444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview:
The transaction banking market serves as a critical component of the global financial system, providing essential services to facilitate financial transactions between businesses, financial institutions, and government entities. Transaction banking encompasses a wide range of services, including cash management, trade finance, liquidity management, and payment processing, which are essential for the efficient functioning of modern economies. As businesses increasingly engage in cross-border trade and seek optimized cash flow management solutions, the demand for transaction banking services continues to grow, driving innovation and competition within the market.
Meaning:
Transaction banking refers to the provision of financial services that facilitate the movement and management of funds between businesses, financial institutions, and government entities. These services include cash management, trade finance, liquidity management, and payment processing, which are essential for businesses to conduct their day-to-day operations and manage their financial resources efficiently. Transaction banking plays a crucial role in supporting domestic and international trade, enabling businesses to streamline their financial processes, mitigate risks, and optimize liquidity management.
Executive Summary:
The transaction banking market is witnessing significant growth driven by globalization, digitalization, and the increasing demand for efficient financial solutions by businesses worldwide. Key trends shaping the market include the adoption of digital technologies, the expansion of cross-border trade, regulatory changes, and the emergence of non-bank competitors. Despite the opportunities presented by market growth, transaction banks face challenges such as margin pressures, regulatory compliance costs, cybersecurity risks, and competition from fintechs. To succeed in this dynamic environment, transaction banks must prioritize innovation, customer-centricity, and operational efficiency.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics:
The transaction banking market operates in a dynamic environment characterized by rapid technological advancements, shifting regulatory landscapes, changing customer expectations, and evolving market dynamics. Banks must adapt to these dynamics by embracing innovation, enhancing operational efficiency, and delivering superior customer value to remain competitive and drive sustainable growth.
Regional Analysis:
The transaction banking market exhibits regional variations in terms of market size, maturity, regulatory frameworks, and competitive dynamics. Major financial centers such as New York, London, Singapore, and Hong Kong serve as hubs for transaction banking activities, attracting multinational corporations, financial institutions, and fintech startups. Regional differences in market dynamics require banks to tailor their strategies and offerings to meet the specific needs and preferences of customers in each market.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in the Transaction Banking Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
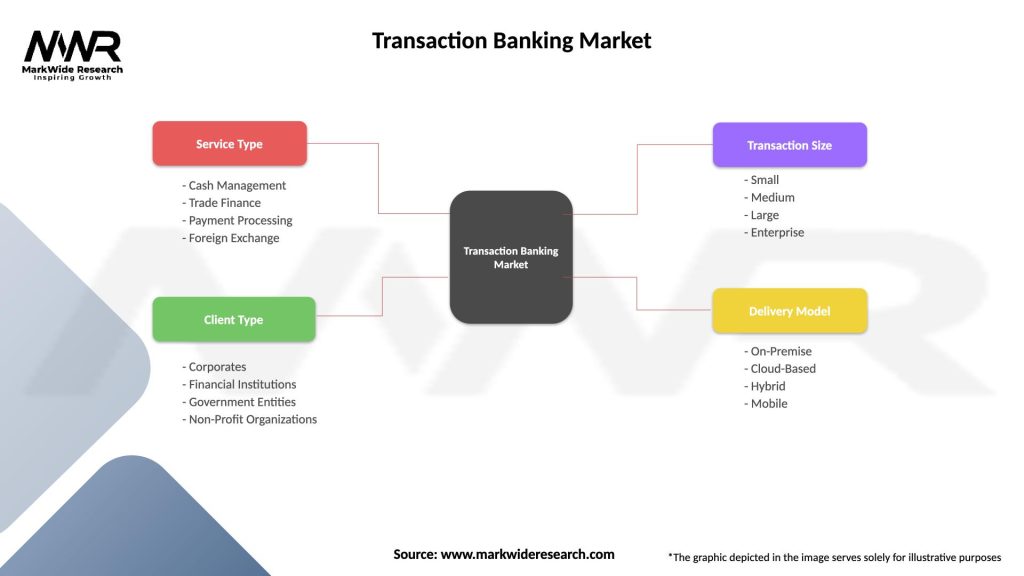
Segmentation:
The transaction banking market can be segmented based on various factors such as:
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Understanding these factors through a SWOT analysis helps transaction banks identify their strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate potential threats to their business operations and market position.
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact:
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the transaction banking market, accelerating digitalization, changing customer behavior, and reshaping market dynamics. Some key impacts of Covid-19 on the market include:
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook:
The transaction banking market is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by digital transformation, globalization, regulatory changes, and evolving customer demands. Banks that prioritize innovation, customer-centricity, and operational excellence are likely to thrive in a rapidly evolving market landscape and capitalize on opportunities for growth and expansion.
Conclusion:
The transaction banking market plays a crucial role in facilitating financial transactions, supporting global trade, and driving economic growth. With increasing digitalization, globalization, and regulatory changes, transaction banks must innovate, adapt, and differentiate themselves to stay competitive and meet the evolving needs of customers. By embracing digital transformation, enhancing operational efficiency, and delivering superior customer value, transaction banks can navigate market challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and drive sustainable growth in the future.
What is Transaction Banking?
Transaction Banking refers to a suite of services provided by banks to facilitate the management of cash flow, payments, and other financial transactions for businesses and institutions. It includes services such as payment processing, trade finance, and liquidity management.
What are the key players in the Transaction Banking Market?
Key players in the Transaction Banking Market include JPMorgan Chase, Citigroup, HSBC, and Deutsche Bank, among others. These institutions offer a range of transaction banking services to corporate clients and financial institutions.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Transaction Banking Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Transaction Banking Market include the increasing demand for efficient payment solutions, the rise of e-commerce, and the need for enhanced cash management services. Additionally, globalization has led to a greater need for cross-border transaction capabilities.
What challenges does the Transaction Banking Market face?
The Transaction Banking Market faces challenges such as regulatory compliance, cybersecurity threats, and the need for technological upgrades. Banks must navigate complex regulations while ensuring the security of transactions and adapting to rapidly changing technology.
What opportunities exist in the Transaction Banking Market?
Opportunities in the Transaction Banking Market include the adoption of digital banking solutions, the integration of artificial intelligence for transaction processing, and the expansion of services to emerging markets. These trends can enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
What trends are shaping the Transaction Banking Market?
Trends shaping the Transaction Banking Market include the increasing use of blockchain technology for secure transactions, the rise of mobile banking applications, and the focus on sustainability in banking practices. These innovations are transforming how banks operate and serve their clients.
Transaction Banking Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Cash Management, Trade Finance, Payment Processing, Foreign Exchange |
| Client Type | Corporates, Financial Institutions, Government Entities, Non-Profit Organizations |
| Transaction Size | Small, Medium, Large, Enterprise |
| Delivery Model | On-Premise, Cloud-Based, Hybrid, Mobile |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Transaction Banking Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at