444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The United States healthcare ERP market represents a rapidly evolving sector that combines enterprise resource planning technology with specialized healthcare management solutions. Healthcare organizations across the nation are increasingly adopting comprehensive ERP systems to streamline operations, enhance patient care delivery, and ensure regulatory compliance. The market encompasses hospitals, clinics, pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers, and healthcare service providers seeking integrated technology solutions.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth driven by digital transformation initiatives, regulatory requirements, and the need for operational efficiency. Healthcare ERP systems integrate various functions including patient management, financial operations, supply chain management, human resources, and clinical workflows into unified platforms. The market is experiencing significant expansion with healthcare organizations recognizing the critical importance of data-driven decision making and streamlined operations.
Technology adoption patterns show increasing preference for cloud-based solutions, mobile accessibility, and artificial intelligence integration. The market benefits from substantial investments in healthcare IT infrastructure, government initiatives promoting electronic health records, and growing emphasis on value-based care models. Regional distribution shows concentration in major metropolitan areas with high healthcare facility density, while rural healthcare providers increasingly seek cost-effective ERP solutions.
The United States healthcare ERP market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of enterprise resource planning software solutions specifically designed and implemented for healthcare organizations across the country. These integrated systems combine multiple business processes including patient management, financial operations, supply chain coordination, human resources management, and clinical workflow optimization into unified digital platforms.
Healthcare ERP systems serve as centralized hubs that enable healthcare providers to manage complex operations efficiently while maintaining compliance with industry regulations such as HIPAA, FDA requirements, and quality standards. The market encompasses various deployment models including on-premise installations, cloud-based solutions, and hybrid configurations tailored to different organizational needs and technical capabilities.
Core functionality includes real-time data processing, automated workflow management, predictive analytics, and seamless integration with existing healthcare technologies. These systems facilitate improved patient outcomes, operational efficiency, cost reduction, and strategic decision-making capabilities for healthcare organizations ranging from small clinics to large hospital networks and pharmaceutical enterprises.
Strategic analysis reveals the United States healthcare ERP market as a dynamic sector experiencing substantial transformation driven by technological innovation and evolving healthcare delivery models. The market demonstrates strong growth momentum supported by increasing digitization initiatives, regulatory compliance requirements, and operational efficiency demands across healthcare organizations.
Key market drivers include the shift toward value-based care models, growing emphasis on patient experience optimization, and the need for integrated data management solutions. Healthcare organizations are investing heavily in ERP systems to achieve operational excellence while managing complex regulatory environments and increasing cost pressures. The market benefits from favorable government policies promoting healthcare IT adoption and interoperability standards.
Competitive landscape features established technology vendors alongside specialized healthcare software providers offering comprehensive ERP solutions. Market participants are focusing on innovation in areas such as artificial intelligence integration, mobile accessibility, and cloud-based deployment models. The market shows strong potential for continued expansion as healthcare organizations prioritize digital transformation initiatives and seek comprehensive technology solutions to support their operational objectives.

Market intelligence reveals several critical insights shaping the United States healthcare ERP landscape:
Digital transformation initiatives serve as the primary catalyst driving healthcare ERP market expansion across the United States. Healthcare organizations are recognizing the critical importance of integrated technology solutions to remain competitive and deliver high-quality patient care. The shift from traditional paper-based processes to digital workflows creates substantial demand for comprehensive ERP systems that can manage complex healthcare operations efficiently.
Regulatory compliance requirements continue to drive ERP adoption as healthcare organizations must navigate increasingly complex regulatory environments. Systems must ensure HIPAA compliance, support FDA reporting requirements, and maintain quality standards while providing audit trails and documentation capabilities. The need for automated compliance monitoring and reporting features makes ERP systems essential for healthcare organizations seeking to minimize regulatory risks.
Value-based care models are transforming healthcare delivery and creating demand for ERP systems that can support outcome-based payment structures. Healthcare providers require sophisticated analytics capabilities to track patient outcomes, measure quality metrics, and optimize care delivery processes. ERP systems enable organizations to collect, analyze, and report on the comprehensive data required for value-based care participation and success.
Operational efficiency demands drive healthcare organizations to seek integrated solutions that can streamline workflows, reduce administrative burden, and optimize resource utilization. ERP systems provide automation capabilities that eliminate manual processes, reduce errors, and enable healthcare professionals to focus on patient care rather than administrative tasks. The growing emphasis on operational excellence makes ERP systems critical investments for healthcare organizations.
Implementation complexity represents a significant barrier to healthcare ERP adoption, particularly for smaller healthcare organizations with limited technical resources. The process of integrating ERP systems with existing healthcare technologies, migrating data, and training staff requires substantial time, expertise, and organizational commitment. Many healthcare providers struggle with the technical challenges and disruption associated with ERP implementation projects.
High initial investment costs create financial barriers for healthcare organizations, especially smaller practices and rural hospitals operating with constrained budgets. ERP systems require significant upfront investments in software licensing, hardware infrastructure, implementation services, and staff training. The total cost of ownership, including ongoing maintenance and support expenses, can be prohibitive for organizations with limited financial resources.
Data security concerns pose ongoing challenges as healthcare organizations must protect sensitive patient information while implementing comprehensive ERP systems. The increasing frequency of cybersecurity threats targeting healthcare data creates reluctance among some organizations to adopt cloud-based ERP solutions or integrate systems across networks. Ensuring robust security measures while maintaining system functionality requires careful planning and ongoing investment.
Change management resistance within healthcare organizations can impede ERP adoption as staff members may resist new technologies and workflow changes. Healthcare professionals often prefer familiar systems and processes, making it challenging to achieve user adoption and realize ERP system benefits. Successful implementation requires comprehensive change management strategies and ongoing support to overcome resistance and ensure system utilization.
Artificial intelligence integration presents substantial opportunities for healthcare ERP vendors to differentiate their solutions and provide enhanced value to healthcare organizations. AI-powered features such as predictive analytics, automated decision support, and intelligent workflow optimization can significantly improve healthcare operations and patient outcomes. The growing availability of healthcare data and advances in machine learning create opportunities for innovative ERP solutions that leverage AI capabilities.
Rural healthcare expansion offers significant market opportunities as rural hospitals and clinics seek cost-effective ERP solutions to improve operations and remain viable. Government initiatives supporting rural healthcare infrastructure development and technology adoption create favorable conditions for ERP market growth in underserved areas. Cloud-based ERP solutions particularly appeal to rural healthcare providers seeking affordable, scalable technology solutions.
Specialty healthcare segments represent emerging opportunities for specialized ERP solutions tailored to specific healthcare sectors such as mental health, rehabilitation services, and long-term care facilities. These segments have unique operational requirements and regulatory considerations that create demand for specialized ERP functionality. Vendors developing sector-specific solutions can capture market share in these growing healthcare segments.
Interoperability standards advancement creates opportunities for ERP vendors to develop solutions that seamlessly integrate with diverse healthcare technologies and support data exchange across healthcare networks. The push for improved healthcare interoperability driven by government initiatives and industry standards creates demand for ERP systems that can facilitate seamless data sharing while maintaining security and compliance requirements.
Technology evolution continues to reshape the healthcare ERP landscape as vendors incorporate advanced capabilities such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics into their solutions. These technological advances enable healthcare organizations to achieve greater operational efficiency, improve patient outcomes, and make data-driven decisions. The rapid pace of technology development creates both opportunities and challenges as organizations must balance innovation adoption with system stability and user training requirements.
Competitive intensity is increasing as established enterprise software vendors compete with specialized healthcare technology providers for market share. This competition drives innovation and creates more options for healthcare organizations while potentially leading to price pressure and market consolidation. Vendors are differentiating through specialized functionality, industry expertise, and comprehensive service offerings to maintain competitive advantages.
Regulatory landscape changes continue to influence market dynamics as new healthcare regulations and standards impact ERP system requirements. Recent developments in healthcare data privacy, interoperability mandates, and quality reporting requirements create ongoing demand for ERP system updates and enhancements. Vendors must maintain agility to adapt their solutions to evolving regulatory requirements while helping customers maintain compliance.
Customer expectations evolution reflects growing sophistication among healthcare organizations seeking ERP solutions that provide comprehensive functionality, user-friendly interfaces, and measurable return on investment. Healthcare buyers increasingly demand proof of concept demonstrations, reference implementations, and detailed ROI projections before making ERP investment decisions. This trend toward more informed purchasing decisions influences vendor sales strategies and solution development priorities.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to provide accurate and actionable insights into the United States healthcare ERP market. Primary research includes extensive interviews with healthcare executives, IT directors, and ERP system users across various healthcare organizations to understand adoption patterns, implementation challenges, and future requirements. This direct feedback provides valuable insights into market trends and customer preferences.
Secondary research analysis incorporates data from healthcare industry reports, technology vendor publications, regulatory filings, and academic research to validate primary findings and provide broader market context. Government healthcare statistics, industry association reports, and technology adoption surveys contribute to comprehensive market understanding and trend identification.
Quantitative data collection utilizes surveys and structured interviews to gather statistical information about ERP adoption rates, implementation timelines, budget allocations, and satisfaction levels across different healthcare organization types and sizes. This quantitative approach enables statistical analysis and market sizing while supporting qualitative insights with measurable data points.
Market validation processes include expert interviews with healthcare technology consultants, ERP implementation specialists, and industry analysts to verify research findings and ensure accuracy. Cross-referencing multiple data sources and validation through industry experts enhances research reliability and provides confidence in market projections and trend analysis.
Northeast region demonstrates the highest concentration of healthcare ERP adoption, driven by the presence of major academic medical centers, large hospital systems, and established healthcare technology infrastructure. States including New York, Massachusetts, and Pennsylvania lead in ERP implementation with approximately 35% market share due to their dense healthcare facility networks and substantial technology investments. The region benefits from proximity to major ERP vendors and access to skilled implementation resources.
West Coast markets show strong growth in cloud-based healthcare ERP adoption, with California representing the largest single-state market for healthcare ERP solutions. The region’s technology-forward healthcare organizations and venture capital availability support innovative ERP implementations and pilot programs. Washington and Oregon demonstrate growing adoption rates, particularly among integrated health systems seeking comprehensive technology solutions.
Southeast region exhibits rapid growth in healthcare ERP adoption as healthcare systems expand and modernize their technology infrastructure. States including Florida, Texas, and Georgia show increasing investment in ERP systems driven by population growth, healthcare facility expansion, and regulatory compliance requirements. The region accounts for approximately 28% market share with strong growth projections.
Midwest and Mountain regions present significant opportunities for healthcare ERP expansion, particularly in rural and community hospital segments. These regions show growing recognition of ERP system benefits while seeking cost-effective implementation approaches. Government initiatives supporting rural healthcare technology adoption create favorable conditions for market growth in these traditionally underserved areas.
Market leadership is distributed among several categories of vendors, each bringing distinct strengths to the healthcare ERP market:
Competitive strategies focus on industry specialization, cloud migration support, and comprehensive service offerings to differentiate solutions and capture market share in this dynamic sector.
By Deployment Model:
By Organization Size:
By Application Area:
Hospital Systems represent the largest category for healthcare ERP adoption, driven by complex operational requirements and substantial technology budgets. Large hospital networks require comprehensive ERP solutions that can integrate multiple facilities, manage diverse service lines, and support complex financial operations. These organizations typically invest in enterprise-level ERP systems with extensive customization and integration capabilities. Implementation timelines for hospital ERP systems typically range from 12-24 months due to complexity and change management requirements.
Ambulatory Care Centers show increasing ERP adoption as outpatient services expand and require more sophisticated operational management. These facilities seek ERP solutions that can manage scheduling, billing, and resource optimization while integrating with hospital systems and electronic health records. Cloud-based solutions are particularly popular in this segment due to cost-effectiveness and scalability benefits.
Pharmaceutical Companies require specialized ERP functionality to manage complex regulatory requirements, clinical trial operations, and supply chain compliance. These organizations invest in ERP systems with robust quality management, regulatory reporting, and batch tracking capabilities. The segment shows strong growth driven by increasing pharmaceutical research and development activities and regulatory compliance requirements.
Long-term Care Facilities represent an emerging category for healthcare ERP adoption as these organizations seek to improve operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. ERP systems help manage resident care, staffing, and financial operations while supporting quality reporting requirements. This segment shows significant growth potential as the aging population drives expansion in long-term care services.
Healthcare Organizations realize substantial operational benefits from ERP implementation including improved efficiency, reduced administrative costs, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. Integrated systems eliminate duplicate data entry, automate routine processes, and provide real-time visibility into operations. Cost reduction typically ranges from 15-25% in administrative expenses while improving accuracy and compliance. Organizations also benefit from better resource utilization, improved patient satisfaction, and enhanced ability to participate in value-based care programs.
Healthcare Professionals experience improved workflow efficiency and reduced administrative burden through ERP system automation. Clinicians gain access to integrated patient information, streamlined documentation processes, and mobile accessibility for critical data. Time savings from automated processes allow healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care activities rather than administrative tasks, improving job satisfaction and patient outcomes.
Patients benefit from improved service delivery, reduced wait times, and better care coordination enabled by ERP systems. Integrated scheduling, registration, and billing processes create smoother patient experiences while reducing errors and delays. Patient satisfaction scores typically improve by 20-30% following successful ERP implementation due to streamlined processes and better service delivery.
Technology Vendors benefit from growing market demand and opportunities for long-term customer relationships through ERP implementations. Successful implementations create opportunities for ongoing support services, system upgrades, and expansion into additional healthcare market segments. The recurring revenue model associated with cloud-based ERP solutions provides stable income streams and growth opportunities for technology providers.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Cloud-first strategies are transforming healthcare ERP adoption as organizations prioritize cloud-based solutions for their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility benefits. Healthcare organizations are moving away from traditional on-premise implementations toward cloud and hybrid deployment models that offer greater flexibility and reduced infrastructure requirements. This trend is particularly strong among smaller healthcare organizations seeking enterprise-level functionality without substantial upfront investments.
Artificial intelligence integration represents a major trend as ERP vendors incorporate AI capabilities to provide predictive analytics, automated decision support, and intelligent workflow optimization. Healthcare organizations are seeking ERP systems that can leverage their data to provide insights for operational improvement, patient care optimization, and strategic planning. AI adoption rates in healthcare ERP systems are growing at 45% annually as organizations recognize the value of intelligent automation.
Mobile-first design is becoming essential as healthcare professionals require access to ERP functionality through mobile devices for real-time decision making and workflow management. Modern healthcare ERP systems prioritize mobile accessibility, responsive design, and offline capabilities to support healthcare workers in diverse clinical environments. This trend reflects the broader shift toward mobile computing in healthcare operations.
Interoperability focus continues to drive ERP development as healthcare organizations require seamless integration with electronic health records, medical devices, and other healthcare technologies. ERP vendors are investing heavily in API development, standards compliance, and integration capabilities to support comprehensive healthcare technology ecosystems. The push for healthcare data interoperability creates ongoing demand for ERP systems that can facilitate seamless data exchange.
Strategic partnerships between ERP vendors and healthcare technology companies are creating more comprehensive solution offerings and accelerating market growth. Recent collaborations focus on integrating ERP systems with electronic health records, medical devices, and specialized healthcare applications to provide unified technology platforms. These partnerships enable healthcare organizations to implement integrated solutions while reducing complexity and implementation risks.
Regulatory compliance enhancements continue to drive ERP system development as vendors adapt their solutions to meet evolving healthcare regulations and standards. Recent updates focus on data privacy requirements, interoperability mandates, and quality reporting capabilities. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that regulatory compliance features represent a key differentiator in healthcare ERP vendor selection processes.
Acquisition activity in the healthcare ERP market reflects consolidation trends as larger technology companies acquire specialized healthcare software providers to expand their market presence and solution capabilities. These acquisitions enable comprehensive solution development while providing acquired companies with resources for enhanced research and development investments.
Innovation investments in emerging technologies such as blockchain, Internet of Things, and advanced analytics are shaping the future direction of healthcare ERP solutions. Vendors are exploring these technologies to enhance security, improve data management, and provide new capabilities for healthcare organizations seeking competitive advantages through technology innovation.
Implementation planning should prioritize comprehensive change management strategies to ensure successful ERP adoption and user acceptance. Healthcare organizations should invest adequate time and resources in staff training, workflow redesign, and communication programs to maximize ERP system benefits. Successful implementations typically allocate 25-30% of project budgets to change management activities and user adoption support.
Vendor selection requires careful evaluation of healthcare industry expertise, integration capabilities, and long-term support commitments. Organizations should prioritize vendors with proven healthcare implementations, robust security measures, and comprehensive service offerings. Reference site visits and proof-of-concept demonstrations provide valuable insights into vendor capabilities and solution fit for specific organizational requirements.
Phased implementation approaches can reduce risk and improve success rates for healthcare ERP projects. Organizations should consider implementing ERP modules incrementally, starting with core financial or administrative functions before expanding to clinical and operational areas. This approach allows for learning and adjustment while minimizing disruption to critical healthcare operations.
Security planning must be integrated throughout the ERP implementation process to protect sensitive healthcare data and maintain regulatory compliance. Organizations should implement comprehensive security frameworks, conduct regular security assessments, and maintain incident response capabilities. Cloud-based implementations require particular attention to data encryption, access controls, and vendor security certifications.
Market growth projections indicate continued expansion driven by digital transformation initiatives, regulatory requirements, and operational efficiency demands across healthcare organizations. The market is expected to maintain strong growth momentum with increasing adoption rates among smaller healthcare organizations and rural providers seeking cost-effective ERP solutions. Growth rates are projected to accelerate at 12-15% annually over the next five years.
Technology evolution will continue to shape the healthcare ERP landscape as vendors incorporate artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics capabilities into their solutions. Future ERP systems will provide more intelligent automation, predictive insights, and personalized user experiences to support healthcare organizations in achieving operational excellence and improved patient outcomes.
Market consolidation is expected to continue as larger technology companies acquire specialized healthcare ERP providers to expand their market presence and solution capabilities. This consolidation will create opportunities for more comprehensive solution offerings while potentially reducing the number of independent vendors in the market. MWR analysis suggests that market consolidation will accelerate over the next three years.
Emerging opportunities in specialty healthcare segments, rural healthcare markets, and international expansion will drive continued market growth and innovation. Healthcare ERP vendors are expected to develop more specialized solutions for specific healthcare sectors while expanding their geographic presence to capture global market opportunities. The integration of emerging technologies will create new value propositions and competitive advantages for innovative ERP providers.
The United States healthcare ERP market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector that plays a critical role in healthcare organization success and patient care delivery. Market analysis reveals strong growth momentum driven by digital transformation initiatives, regulatory compliance requirements, and the ongoing need for operational efficiency in healthcare operations. The market benefits from technological innovation, government support for healthcare IT adoption, and increasing recognition of ERP system value among healthcare organizations.
Key success factors for market participants include comprehensive healthcare industry expertise, robust integration capabilities, and strong support for implementation and change management. Organizations seeking ERP solutions should prioritize vendors with proven healthcare experience, comprehensive security measures, and long-term commitment to the healthcare market. The trend toward cloud-based solutions, artificial intelligence integration, and mobile accessibility will continue to shape market development and vendor strategies.
Future market prospects remain highly positive with continued growth expected across all healthcare organization segments and geographic regions. The market will benefit from ongoing healthcare industry evolution, technological advancement, and increasing sophistication among healthcare buyers seeking comprehensive ERP solutions. Success in this market requires ongoing innovation, customer focus, and adaptation to evolving healthcare industry requirements and regulatory standards.
What is Healthcare ERP?
Healthcare ERP refers to Enterprise Resource Planning systems specifically designed for the healthcare sector, integrating various functions such as finance, supply chain, human resources, and patient management to enhance operational efficiency and data accuracy.
What are the key players in the United States Healthcare ERP Market?
Key players in the United States Healthcare ERP Market include Oracle, SAP, Infor, and Microsoft, which provide comprehensive solutions tailored for healthcare organizations to streamline their operations and improve patient care, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the United States Healthcare ERP Market?
The main drivers of growth in the United States Healthcare ERP Market include the increasing need for operational efficiency, the rising demand for integrated healthcare solutions, and the growing focus on regulatory compliance and data security.
What challenges does the United States Healthcare ERP Market face?
Challenges in the United States Healthcare ERP Market include high implementation costs, resistance to change from staff, and the complexity of integrating ERP systems with existing healthcare technologies.
What opportunities exist in the United States Healthcare ERP Market?
Opportunities in the United States Healthcare ERP Market include the adoption of cloud-based solutions, advancements in artificial intelligence for data analytics, and the increasing trend of telehealth services that require robust ERP systems.
What trends are shaping the United States Healthcare ERP Market?
Trends shaping the United States Healthcare ERP Market include the shift towards patient-centered care, the integration of mobile technologies for healthcare management, and the emphasis on data-driven decision-making to enhance operational performance.
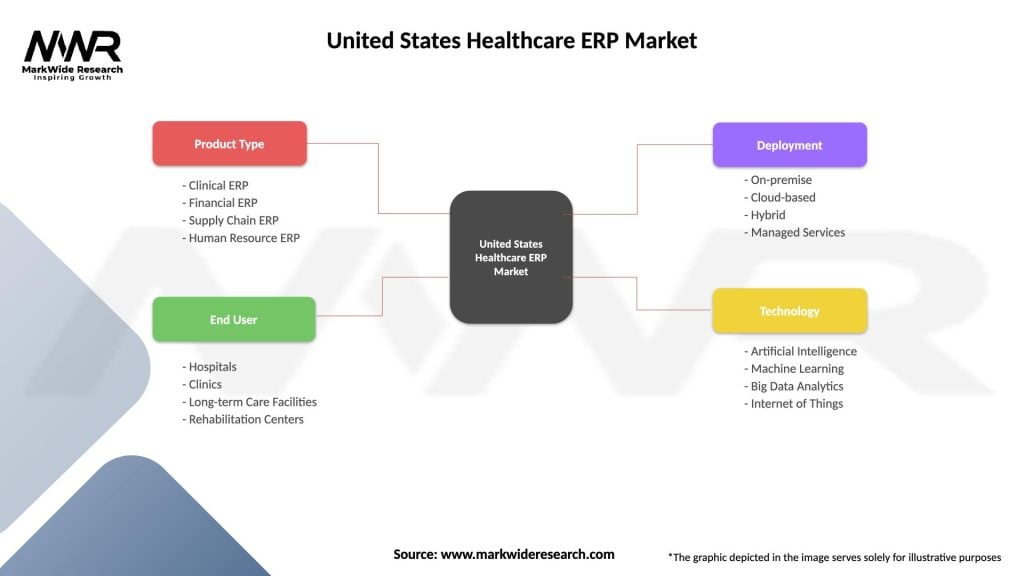
United States Healthcare ERP Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Clinical ERP, Financial ERP, Supply Chain ERP, Human Resource ERP |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Long-term Care Facilities, Rehabilitation Centers |
| Deployment | On-premise, Cloud-based, Hybrid, Managed Services |
| Technology | Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Big Data Analytics, Internet of Things |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the United States Healthcare ERP Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at