities.
Community benefits encompass tourism promotion, cultural exchange facilitation, and economic development support that enhances destination attractiveness and creates sustainable growth opportunities for local businesses and service providers.
Technology advantages enable operational optimization, guest experience enhancement, and data-driven decision making that improve efficiency while reducing costs and environmental impact through smart building systems and resource management technologies.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital transformation accelerates across the accommodation sector with contactless check-in, mobile key access, and artificial intelligence-powered guest services becoming standard offerings rather than premium features. Properties invest in technology infrastructure to meet evolving guest expectations and improve operational efficiency.
Sustainability initiatives gain prominence as environmental consciousness influences guest preferences and corporate travel policies. Hotels implement comprehensive sustainability programs including renewable energy adoption, waste reduction, and local sourcing that appeal to environmentally aware travelers while reducing operational costs.
Personalization strategies leverage guest data and preferences to create customized experiences, targeted marketing campaigns, and tailored service offerings that enhance guest satisfaction and loyalty. Advanced analytics enable properties to anticipate guest needs and deliver proactive service solutions.
Wellness integration expands beyond traditional spa services to include fitness facilities, healthy dining options, and mental wellness programs that address growing consumer focus on health and well-being during travel experiences.
Flexible booking policies become competitive necessities as travelers demand cancellation flexibility, modification options, and transparent pricing structures that accommodate uncertain travel plans and changing circumstances.
Local experience emphasis drives properties to partner with local businesses, cultural attractions, and activity providers to offer authentic destination experiences that differentiate their offerings from standardized chain accommodations.
Strategic acquisitions and mergers reshape the competitive landscape as major hotel companies expand their portfolio diversity and geographic presence through targeted transactions. These consolidation activities create operational synergies and enhanced distribution capabilities.
Technology partnerships between accommodation providers and technology companies accelerate innovation adoption and service enhancement capabilities. Collaborations focus on guest experience platforms, operational automation, and data analytics solutions that improve efficiency and service quality.
Sustainability certifications become increasingly important as properties pursue LEED certification, Green Key recognition, and other environmental standards that validate their commitment to sustainable operations and appeal to environmentally conscious guests and corporate clients.
Franchise expansion strategies enable hotel brands to grow their presence while minimizing capital investment requirements. Franchise models provide operational flexibility and local market expertise while maintaining brand standards and guest experience consistency.
Alternative accommodation integration sees traditional hotel companies launching their own home-sharing platforms and boutique property collections to compete with independent alternative accommodation providers and capture market share in this growing segment.
Workforce development initiatives address labor shortage challenges through enhanced training programs, competitive compensation packages, and career advancement opportunities that improve employee retention and service quality standards.
Strategic recommendations for accommodation market participants emphasize technology investment, operational efficiency optimization, and guest experience enhancement as critical success factors in the evolving hospitality landscape. MWR analysis suggests focusing on differentiation strategies that leverage unique property characteristics and local market advantages.
Investment priorities should emphasize revenue management systems, guest experience technologies, and sustainability initiatives that provide competitive advantages while improving operational efficiency. Properties that successfully integrate these elements demonstrate superior financial performance and guest satisfaction metrics.
Market positioning strategies require clear value propositions that address specific guest segments and travel purposes. Successful operators identify their target markets and align their service offerings, amenities, and pricing strategies to meet those specific needs effectively.
Operational excellence initiatives should focus on staff training, service consistency, and quality assurance programs that maintain brand standards while adapting to local market preferences and cultural expectations.
Growth strategies benefit from geographic diversification, segment expansion, and strategic partnerships that provide access to new markets and customer segments while managing risk through portfolio diversification.
Financial management approaches should emphasize cash flow optimization, cost control measures, and capital allocation strategies that balance growth investments with profitability maintenance during varying market conditions.
Long-term prospects for the US accommodation market remain positive, supported by demographic trends, economic growth expectations, and evolving travel preferences that create sustained demand for diverse lodging options. The market is projected to achieve a compound annual growth rate of 5.8% over the next five years, driven by domestic tourism growth and business travel normalization.
Technology evolution will continue transforming guest experiences and operational capabilities through artificial intelligence, Internet of Things integration, and advanced analytics that enable predictive service delivery and operational optimization. Properties that successfully implement these technologies will gain competitive advantages through improved efficiency and guest satisfaction.
Sustainability requirements will become increasingly important as environmental regulations tighten and guest preferences shift toward eco-friendly accommodations. Properties investing in renewable energy, waste reduction, and sustainable operations will benefit from cost savings and enhanced market positioning.
Market consolidation trends may accelerate as smaller operators seek strategic partnerships or acquisition opportunities to compete effectively against larger chains with superior technology capabilities and distribution networks. This consolidation could create opportunities for well-positioned independent operators and niche market specialists.
Consumer behavior evolution toward experience-focused travel and flexible accommodation arrangements will drive continued innovation in service delivery models, property design, and amenity offerings that cater to changing lifestyle preferences and work patterns.
Market assessment reveals the US accommodation market demonstrates strong fundamentals and positive growth trajectory supported by recovering travel demand, technological innovation, and evolving consumer preferences that create opportunities across diverse property segments and geographic regions. The sector’s resilience and adaptability position it well for sustained growth despite ongoing challenges related to labor availability and economic uncertainties.
Strategic success in this dynamic market requires focus on operational excellence, technology integration, and guest experience enhancement while maintaining financial discipline and market responsiveness. Properties that successfully balance these priorities while adapting to changing market conditions will achieve superior performance and sustainable competitive advantages.
Investment outlook remains favorable for well-positioned accommodation providers that can demonstrate operational efficiency, market differentiation, and growth potential through strategic positioning and execution capabilities. The market offers attractive opportunities for stakeholders who understand regional dynamics, segment preferences, and emerging trends that shape future demand patterns and competitive requirements.
What is Accommodation?
Accommodation refers to the provision of lodging or housing for travelers and tourists, including hotels, motels, hostels, and vacation rentals. It plays a crucial role in the hospitality industry by offering various options to meet the needs of different types of guests.
What are the key players in the US Accommodation Market?
Key players in the US Accommodation Market include major hotel chains like Marriott International, Hilton Worldwide, and Hyatt Hotels Corporation. These companies dominate the market by offering a range of services and amenities to cater to diverse customer preferences, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the US Accommodation Market?
The US Accommodation Market is driven by factors such as increasing domestic and international travel, a growing preference for unique lodging experiences, and the rise of online booking platforms. Additionally, the expansion of business travel and tourism contributes to market growth.
What challenges does the US Accommodation Market face?
The US Accommodation Market faces challenges such as fluctuating demand due to economic conditions, competition from alternative lodging options like Airbnb, and regulatory hurdles. These factors can impact occupancy rates and profitability for accommodation providers.
What opportunities exist in the US Accommodation Market?
Opportunities in the US Accommodation Market include the potential for growth in eco-friendly accommodations, the integration of technology for enhanced guest experiences, and the expansion of niche markets such as wellness tourism. These trends can attract new customer segments and increase revenue.
What trends are shaping the US Accommodation Market?
Trends shaping the US Accommodation Market include the rise of experiential travel, increased focus on sustainability, and the adoption of smart technology in accommodations. These trends reflect changing consumer preferences and the industry’s response to evolving market demands.
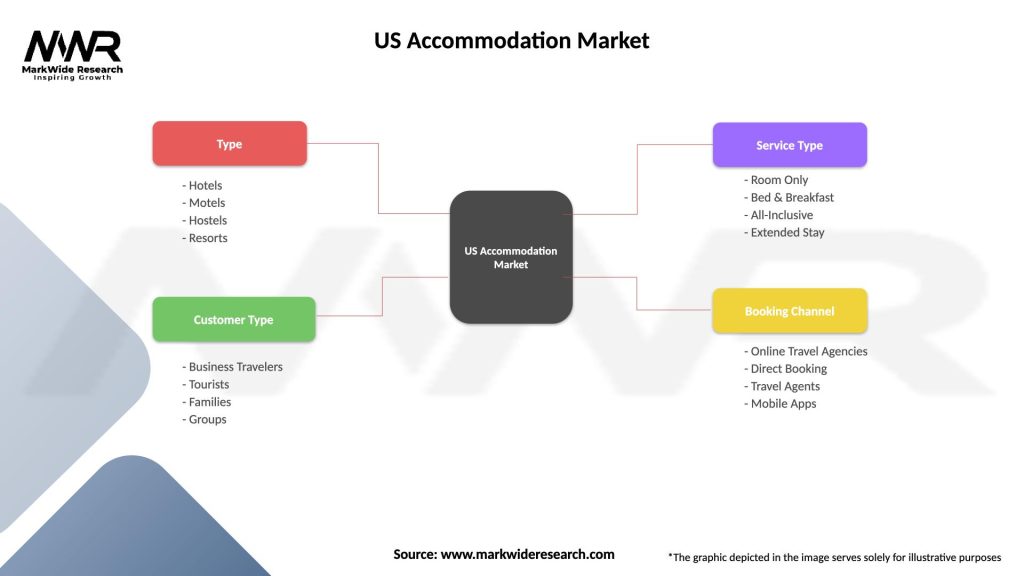
US Accommodation Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Hotels, Motels, Hostels, Resorts |
| Customer Type | Business Travelers, Tourists, Families, Groups |
| Service Type | Room Only, Bed & Breakfast, All-Inclusive, Extended Stay |
| Booking Channel | Online Travel Agencies, Direct Booking, Travel Agents, Mobile Apps |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the US Accommodation Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at