444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The United States distributed solar power generation market has experienced remarkable growth in recent years. Distributed solar power generation refers to the production of electricity from solar energy at a localized level, typically through rooftop solar panels or small-scale solar installations. This approach allows individuals, businesses, and communities to generate their own clean and renewable energy, reducing reliance on traditional power sources and contributing to a more sustainable future.
Meaning
Distributed solar power generation involves harnessing the energy of the sun to produce electricity at a smaller, decentralized scale. Unlike large-scale solar power plants that feed electricity into the grid, distributed solar power systems are installed closer to the point of consumption. This means that the generated electricity can be used directly by the location where it is produced, reducing transmission losses and increasing overall efficiency.
Executive Summary
The United States distributed solar power generation market has experienced significant growth due to several factors. Increasing awareness about the environmental impact of traditional energy sources, coupled with government incentives and falling costs of solar technologies, has driven the adoption of distributed solar power generation across the country. This has resulted in a shift towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy landscape.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The United States distributed solar power generation market is driven by a combination of factors, including environmental concerns, government policies, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. The market dynamics are influenced by:
Regional Analysis
The United States distributed solar power generation market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as solar resource availability, state policies, and local incentives. The market can be broadly divided into the following regions:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The United States distributed solar power generation market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had both positive and negative impacts on the United States distributed solar power generation market. While the initial lockdowns and disruptions in the supply chain caused temporary setbacks, the market quickly rebounded due to various factors:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the United States distributed solar power generation market looks promising. Factors such as declining costs, increasing environmental concerns, supportive government policies, and technological advancements will continue to drive market growth. As solar technologies improve, energy storage becomes more integrated, and grid infrastructure evolves, distributed solar power generation is expected to play an increasingly vital role in the transition to a clean and sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
The United States distributed solar power generation market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by factors such as environmental concerns, government incentives, falling costs, and technological advancements. Distributed solar power generation offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, environmental sustainability, energy independence, and job creation. Despite challenges such as high upfront costs and intermittency, the market presents opportunities for expansion, particularly in residential, commercial, and industrial segments. Continued policy support, technological advancements, and industry collaboration will be crucial in realizing the full potential of distributed solar power generation and ensuring a cleaner and more sustainable energy landscape for the United States.
What is Distributed Solar Power Generation?
Distributed Solar Power Generation refers to the production of solar energy from small-scale solar installations, typically located close to the point of use. This includes residential rooftop systems, community solar projects, and commercial solar installations that contribute to local energy needs.
What are the key players in the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market?
Key players in the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market include Sunrun, Vivint Solar, and First Solar, among others. These companies are involved in various aspects of solar energy production, installation, and financing.
What are the growth factors driving the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market?
The growth of the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market is driven by increasing demand for renewable energy, advancements in solar technology, and supportive government policies. Additionally, rising electricity costs and consumer awareness of environmental issues contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market face?
The United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, grid integration issues, and competition from traditional energy sources. Additionally, fluctuations in government incentives can impact market stability.
What opportunities exist in the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market?
Opportunities in the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market include the expansion of energy storage solutions, increased investment in solar infrastructure, and the potential for innovative financing models. These factors can enhance the accessibility and adoption of solar technologies.
What trends are shaping the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market?
Trends shaping the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market include the rise of community solar projects, advancements in solar panel efficiency, and the integration of smart grid technologies. These trends are enhancing the viability and attractiveness of distributed solar solutions.
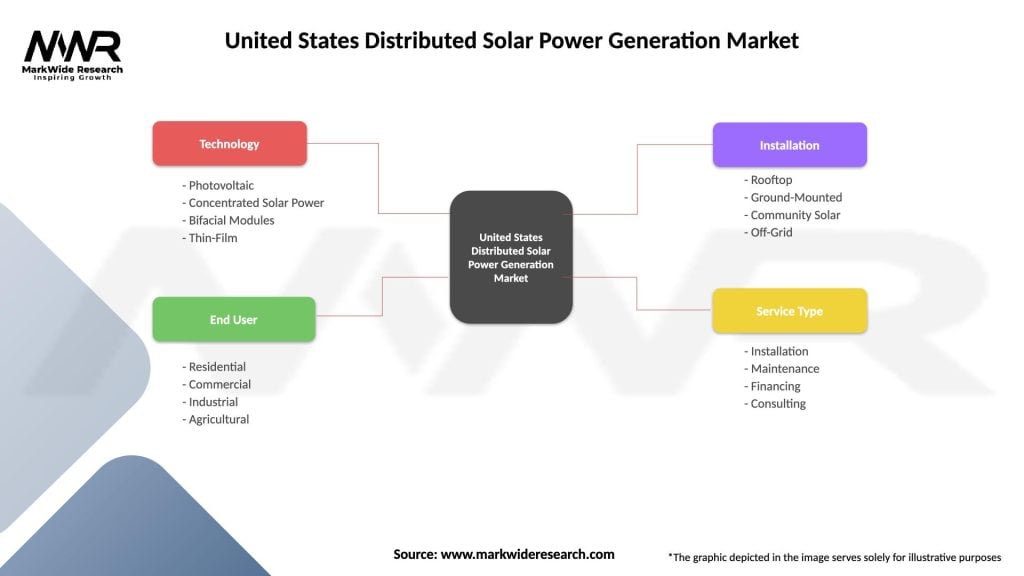
United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Photovoltaic, Concentrated Solar Power, Bifacial Modules, Thin-Film |
| End User | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Agricultural |
| Installation | Rooftop, Ground-Mounted, Community Solar, Off-Grid |
| Service Type | Installation, Maintenance, Financing, Consulting |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the United States Distributed Solar Power Generation Market:
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at