444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The United States primary care physician market represents a cornerstone of the American healthcare system, encompassing family medicine practitioners, internal medicine specialists, and general practitioners who serve as the first point of contact for patients seeking medical care. This critical healthcare segment has experienced significant transformation driven by evolving patient demographics, technological advancements, and changing healthcare delivery models.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth potential, with the sector experiencing a 4.2% annual growth rate in physician demand over recent years. The increasing emphasis on preventive care, population health management, and value-based care models has positioned primary care physicians as essential gatekeepers in the healthcare ecosystem. Geographic distribution shows concentrated demand in metropolitan areas, while rural regions face persistent physician shortages affecting healthcare accessibility.
Healthcare policy changes and insurance reforms have substantially impacted primary care delivery, creating new opportunities for practice consolidation, telemedicine integration, and innovative care models. The market encompasses various practice settings including independent practices, hospital-employed physicians, federally qualified health centers, and emerging retail health clinics. Patient satisfaction metrics consistently rank primary care accessibility and quality as top healthcare priorities, driving continued investment in this sector.
The United States primary care physician market refers to the comprehensive healthcare sector encompassing medical professionals who provide first-contact, continuous, comprehensive, and coordinated care to patients across all demographics and health conditions. This market includes family medicine physicians, internal medicine specialists, pediatricians, and geriatricians who serve as primary healthcare providers.
Primary care physicians function as healthcare coordinators, managing patient relationships, providing preventive care, treating common illnesses, and coordinating referrals to specialists when necessary. The market encompasses various practice models including traditional fee-for-service arrangements, value-based care contracts, direct primary care models, and concierge medicine practices. Scope of services typically includes routine check-ups, chronic disease management, preventive screenings, immunizations, and basic diagnostic procedures.
Market participants include individual practitioners, multi-specialty group practices, hospital systems, healthcare networks, and emerging digital health platforms. The sector plays a crucial role in healthcare cost containment, population health improvement, and patient satisfaction enhancement through accessible, coordinated care delivery.
Strategic analysis reveals the United States primary care physician market is experiencing unprecedented transformation driven by demographic shifts, technological innovation, and evolving healthcare policies. The sector demonstrates resilient growth patterns despite facing significant challenges including physician shortages, burnout concerns, and changing reimbursement models.
Key market drivers include an aging population requiring increased medical attention, growing emphasis on preventive care, and healthcare policy reforms promoting primary care accessibility. The market benefits from a 68% patient preference for establishing long-term relationships with primary care providers, supporting practice stability and growth potential. Technology integration has accelerated dramatically, with electronic health records adoption reaching near-universal levels and telemedicine utilization expanding significantly.
Competitive landscape features increasing consolidation as independent practices join larger healthcare systems seeking operational efficiencies and improved bargaining power with insurance providers. The emergence of retail health clinics, urgent care centers, and digital health platforms creates both competitive pressure and collaboration opportunities for traditional primary care practices. Market outlook remains positive, supported by fundamental healthcare needs and continued policy emphasis on primary care strengthening.
Market intelligence reveals several critical insights shaping the United States primary care physician landscape:
According to MarkWide Research, these insights reflect fundamental market shifts that will continue shaping primary care delivery models and practice operations throughout the coming decade.
Demographic transformation serves as the primary catalyst driving United States primary care physician market expansion. The aging baby boomer population requires increased medical attention, with individuals over 65 typically requiring 2.5 times more primary care visits than younger demographics. This demographic shift creates sustained demand for primary care services across multiple specialties.
Healthcare policy initiatives continue promoting primary care accessibility and quality improvement. The Affordable Care Act expanded insurance coverage, increasing patient access to primary care services while emphasizing preventive care benefits. Medicare and Medicaid programs have implemented enhanced reimbursement rates for primary care services, improving practice economics and sustainability.
Chronic disease prevalence drives consistent demand for ongoing primary care management. Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease require regular monitoring and medication management, creating stable patient relationships and revenue streams for primary care practices. Preventive care emphasis has shifted healthcare focus toward early intervention and wellness programs, positioning primary care physicians as essential healthcare coordinators.
Technology advancement enables improved care delivery efficiency and patient engagement. Electronic health records, telemedicine platforms, and remote monitoring devices allow primary care physicians to manage larger patient panels while maintaining quality care standards. These technological capabilities support practice growth and operational optimization.
Physician shortage challenges represent the most significant constraint facing the United States primary care physician market. Medical school graduates increasingly choose specialty fields over primary care due to income disparities and lifestyle considerations. This shortage creates access barriers for patients and limits market growth potential in underserved regions.
Reimbursement pressures continue challenging practice economics, particularly for independent physicians. Insurance companies often provide lower reimbursement rates for primary care services compared to specialty procedures, creating financial sustainability concerns. Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement levels frequently fail to cover actual care delivery costs, impacting practice profitability.
Regulatory compliance burden increases administrative costs and complexity for primary care practices. Electronic health record meaningful use requirements, quality reporting mandates, and insurance authorization processes consume significant physician time and staff resources. These administrative demands reduce time available for patient care and increase operational expenses.
Burnout and workforce retention issues affect physician availability and practice stability. High patient volumes, administrative burdens, and work-life balance challenges contribute to physician burnout rates exceeding 42% among primary care providers. This burnout leads to early retirement, career changes, and reduced practice hours, constraining market capacity.
Telemedicine expansion presents substantial growth opportunities for primary care physicians to extend their reach and improve patient accessibility. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated telemedicine adoption, with many patients now preferring virtual consultations for routine care. This technology enables physicians to serve patients across broader geographic areas while reducing overhead costs.
Value-based care contracts offer financial incentives for primary care physicians who demonstrate improved patient outcomes and cost management. These arrangements provide opportunities for higher reimbursement rates while aligning physician incentives with patient health goals. Successful participation in value-based programs can significantly enhance practice revenue and sustainability.
Direct primary care models eliminate insurance intermediaries, allowing physicians to establish direct payment relationships with patients. This approach reduces administrative burden while providing predictable revenue streams and enhanced patient relationships. The model appeals to both physicians seeking practice autonomy and patients desiring personalized care access.
Rural healthcare initiatives create opportunities for primary care physicians to serve underserved communities with government support and loan forgiveness programs. Federal and state programs offer financial incentives, including student loan forgiveness and enhanced reimbursement rates, for physicians practicing in designated shortage areas. These initiatives address critical access needs while providing attractive career opportunities.
Supply and demand imbalances create complex market dynamics affecting physician distribution, reimbursement rates, and practice models. High-demand regions experience competitive physician recruitment while rural areas struggle with access challenges. This geographic disparity influences practice location decisions and compensation levels across different markets.
Insurance market evolution impacts primary care physician relationships with payers and patients. High-deductible health plans shift more healthcare costs to patients, affecting care-seeking behavior and practice revenue patterns. Insurance network participation decisions significantly influence patient access and practice growth potential.
Technology integration costs versus efficiency gains create ongoing investment decisions for primary care practices. Electronic health record systems, telemedicine platforms, and practice management software require substantial upfront investments but offer long-term operational improvements. Practices must balance technology costs with productivity enhancements and patient satisfaction benefits.
Competitive pressure from alternative care delivery models influences traditional primary care practice strategies. Retail health clinics, urgent care centers, and digital health platforms provide convenient alternatives for certain patient needs. Primary care physicians must differentiate their services through comprehensive care coordination, relationship continuity, and specialized expertise.
Comprehensive market analysis employed multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into the United States primary care physician market. Primary research included surveys and interviews with practicing physicians, healthcare administrators, and industry experts across diverse geographic regions and practice settings.
Secondary research sources encompassed government healthcare databases, professional medical associations, academic research publications, and industry reports. Data collection focused on physician supply trends, practice economics, patient demographics, and healthcare policy impacts. Quantitative analysis utilized statistical modeling to project market trends and identify growth opportunities.
Geographic segmentation analyzed market conditions across urban, suburban, and rural regions to understand regional variations in physician supply, demand patterns, and practice characteristics. This approach provided insights into market disparities and growth potential across different geographic markets.
Stakeholder interviews included healthcare system executives, insurance company representatives, technology vendors, and policy makers to gather diverse perspectives on market dynamics and future trends. These qualitative insights complemented quantitative data analysis to provide comprehensive market understanding.
Northeast region demonstrates the highest concentration of primary care physicians per capita, with established medical schools and healthcare systems supporting robust physician supply. Urban areas like Boston, New York, and Philadelphia maintain 15% higher physician density compared to national averages. However, rural areas within the region still experience access challenges despite overall physician abundance.
Southeast markets show rapid population growth driving increased demand for primary care services, particularly in Florida, North Carolina, and Texas. These states have implemented physician recruitment programs and expanded medical education capacity to address growing healthcare needs. The region benefits from favorable practice economics and lower operational costs compared to northeastern markets.
Midwest region faces mixed market conditions with strong physician supply in major metropolitan areas but significant shortages in rural communities. States like Ohio, Illinois, and Michigan have established telemedicine programs and rural health initiatives to improve access in underserved areas. The region maintains stable practice economics with moderate reimbursement rates and operational costs.
Western states experience diverse market conditions ranging from physician oversupply in California urban areas to critical shortages in rural Nevada, Wyoming, and Montana. The region leads in healthcare innovation and technology adoption, with many practices implementing advanced telemedicine and digital health solutions. Market share distribution shows California accounting for approximately 22% of national primary care physician demand.
Market structure encompasses diverse participants ranging from individual practitioners to large healthcare systems and emerging digital health platforms. The competitive environment continues evolving as traditional practice models adapt to changing healthcare delivery expectations and reimbursement pressures.
Major healthcare systems dominate urban markets through physician employment and practice acquisition strategies:
Independent practice associations and physician groups maintain significant market presence, particularly in suburban and rural markets. These organizations provide operational support and negotiating power while preserving physician autonomy. Retail health clinics operated by CVS Health, Walgreens, and other retailers create competitive pressure for routine care services.
Digital health platforms including telemedicine providers and virtual care companies represent emerging competitive forces offering convenient access alternatives for certain patient needs.
By Specialty Type:
By Practice Setting:
By Geographic Region:
Family Medicine segment represents the largest category within primary care, accounting for approximately 35% of primary care physician workforce. These practitioners provide comprehensive care across all age groups, making them particularly valuable in rural and underserved communities. Family medicine physicians often serve as healthcare coordinators, managing both acute and chronic conditions while emphasizing preventive care and patient education.
Internal Medicine specialists focus on adult primary care with expertise in complex medical conditions and chronic disease management. This segment demonstrates strong growth in urban markets where adult populations require sophisticated medical management. Internal medicine physicians often serve as consultants to other primary care providers for challenging diagnostic cases.
Pediatric primary care addresses the unique healthcare needs of children and adolescents, emphasizing developmental milestones, immunizations, and family-centered care. This segment benefits from stable patient relationships and predictable care patterns, though it faces challenges from declining birth rates in some regions.
Geriatric medicine represents a rapidly growing segment driven by population aging trends. These specialists focus on the complex medical needs of elderly patients, including medication management, cognitive health, and care coordination across multiple specialists. The segment offers significant growth opportunities as baby boomers age and require specialized primary care attention.
Healthcare Systems benefit from primary care physician integration through improved care coordination, enhanced patient satisfaction, and stronger referral networks. Primary care serves as a foundation for specialty services while supporting population health management initiatives and value-based care contracts.
Insurance Companies realize cost savings through primary care emphasis, as these physicians provide preventive care and early intervention that reduces expensive emergency department visits and hospitalizations. Strong primary care networks improve member satisfaction and support managed care objectives.
Patients gain access to comprehensive, coordinated healthcare through established primary care relationships. Benefits include continuity of care, preventive health maintenance, chronic disease management, and navigation support for complex healthcare needs. Primary care physicians serve as trusted healthcare advisors and advocates.
Government Programs achieve healthcare policy objectives through primary care strengthening, including improved population health outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and enhanced access in underserved communities. Primary care emphasis supports public health initiatives and healthcare equity goals.
Technology Vendors find significant market opportunities in providing electronic health records, telemedicine platforms, practice management systems, and clinical decision support tools specifically designed for primary care workflows and requirements.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Practice consolidation continues accelerating as independent physicians join larger healthcare systems seeking operational support, improved bargaining power, and reduced administrative burden. This trend reflects economic pressures and the complexity of modern healthcare delivery requirements.
Telemedicine integration has become a permanent feature of primary care delivery, with patients expecting virtual consultation options for routine care and follow-up visits. Physicians are developing hybrid care models combining in-person and virtual interactions to optimize patient convenience and practice efficiency.
Value-based care adoption is transforming reimbursement models from fee-for-service to outcome-based payments. Primary care physicians are increasingly participating in accountable care organizations and risk-sharing arrangements that reward quality outcomes and cost management.
Workforce diversification includes expanded roles for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in primary care delivery. These professionals help address physician shortages while providing cost-effective care for routine services and chronic disease management.
Patient experience focus emphasizes convenience, accessibility, and communication quality. Practices are implementing online scheduling, patient portals, extended hours, and same-day appointments to meet evolving patient expectations and competitive pressures.
Medicare payment reforms have increased primary care reimbursement rates and introduced new payment models recognizing the value of comprehensive primary care services. These changes include enhanced payments for chronic care management and care coordination activities.
State-level initiatives across multiple states have implemented primary care investment programs, loan forgiveness for rural practice, and scope of practice expansions for nurse practitioners and physician assistants. These efforts address physician shortage challenges and improve healthcare access.
Technology advancement in artificial intelligence and clinical decision support tools is beginning to augment primary care physician capabilities. These systems help with diagnosis, treatment recommendations, and population health management while reducing administrative burden.
Corporate healthcare entry by technology companies and retailers is creating new competitive dynamics. Companies like Amazon, Apple, and major retailers are developing primary care delivery models that challenge traditional practice structures.
MWR analysis indicates these developments represent fundamental shifts in primary care delivery models rather than temporary market adjustments, suggesting sustained transformation in the coming years.
Practice optimization should focus on technology integration, operational efficiency improvements, and patient experience enhancement. Primary care physicians should invest in electronic health record optimization, telemedicine capabilities, and practice management systems that reduce administrative burden while improving care quality.
Financial sustainability requires diversified revenue strategies including value-based care participation, direct primary care models, and ancillary service development. Practices should evaluate alternative payment arrangements and consider joining accountable care organizations or other risk-sharing programs.
Workforce development strategies should include nurse practitioner and physician assistant integration, staff cross-training, and physician wellness programs. Addressing burnout and work-life balance issues is essential for maintaining physician satisfaction and practice stability.
Market positioning should emphasize comprehensive care coordination, patient relationship continuity, and preventive health expertise. Primary care practices must differentiate themselves from convenient care alternatives through superior clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Geographic expansion opportunities exist in underserved rural and urban areas with government support programs and enhanced reimbursement rates. Practices should evaluate telemedicine capabilities for serving broader geographic regions while maintaining quality care standards.
Market projections indicate continued growth in primary care physician demand driven by demographic trends, healthcare policy support, and evolving care delivery models. The sector is expected to maintain a 3.8% annual growth rate over the next decade, supported by population aging and increased emphasis on preventive care.
Technology integration will accelerate with artificial intelligence, remote monitoring, and digital health platforms becoming standard primary care tools. These technologies will enable physicians to manage larger patient panels while maintaining personalized care relationships and improving clinical outcomes.
Payment model evolution toward value-based care will continue, with an estimated 75% of primary care physicians participating in some form of alternative payment arrangement within five years. This shift will reward quality outcomes and cost management while providing financial stability for practices.
Workforce solutions will include expanded scope of practice for advanced practice providers, international medical graduate recruitment, and innovative training programs. Technology will augment physician capabilities while addressing shortage challenges in underserved areas.
Market consolidation will continue as independent practices join larger healthcare systems, though direct primary care and concierge medicine models will provide alternatives for physicians seeking practice autonomy. The competitive landscape will feature diverse delivery models serving different patient populations and preferences.
The United States primary care physician market stands at a critical juncture, facing both significant challenges and substantial opportunities. While physician shortages and reimbursement pressures create ongoing constraints, demographic trends, technology advancement, and policy support provide strong growth foundations for the sector.
Market transformation toward value-based care, technology integration, and alternative delivery models will continue reshaping primary care practice. Successful physicians and healthcare systems will adapt to these changes while maintaining focus on comprehensive patient care, clinical quality, and operational efficiency. The sector’s essential role in healthcare delivery ensures continued investment and policy support, positioning primary care physicians as central figures in America’s evolving healthcare landscape.
What is Primary Care Physician?
Primary care physicians are medical doctors who provide comprehensive healthcare services, focusing on overall health management, preventive care, and the treatment of common illnesses. They serve as the first point of contact for patients and coordinate care with specialists when necessary.
What are the key players in the United States Primary Care Physician Market?
Key players in the United States Primary Care Physician Market include companies like UnitedHealth Group, Anthem, and Cigna, which provide health insurance and support services for primary care. Additionally, healthcare systems such as HCA Healthcare and Tenet Healthcare play significant roles in this market, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the United States Primary Care Physician Market?
The growth of the United States Primary Care Physician Market is driven by factors such as an increasing aging population, a rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and a growing emphasis on preventive care. Additionally, the expansion of telehealth services has made primary care more accessible.
What challenges does the United States Primary Care Physician Market face?
The United States Primary Care Physician Market faces challenges such as physician burnout, a shortage of primary care providers, and reimbursement issues. These factors can hinder the ability to deliver timely and effective care to patients.
What opportunities exist in the United States Primary Care Physician Market?
Opportunities in the United States Primary Care Physician Market include the integration of technology in healthcare, such as telemedicine and electronic health records, which can enhance patient care. Additionally, there is potential for growth in value-based care models that focus on patient outcomes.
What trends are shaping the United States Primary Care Physician Market?
Trends shaping the United States Primary Care Physician Market include the increasing adoption of telehealth services, a shift towards value-based care, and a focus on holistic patient management. These trends are influencing how primary care is delivered and accessed.
United States Primary Care Physician Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
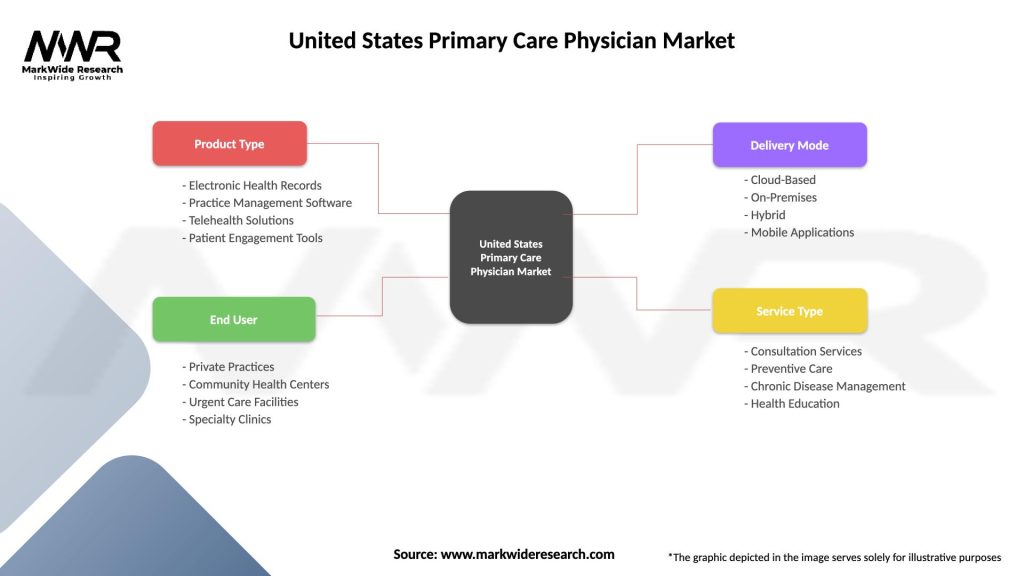
| Product Type | Electronic Health Records, Practice Management Software, Telehealth Solutions, Patient Engagement Tools |
| End User | Private Practices, Community Health Centers, Urgent Care Facilities, Specialty Clinics |
| Delivery Mode | Cloud-Based, On-Premises, Hybrid, Mobile Applications |
| Service Type | Consultation Services, Preventive Care, Chronic Disease Management, Health Education |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the United States Primary Care Physician Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at