444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Ukraine logistics market represents a critical component of Eastern Europe’s supply chain infrastructure, serving as a strategic gateway between Europe and Asia. Despite facing unprecedented challenges due to geopolitical tensions and conflict, the Ukrainian logistics sector demonstrates remarkable resilience and adaptation capabilities. Transportation networks, warehousing facilities, and distribution centers continue to evolve, supported by international humanitarian aid and reconstruction efforts.
Market dynamics indicate significant transformation patterns, with the sector experiencing a 15% shift toward alternative transportation routes and modal diversification. The logistics infrastructure encompasses road transport, rail networks, maritime facilities, and emerging air cargo operations. Digital transformation initiatives are accelerating, with logistics companies adopting advanced tracking systems and automated warehouse management solutions at an unprecedented pace.
Regional connectivity remains a cornerstone of Ukraine’s logistics value proposition, with the country maintaining strategic positions along major European trade corridors. The sector supports various industries including agriculture, manufacturing, retail, and e-commerce, demonstrating adaptability in supply chain management during challenging operational conditions.
The Ukraine logistics market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of transportation, warehousing, distribution, and supply chain management services operating within Ukrainian territory and connecting to international trade networks. This market encompasses freight forwarding, third-party logistics providers, transportation companies, and integrated supply chain solutions serving domestic and cross-border commerce requirements.
Logistics operations in Ukraine include road freight transportation, railway cargo services, maritime shipping through Black Sea ports, air cargo handling, and specialized services such as cold chain logistics and hazardous materials transportation. The market integrates traditional logistics functions with modern technology solutions, including warehouse management systems, transportation management platforms, and digital freight matching services.
Supply chain integration represents a fundamental aspect of the Ukrainian logistics landscape, connecting agricultural producers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers through efficient distribution networks. The market serves both domestic consumption needs and international export requirements, particularly in agricultural commodities, manufactured goods, and raw materials sectors.
Strategic positioning defines Ukraine’s logistics market as a resilient and adaptive sector navigating complex operational challenges while maintaining essential supply chain functions. The market demonstrates strong fundamentals in transportation infrastructure, with particular strengths in rail connectivity and agricultural logistics capabilities. Modal diversification trends show increasing adoption of multimodal transportation solutions, with road transport accounting for approximately 68% of domestic freight movement.
Technology adoption accelerates across the sector, driven by efficiency requirements and international best practices integration. Digital logistics platforms experience growing utilization rates, while automated warehouse solutions gain traction among larger logistics service providers. E-commerce growth contributes significantly to last-mile delivery service expansion, particularly in urban markets.
International cooperation strengthens through partnerships with European logistics companies and humanitarian organizations, facilitating knowledge transfer and infrastructure development. The market benefits from EU integration initiatives and international development programs supporting logistics modernization efforts.
Operational resilience emerges as a defining characteristic of Ukraine’s logistics sector, with companies demonstrating remarkable adaptability in maintaining supply chain continuity. Key insights reveal fundamental market strengths and emerging opportunities:
Economic reconstruction serves as a primary driver for logistics market development, creating substantial demand for transportation and distribution services. Infrastructure rebuilding efforts generate significant opportunities for logistics companies specializing in construction materials, equipment transportation, and project logistics management.
Agricultural export requirements continue driving logistics demand, with Ukraine maintaining its position as a major global grain exporter. Specialized agricultural logistics services, including grain handling facilities, bulk transportation, and port operations, benefit from consistent demand patterns. Seasonal logistics peaks during harvest periods create substantial capacity utilization opportunities.
E-commerce expansion accelerates demand for last-mile delivery services and urban distribution networks. Online retail growth, particularly in consumer goods and food delivery segments, drives investment in delivery infrastructure and technology platforms. Consumer expectations for faster delivery times and tracking capabilities push logistics providers toward service enhancement initiatives.
European integration initiatives create opportunities for cross-border logistics services and international supply chain participation. EU market access requirements drive logistics standardization and quality improvement efforts, benefiting companies investing in compliance and certification programs.
Infrastructure challenges present significant constraints on logistics market development, with damaged transportation networks requiring extensive repair and modernization efforts. Road quality issues, bridge capacity limitations, and rail network maintenance requirements create operational inefficiencies and increased transportation costs.
Security concerns impact logistics operations, requiring additional safety measures and alternative routing strategies. Insurance costs increase for logistics operations, while security investments strain company resources. Risk management becomes a critical factor in logistics planning and pricing strategies.
Labor shortages affect logistics operations, particularly in specialized roles such as truck drivers, warehouse operators, and logistics coordinators. Workforce migration and military service requirements create staffing challenges for logistics companies. Skills gaps in technology adoption and modern logistics practices limit operational efficiency improvements.
Energy costs and fuel price volatility impact transportation economics, creating pressure on logistics service pricing and profitability. Power supply reliability issues affect warehouse operations and cold chain logistics capabilities, requiring backup systems and alternative energy solutions.
Reconstruction logistics presents substantial opportunities for specialized transportation and project logistics services. Infrastructure rebuilding efforts require extensive materials transportation, equipment handling, and coordination services. International aid distribution creates demand for humanitarian logistics expertise and specialized handling capabilities.
Technology modernization opportunities emerge as logistics companies seek competitive advantages through digital transformation. Warehouse automation, transportation management systems, and IoT tracking solutions offer significant efficiency improvements. Data analytics capabilities enable better demand forecasting and route optimization.
Regional hub development opportunities arise from Ukraine’s strategic geographic position connecting European and Asian markets. Transit logistics services, cross-docking facilities, and multimodal transportation hubs can capture international freight flows. Free economic zones and special logistics areas offer favorable conditions for logistics infrastructure development.
Sustainable logistics initiatives create opportunities for companies investing in green transportation solutions and environmentally friendly warehouse operations. Electric vehicle adoption, renewable energy utilization, and carbon footprint reduction programs align with international sustainability requirements and customer preferences.
Supply and demand dynamics in Ukraine’s logistics market reflect complex interactions between reconstruction needs, agricultural cycles, and international trade patterns. Demand fluctuations create both challenges and opportunities for logistics service providers, requiring flexible capacity management and diversified service offerings.
Competitive landscape evolution shows increasing consolidation among larger logistics providers while creating niches for specialized service companies. International logistics companies establish partnerships with local operators, bringing advanced technologies and best practices to the market. Service differentiation becomes crucial for maintaining competitive positioning.
Pricing dynamics reflect increased operational costs balanced against customer price sensitivity. Logistics companies implement dynamic pricing models accounting for fuel costs, security requirements, and route complexity. Value-added services such as tracking, insurance, and specialized handling command premium pricing.
Technology integration accelerates market transformation, with digital platforms enabling better coordination between shippers, carriers, and receivers. Real-time visibility solutions improve customer satisfaction while reducing operational inefficiencies. Automation adoption in warehousing and transportation planning enhances productivity and accuracy.
Comprehensive analysis of Ukraine’s logistics market employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights. Primary research includes interviews with logistics company executives, transportation managers, and industry association representatives. Field observations of logistics operations provide practical insights into current market conditions and operational challenges.
Secondary research incorporates analysis of government statistics, industry reports, and international trade data. Transportation ministry publications, customs data, and port authority statistics contribute to market size estimations and trend analysis. Academic research from Ukrainian universities and international institutions provides theoretical frameworks and comparative analysis.
Quantitative analysis utilizes statistical modeling to identify market trends and growth patterns. Freight volume data, modal share analysis, and regional distribution patterns inform market segmentation insights. Qualitative assessment through expert interviews and focus groups provides context for quantitative findings and identifies emerging market dynamics.
Data validation processes ensure research accuracy through cross-referencing multiple sources and expert review. Market estimates undergo sensitivity analysis to account for uncertainty factors and potential scenario variations. Continuous monitoring of market developments enables real-time updates to research findings and projections.
Western Ukraine demonstrates strong logistics performance, benefiting from proximity to European markets and relatively stable infrastructure conditions. The region accounts for approximately 35% of cross-border logistics activity, with major logistics hubs in Lviv and Ivano-Frankivsk. Border crossing facilities handle significant freight volumes, supporting both import and export operations.
Central Ukraine serves as the primary logistics coordination center, with Kyiv functioning as the main distribution hub for domestic and international freight. The region benefits from convergent transportation networks and established logistics infrastructure. Warehousing capacity concentration in central regions supports nationwide distribution requirements.
Eastern regions face operational challenges but maintain important industrial logistics functions, particularly in heavy industry and manufacturing support. Alternative transportation routes develop to maintain connectivity with national logistics networks. Industrial logistics specialization continues in areas with active manufacturing operations.
Southern Ukraine retains strategic importance for agricultural exports and maritime logistics, despite operational constraints. Port facilities adapt operations to maintain grain export capabilities, while inland transportation networks adjust to changing routing requirements. Agricultural logistics infrastructure demonstrates resilience in supporting harvest transportation and storage needs.
Market leadership in Ukraine’s logistics sector encompasses both domestic companies and international partnerships, creating a diverse competitive environment. Leading logistics providers demonstrate adaptability and innovation in maintaining service quality under challenging conditions.
Competitive strategies emphasize service reliability, technology adoption, and customer relationship management. Companies invest in tracking systems, mobile applications, and customer service capabilities to differentiate their offerings. Partnership development with international logistics providers enables access to global networks and best practices.
By Service Type: Ukraine’s logistics market segments into distinct service categories, each addressing specific customer requirements and operational characteristics. Express delivery services lead in growth rates, driven by e-commerce expansion and consumer demand for fast delivery options.
By Transportation Mode: Modal distribution reflects infrastructure capabilities and customer preferences, with road transport maintaining dominant market share while rail and multimodal solutions gain importance.
By End-User Industry: Sector-specific logistics requirements drive specialized service development and market segmentation strategies.
E-commerce Logistics represents the fastest-growing category, with online retail expansion driving demand for last-mile delivery services and urban distribution networks. Consumer expectations for same-day and next-day delivery create opportunities for logistics providers investing in urban fulfillment centers and delivery technology.
Agricultural Logistics maintains strategic importance for Ukraine’s economy, with specialized services for grain handling, storage, and transportation. Seasonal demand patterns require flexible capacity management and specialized equipment for harvest logistics. Cold chain capabilities support fresh produce exports and domestic food distribution.
Industrial Logistics serves manufacturing and construction sectors with specialized transportation and project logistics services. Heavy cargo handling capabilities and oversized equipment transportation create niche opportunities for specialized logistics providers. Just-in-time delivery requirements drive efficiency improvements in industrial supply chains.
Healthcare Logistics gains importance with specialized requirements for pharmaceutical distribution and medical equipment transportation. Temperature-controlled logistics and regulatory compliance capabilities become critical success factors. International humanitarian aid distribution creates additional demand for healthcare logistics expertise.
Logistics Service Providers benefit from diversified revenue opportunities across multiple industry segments and service categories. Market conditions create demand for innovative solutions and technology adoption, enabling competitive differentiation. Operational efficiency improvements through technology integration reduce costs while improving service quality.
Shippers and Manufacturers gain access to improved logistics services with better tracking, reliability, and cost optimization. Supply chain visibility enhancements enable better inventory management and customer service. Specialized logistics solutions support business growth and market expansion opportunities.
E-commerce Companies benefit from expanding delivery networks and improved last-mile capabilities. Customer satisfaction improvements through faster delivery times and better tracking support business growth. Integration with logistics technology platforms streamlines operations and reduces complexity.
Agricultural Producers access specialized logistics services for crop transportation and export facilitation. Storage solutions and grain handling capabilities support harvest management and market timing optimization. International logistics connections enable global market access and export revenue maximization.
Government and Regulatory Bodies benefit from improved economic activity and tax revenue generation through logistics sector development. Infrastructure utilization optimization supports national transportation policy objectives and regional development goals.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital Transformation Acceleration emerges as the dominant trend, with logistics companies rapidly adopting technology solutions for competitive advantage. Cloud-based platforms enable better coordination and real-time visibility across supply chains. Mobile applications and customer portals improve service accessibility and user experience.
Sustainability Integration gains momentum as logistics providers implement environmentally friendly practices and green transportation solutions. Electric vehicle adoption in urban delivery operations reduces emissions while improving operational efficiency. Renewable energy utilization in warehouse operations supports sustainability goals and cost reduction objectives.
Multimodal Transportation Growth reflects customer demand for efficient and cost-effective shipping solutions. Intermodal facilities development enables seamless transfers between transportation modes. Combined transport solutions optimize costs while improving delivery reliability and reducing environmental impact.
Last-Mile Innovation drives development of new delivery methods and urban distribution strategies. Automated delivery solutions including drones and autonomous vehicles gain testing and pilot implementation. Micro-fulfillment centers in urban areas reduce delivery times and improve customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain Resilience Focus emphasizes risk management and alternative routing capabilities. Diversification strategies reduce dependency on single transportation modes or routes. Backup systems and contingency planning become standard operational practices across the logistics sector.
Infrastructure Modernization Projects receive international funding and support, enabling systematic upgrading of transportation networks and logistics facilities. European Union assistance programs provide technical expertise and financial resources for infrastructure development. Public-private partnerships facilitate logistics hub development and technology implementation.
Technology Platform Launches by major logistics providers introduce advanced tracking, routing, and customer service capabilities. MarkWide Research analysis indicates significant investment in digital infrastructure by leading logistics companies. Integration with international logistics networks enables global service capabilities and best practices adoption.
Strategic Partnerships between Ukrainian and international logistics companies create opportunities for knowledge transfer and market expansion. Joint ventures enable access to advanced technologies and international customer networks. Collaboration agreements facilitate cross-border logistics services and European market integration.
Regulatory Framework Updates align Ukrainian logistics standards with European Union requirements, facilitating international trade and market access. Customs procedures modernization improves cross-border logistics efficiency and reduces processing times. Transportation safety regulations enhance operational standards and international competitiveness.
Warehouse Automation Implementations by major logistics providers improve operational efficiency and service quality. Automated sorting systems and inventory management technologies reduce processing times and error rates. Robotics integration in warehouse operations enhances productivity while reducing labor dependencies.
Technology Investment Prioritization should focus on solutions providing immediate operational benefits and customer value enhancement. MWR recommends logistics companies prioritize tracking systems, mobile applications, and warehouse management platforms for maximum impact. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and cost-effectiveness for growing logistics operations.
Service Diversification Strategies enable logistics providers to reduce risk while capturing growth opportunities across multiple market segments. Value-added services such as packaging, assembly, and reverse logistics create additional revenue streams and customer loyalty. Specialized services for healthcare, e-commerce, and industrial sectors offer premium pricing opportunities.
Partnership Development with international logistics companies provides access to advanced technologies, best practices, and global customer networks. Strategic alliances enable market expansion while sharing investment risks and operational expertise. Joint service offerings create competitive advantages and improved customer value propositions.
Infrastructure Investment Focus should prioritize facilities and equipment providing long-term competitive advantages and operational efficiency improvements. Warehouse modernization and transportation fleet upgrades enhance service capabilities and customer satisfaction. Energy-efficient solutions reduce operational costs while supporting sustainability objectives.
Talent Development Programs address skills gaps while building organizational capabilities for future growth. Training initiatives in technology utilization, customer service, and operational efficiency improve workforce productivity. Leadership development programs prepare organizations for market expansion and increased complexity.
Market expansion prospects for Ukraine’s logistics sector remain positive, driven by reconstruction demand, economic recovery, and European integration opportunities. Growth projections indicate potential for 12-15% annual expansion in key logistics segments over the medium term, supported by infrastructure investment and technology adoption.
Technology integration will accelerate, with artificial intelligence, IoT sensors, and automated systems becoming standard operational tools. Digital platforms will enable seamless integration between logistics providers, customers, and transportation networks. Predictive analytics and machine learning applications will optimize routing, inventory management, and demand forecasting.
Infrastructure development supported by international assistance will enhance transportation networks and logistics capabilities. Multimodal facilities and regional logistics hubs will improve connectivity and operational efficiency. Smart infrastructure incorporating digital technologies will provide real-time monitoring and optimization capabilities.
Market consolidation trends may emerge as larger logistics providers acquire specialized companies and expand service capabilities. International expansion opportunities will develop as Ukrainian logistics companies gain experience and build partnerships with global networks. Regional leadership positions in agricultural logistics and transit services will strengthen competitive advantages.
Sustainability requirements will drive adoption of green logistics practices and environmentally friendly transportation solutions. Carbon footprint reduction initiatives will become competitive differentiators and customer requirements. Circular economy principles will influence logistics service design and operational practices.
Ukraine’s logistics market demonstrates remarkable resilience and adaptation capabilities while navigating complex operational challenges and transformation opportunities. The sector’s strategic geographic position, agricultural logistics expertise, and growing technology adoption create strong foundations for future growth and development.
Market dynamics reflect both challenges and opportunities, with reconstruction demand, e-commerce growth, and European integration driving positive development trends. Technology adoption accelerates across the sector, enabling improved operational efficiency, customer service, and competitive positioning. Digital transformation initiatives position Ukrainian logistics providers for participation in global supply chain networks.
Future prospects remain optimistic, supported by international assistance, infrastructure investment, and market diversification opportunities. The logistics sector’s contribution to economic recovery and development will continue growing as operational conditions stabilize and market access improves. Strategic investments in technology, infrastructure, and human capital will determine competitive success in evolving market conditions.
Industry participants benefit from multiple growth drivers and market opportunities, while facing the need for continuous adaptation and innovation. Success factors include technology adoption, service diversification, international partnerships, and operational excellence. The Ukraine logistics market positions itself as a critical component of regional supply chain networks and European trade integration, offering substantial opportunities for growth-oriented logistics service providers and stakeholders.
What is Ukraine Logistics?
Ukraine Logistics refers to the processes involved in the transportation, warehousing, and distribution of goods within Ukraine. It encompasses various activities such as freight forwarding, supply chain management, and inventory control.
What are the key players in the Ukraine Logistics Market?
Key players in the Ukraine Logistics Market include companies like Nova Poshta, Meest Group, and Ukrposhta, which provide a range of logistics services from parcel delivery to freight transportation, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Ukraine Logistics Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Ukraine Logistics Market include the increasing demand for e-commerce, improvements in infrastructure, and the expansion of international trade. These factors contribute to a more efficient logistics network.
What challenges does the Ukraine Logistics Market face?
The Ukraine Logistics Market faces challenges such as political instability, outdated infrastructure, and regulatory hurdles. These issues can hinder the efficiency and reliability of logistics operations.
What opportunities exist in the Ukraine Logistics Market?
Opportunities in the Ukraine Logistics Market include the potential for technological advancements, such as automation and digitalization, and the growth of green logistics practices. These trends can enhance operational efficiency and sustainability.
What trends are shaping the Ukraine Logistics Market?
Trends shaping the Ukraine Logistics Market include the rise of last-mile delivery solutions, increased use of data analytics for supply chain optimization, and a focus on sustainability initiatives. These trends are transforming how logistics services are delivered.
Ukraine Logistics Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
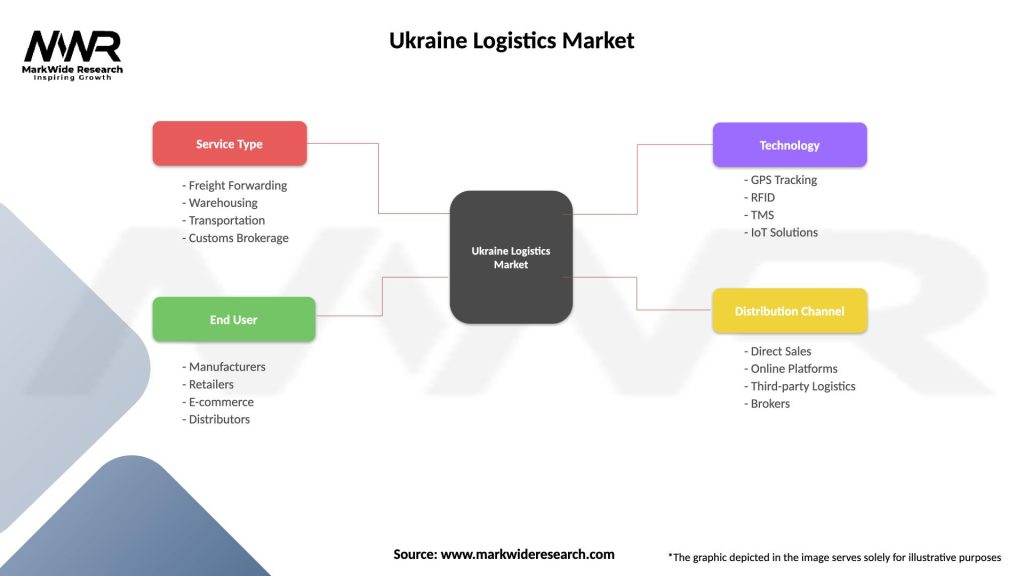
| Service Type | Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Transportation, Customs Brokerage |
| End User | Manufacturers, Retailers, E-commerce, Distributors |
| Technology | GPS Tracking, RFID, TMS, IoT Solutions |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Online Platforms, Third-party Logistics, Brokers |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Ukraine Logistics Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at