444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview: The UK Advanced Energy Market represents a dynamic and evolving sector at the forefront of energy innovation, sustainability, and decarbonization efforts. Advanced energy technologies encompass a wide range of renewable energy sources, energy storage solutions, smart grid infrastructure, and energy management systems designed to enhance energy efficiency, resilience, and environmental sustainability. As the UK transitions towards a low-carbon economy, the advanced energy market plays a pivotal role in driving clean energy adoption, reducing carbon emissions, and fostering energy security and resilience.
Meaning: The UK Advanced Energy Market encompasses innovative technologies, policies, and business models aimed at transforming the energy landscape towards a more sustainable and resilient future. Advanced energy solutions leverage renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and biomass, coupled with energy storage, grid modernization, and demand-side management technologies, to optimize energy production, distribution, and consumption, and reduce reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
Executive Summary: The UK Advanced Energy Market is characterized by rapid technological advancements, policy incentives, and market dynamics driving the adoption of clean, reliable, and affordable energy solutions. As the UK seeks to achieve its climate targets and transition towards a net-zero carbon economy, the advanced energy market offers significant opportunities for innovation, investment, and collaboration across the public and private sectors to accelerate the deployment of renewable energy, energy efficiency measures, and grid modernization initiatives.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics: The UK Advanced Energy Market operates within a dynamic ecosystem shaped by technological innovation, policy evolution, market forces, and consumer preferences. Market dynamics influence investment decisions, technology adoption, and industry trends, driving collaboration, competition, and transformative change across the energy value chain.
Regional Analysis: The UK advanced energy market exhibits regional variations in renewable energy resource availability, grid infrastructure, policy priorities, and market dynamics. Regions with abundant renewable energy resources, supportive policies, and robust grid infrastructure are well-positioned to accelerate the transition towards a low-carbon energy future and reap the economic, environmental, and social benefits of advanced energy deployment and innovation.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in UK Advanced Energy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
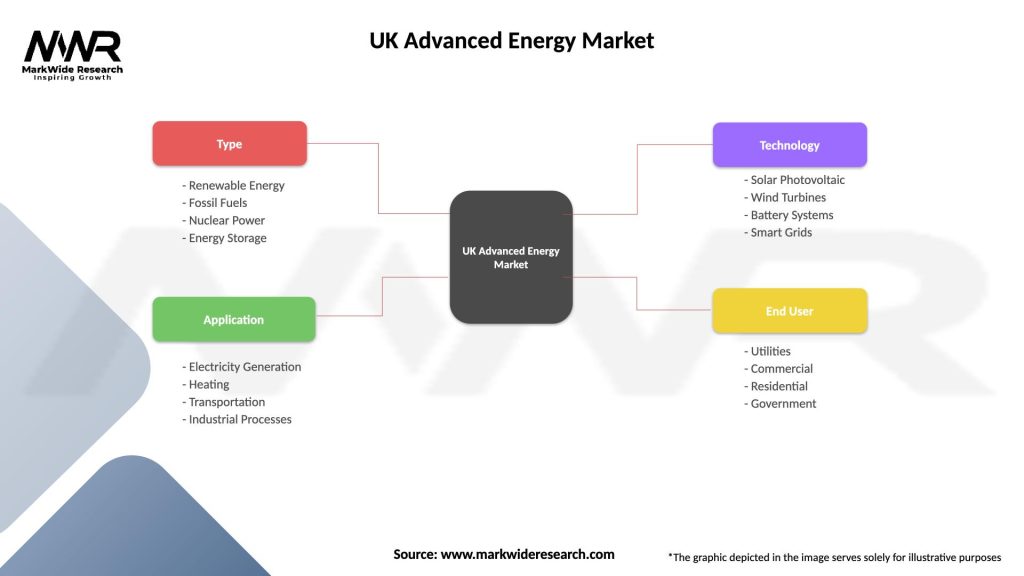
Segmentation: The UK advanced energy market can be segmented based on technology type, end-user sector, application, and geographic region, providing insights into market trends, opportunities, and challenges across different segments of the energy value chain. Segmentation facilitates targeted market analysis, strategic planning, and resource allocation for industry stakeholders and decision-makers.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis: A SWOT analysis provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the UK Advanced Energy Market:
Understanding these factors enables industry stakeholders to leverage strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats, fostering sustainable growth, innovation, and resilience in the UK Advanced Energy Market.
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact: The Covid-19 pandemic has reshaped the energy landscape, disrupting supply chains, impacting demand patterns, and accelerating digitalization and innovation in the UK Advanced Energy Market:
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook: The future outlook for the UK Advanced Energy Market is characterized by transformative change, innovation, and resilience, driven by climate imperatives, technological advancements, and market dynamics shaping the energy transition:
Conclusion: The UK Advanced Energy Market represents a dynamic, transformative, and resilient sector driving the transition towards a low-carbon, sustainable, and inclusive energy future. As the UK navigates challenges and opportunities in the energy transition, collaboration, innovation, and leadership are essential to realizing the full potential of advanced energy solutions in achieving climate goals, enhancing energy security, and fostering economic prosperity and social equity for current and future generations. By embracing innovation, policy alignment, and stakeholder engagement, the UK advances towards a clean, resilient, and prosperous energy future, inspiring global action and catalyzing transformative change in the quest for a sustainable planet.
What is Advanced Energy?
Advanced Energy refers to innovative technologies and solutions that enhance energy efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and promote the use of renewable energy sources. This includes advancements in energy storage, smart grids, and sustainable energy practices.
What are the key players in the UK Advanced Energy Market?
Key players in the UK Advanced Energy Market include companies like Octopus Energy, SSE, and EDF Energy, which are involved in renewable energy generation and innovative energy solutions. These companies are focusing on integrating advanced technologies to improve energy efficiency and sustainability, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the UK Advanced Energy Market?
The UK Advanced Energy Market is driven by factors such as increasing government support for renewable energy initiatives, rising consumer demand for sustainable energy solutions, and advancements in energy storage technologies. These elements are crucial for transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
What challenges does the UK Advanced Energy Market face?
Challenges in the UK Advanced Energy Market include regulatory hurdles, the need for significant investment in infrastructure, and competition from traditional energy sources. These factors can hinder the pace of innovation and adoption of advanced energy technologies.
What opportunities exist in the UK Advanced Energy Market?
Opportunities in the UK Advanced Energy Market include the expansion of electric vehicle charging infrastructure, the development of smart grid technologies, and the potential for energy efficiency improvements in residential and commercial sectors. These areas present significant growth potential for businesses and investors.
What trends are shaping the UK Advanced Energy Market?
Trends in the UK Advanced Energy Market include the increasing adoption of decentralized energy systems, the rise of energy-as-a-service models, and the integration of artificial intelligence in energy management. These trends are transforming how energy is produced, consumed, and managed.
UK Advanced Energy Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Renewable Energy, Fossil Fuels, Nuclear Power, Energy Storage |
| Application | Electricity Generation, Heating, Transportation, Industrial Processes |
| Technology | Solar Photovoltaic, Wind Turbines, Battery Systems, Smart Grids |
| End User | Utilities, Commercial, Residential, Government |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in UK Advanced Energy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at