444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The United States residential real estate market represents one of the most dynamic and influential sectors of the American economy, encompassing single-family homes, condominiums, townhouses, and multi-family residential properties. This market has experienced unprecedented transformation over the past decade, driven by demographic shifts, technological innovations, and evolving consumer preferences. Market dynamics indicate substantial growth potential, with the sector demonstrating remarkable resilience despite economic fluctuations and regulatory changes.
Current market conditions reflect a complex interplay of supply constraints, demand pressures, and regional variations that create diverse opportunities across different geographic markets. The residential real estate landscape continues to evolve with digital transformation reshaping traditional buying and selling processes, while demographic trends such as millennial homebuying and remote work adoption fundamentally alter housing preferences and location priorities.
Regional variations across the United States create distinct market characteristics, with coastal markets, suburban communities, and emerging metropolitan areas each presenting unique growth trajectories and investment opportunities. The market’s performance is closely tied to broader economic indicators including employment rates, interest rates, and consumer confidence levels, making it a critical barometer of overall economic health.
The United States residential real estate market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of buying, selling, renting, and developing residential properties across all 50 states and territories, encompassing primary residences, investment properties, and vacation homes. This market includes all transactions involving single-family detached homes, condominiums, townhouses, duplexes, and small multi-family residential buildings designed for individual or family occupancy.
Market participants include homebuyers, sellers, real estate agents, brokers, mortgage lenders, property developers, investors, and various service providers who facilitate residential property transactions. The market operates through multiple channels including traditional real estate agencies, online platforms, direct sales, and auction systems, creating a diverse and competitive landscape for property transactions.
Residential real estate encompasses both new construction and existing home sales, with market dynamics influenced by factors such as local zoning regulations, construction costs, land availability, demographic trends, and economic conditions. The market serves as both a consumption good for homeowners seeking shelter and an investment vehicle for individuals and institutions building wealth through property appreciation and rental income.
Market performance in the United States residential real estate sector demonstrates continued strength despite facing headwinds from interest rate fluctuations and affordability challenges. The market has shown remarkable adaptability, with innovative financing solutions, technology adoption, and evolving consumer preferences driving sustained activity across multiple price segments and geographic regions.
Key growth drivers include demographic shifts with millennials entering peak homebuying years, remote work flexibility expanding geographic options, and limited housing inventory creating competitive market conditions. Technology integration has revolutionized property search, virtual tours, digital transactions, and market analysis, making real estate more accessible while improving efficiency for all market participants.
Regional market dynamics vary significantly, with Sun Belt states experiencing robust population growth and housing demand, while traditional markets in the Northeast and Midwest face different challenges and opportunities. The market continues to benefit from strong underlying fundamentals including household formation, employment growth, and long-term demographic trends supporting housing demand.
Investment activity remains elevated with institutional investors, individual investors, and foreign buyers maintaining active participation across various market segments. The sector’s performance reflects broader economic confidence while serving as a hedge against inflation and a cornerstone of American wealth building strategies.
Market fundamentals reveal several critical insights that shape the residential real estate landscape across the United States. These insights provide essential understanding for stakeholders navigating this complex and dynamic market environment.
Demographic trends serve as the primary catalyst driving residential real estate demand across the United States. The millennial generation, now in their prime homebuying years, represents the largest demographic cohort seeking homeownership, creating sustained demand pressure across multiple price points and geographic markets. This generational shift brings distinct preferences for technology integration, urban amenities, and flexible living spaces that accommodate remote work arrangements.
Employment growth and wage increases in key metropolitan areas continue supporting housing demand, particularly in technology hubs, financial centers, and emerging business districts. Strong job markets create confidence among potential homebuyers while attracting new residents to growing metropolitan areas, driving both owner-occupied and rental housing demand.
Low interest rate environments historically have enhanced affordability and purchasing power for qualified buyers, though recent rate fluctuations have created new market dynamics. Mortgage accessibility improvements and innovative financing products help address affordability challenges while expanding homeownership opportunities for diverse buyer segments.
Investment demand from both institutional and individual investors continues driving market activity, particularly in single-family rental properties and emerging markets with strong appreciation potential. Real estate investment trusts, private equity firms, and individual investors view residential properties as attractive long-term investments offering both income generation and capital appreciation opportunities.
Government policies including first-time homebuyer programs, tax incentives, and zoning reforms support market growth while addressing affordability and supply constraints. Federal, state, and local initiatives aimed at increasing housing supply and improving affordability create positive market conditions for both buyers and developers.
Affordability challenges represent the most significant constraint facing the residential real estate market, with home prices rising faster than income growth in many metropolitan areas. This affordability gap particularly impacts first-time homebuyers, young families, and moderate-income households, potentially limiting market participation and long-term demand sustainability.
Interest rate volatility creates uncertainty for both buyers and sellers, affecting purchasing decisions and market timing strategies. Rising mortgage rates can significantly impact buyer purchasing power while creating hesitation among potential sellers who may be reluctant to give up favorable existing mortgage terms.
Supply constraints continue limiting market growth, with housing inventory shortages creating competitive conditions that drive price appreciation beyond sustainable levels. Limited land availability in desirable locations, lengthy permitting processes, and construction industry capacity constraints restrict new supply development.
Construction costs including materials, labor, and regulatory compliance expenses have increased substantially, making new home development challenging in many markets. These cost pressures affect both new construction and renovation projects, limiting supply growth and contributing to affordability challenges.
Regulatory barriers including zoning restrictions, environmental regulations, and lengthy approval processes can delay or prevent new housing development. These regulatory constraints particularly impact affordable housing development and urban infill projects that could help address supply shortages.
Economic uncertainty related to inflation, employment volatility, and broader economic conditions can create hesitation among potential buyers and sellers. Market participants may delay transactions during periods of economic uncertainty, reducing overall market activity and liquidity.
Emerging markets across the Sun Belt and Mountain West regions present significant growth opportunities as population migration patterns favor these areas. Cities experiencing job growth, business relocations, and lifestyle attractions offer substantial potential for residential development and investment activity.
Technology integration creates opportunities for market participants to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and develop innovative service offerings. PropTech solutions including virtual reality tours, artificial intelligence-powered property valuation, and blockchain-based transactions represent growing market segments with substantial potential.
Affordable housing development presents opportunities for developers, investors, and policymakers to address critical housing needs while generating sustainable returns. Public-private partnerships, innovative financing structures, and alternative construction methods can help deliver affordable housing solutions in high-demand markets.
Rental market expansion offers opportunities for investors and developers as demographic trends favor rental housing in many markets. Single-family rental properties, build-to-rent communities, and multifamily developments serve growing renter populations seeking quality housing options with flexible lease terms.
Sustainable housing development addresses growing consumer demand for energy-efficient, environmentally responsible housing options. Green building practices, renewable energy integration, and climate-resilient design features create differentiation opportunities while meeting evolving buyer preferences.
Senior housing represents a significant opportunity as baby boomers age and seek housing options that accommodate changing lifestyle needs. Age-in-place modifications, senior-friendly communities, and specialized housing products serve this growing demographic segment.
Supply and demand imbalances continue shaping market dynamics across the United States, with most metropolitan areas experiencing housing shortages that favor sellers while challenging buyers. These imbalances create competitive bidding situations, rapid price appreciation, and reduced time on market for well-positioned properties.
Regional variations in market performance reflect local economic conditions, population growth patterns, and housing supply availability. High-growth markets in Texas, Florida, and the Mountain West experience different dynamics compared to mature markets in California, New York, and the Northeast, creating diverse investment and development opportunities.
Seasonal patterns influence market activity with traditional spring and summer peak seasons, though these patterns have evolved with increased year-round activity driven by remote work flexibility and competitive market conditions. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that seasonal variations have become less pronounced as buyers and sellers adapt to market realities.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across different buyer segments and price ranges, with luxury markets showing different dynamics compared to entry-level and mid-market segments. First-time homebuyers face particular challenges while move-up buyers benefit from existing home equity appreciation.
Financing conditions directly impact market dynamics through mortgage rate fluctuations, lending standard changes, and product availability. Alternative financing options including seller financing, lease-to-own arrangements, and investor partnerships create additional market flexibility.
Investment activity influences local market dynamics through institutional buyer participation, investor competition with owner-occupants, and rental property conversion activities. These dynamics vary significantly by market segment and geographic location.
Comprehensive data collection methodologies ensure accurate and reliable market analysis through multiple primary and secondary research sources. Market research incorporates transaction data from multiple listing services, public records, mortgage origination reports, and construction permit databases to provide complete market coverage.
Primary research includes surveys and interviews with real estate professionals, homebuyers, sellers, lenders, and industry experts to capture qualitative insights and emerging trends. This direct market feedback provides context for quantitative data while identifying developing market conditions and participant sentiment.
Secondary research utilizes government databases, industry reports, economic indicators, and demographic studies to establish market context and validate primary research findings. Federal housing data, census information, and economic statistics provide essential baseline information for market analysis.
Geographic analysis examines market conditions across metropolitan statistical areas, states, and regions to identify local variations and trends. This geographic segmentation reveals market opportunities and challenges specific to different locations and property types.
Temporal analysis tracks market changes over multiple time periods including monthly, quarterly, and annual comparisons to identify trends and cyclical patterns. Historical data analysis provides context for current market conditions while supporting future projections.
Statistical modeling employs advanced analytical techniques to identify correlations, predict market trends, and assess risk factors. These models incorporate multiple variables including economic indicators, demographic trends, and market-specific factors to generate reliable insights.
Northeast Region markets including New York, Boston, and Philadelphia demonstrate mature market characteristics with established neighborhoods, historic properties, and high property values. These markets face affordability challenges while offering stability and long-term appreciation potential. Market share in the Northeast represents approximately 18% of national activity, with strong international buyer interest and institutional investment participation.
Southeast Region leads national growth with markets in Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, and Tennessee experiencing robust population growth and housing demand. The region benefits from favorable business climates, lower costs of living, and attractive lifestyle amenities. Growth rates in key Southeast markets exceed national averages by 25-40%, driven by domestic migration and job creation.
Midwest Region offers affordability advantages and stable market conditions in cities like Chicago, Minneapolis, and Columbus. These markets provide opportunities for first-time homebuyers and investors seeking cash flow properties. The region maintains approximately 22% market share nationally, with steady appreciation and lower volatility compared to coastal markets.
Southwest Region including Texas, Arizona, and Nevada markets experience strong growth driven by business relocations, population growth, and energy sector development. Major metropolitan areas like Dallas, Phoenix, and Las Vegas demonstrate robust market fundamentals with diverse economic bases supporting housing demand.
West Coast markets in California, Washington, and Oregon face unique challenges including high property values, regulatory constraints, and affordability issues. Despite these challenges, these markets maintain strong demand due to employment opportunities, lifestyle attractions, and limited supply availability.
Mountain West Region emerges as a high-growth area with markets in Colorado, Utah, and Idaho attracting residents seeking outdoor recreation, lower costs, and business opportunities. These markets demonstrate some of the strongest appreciation rates nationally while maintaining relative affordability compared to coastal alternatives.
Market leadership in the residential real estate sector encompasses various participant categories including national franchises, regional brokerages, independent agents, and technology-enabled platforms. The competitive landscape continues evolving with traditional players adapting to digital transformation while new entrants introduce innovative service models.
Competitive differentiation increasingly focuses on technology integration, customer experience enhancement, and specialized service offerings. Market participants invest heavily in digital platforms, data analytics, and customer relationship management systems to maintain competitive advantages.
Market consolidation trends include franchise expansion, technology platform acquisitions, and strategic partnerships that enhance service capabilities while improving operational efficiency. These consolidation activities reshape competitive dynamics while creating new market opportunities.
By Property Type: The residential real estate market segments into distinct property categories, each serving different buyer preferences and investment strategies. Single-family detached homes represent the largest segment, offering privacy, space, and long-term appreciation potential. Condominiums and townhouses serve urban and suburban markets with lower maintenance requirements and community amenities.
By Price Range: Market segmentation by price reveals distinct dynamics across entry-level, mid-market, and luxury segments. Entry-level properties face the greatest affordability challenges while luxury markets demonstrate different seasonal patterns and buyer motivations. Mid-market properties represent the largest transaction volume with diverse buyer profiles.
By Buyer Type: First-time homebuyers, move-up buyers, downsizing buyers, and investors each demonstrate unique market behaviors and requirements. First-time buyers often require financing assistance and education, while move-up buyers leverage existing equity for larger purchases. Investors focus on cash flow potential and appreciation prospects.
By Geographic Location: Urban, suburban, and rural markets each present distinct characteristics and opportunities. Urban markets emphasize walkability and amenities, suburban markets offer space and schools, while rural markets provide privacy and lifestyle benefits.
By Transaction Type: New construction sales, existing home sales, and distressed property sales each require different marketing approaches and service capabilities. New construction offers customization options while existing homes provide immediate availability and established neighborhoods.
Single-Family Homes: This dominant category continues attracting the majority of homebuyers seeking privacy, space, and long-term investment potential. Single-family properties demonstrate strong appreciation trends and provide flexibility for modifications and improvements. Market demand remains robust across all price segments, with particular strength in suburban and emerging metropolitan areas.
Condominiums: Urban and suburban condominium markets serve buyers seeking lower maintenance lifestyles and community amenities. This category appeals particularly to young professionals, empty nesters, and investors seeking rental income opportunities. Condominium markets demonstrate strong performance in high-density urban areas and resort destinations.
Townhouses: This category bridges single-family and condominium markets, offering more space than condos while maintaining some community benefits. Townhouse developments appeal to families seeking affordable alternatives to single-family homes while providing yard space and privacy.
Multi-Family Properties: Small multi-family properties including duplexes and triplexes attract investors seeking rental income while providing owner-occupancy opportunities. This category benefits from strong rental demand and favorable financing options for owner-occupants.
Luxury Properties: High-end residential properties demonstrate unique market dynamics with international buyer participation, extended marketing periods, and specialized service requirements. Luxury markets often lead economic cycles and demonstrate different seasonal patterns compared to mainstream markets.
Affordable Housing: This critical category addresses workforce housing needs while presenting opportunities for developers and investors focused on social impact. Affordable housing development benefits from government incentives and public-private partnerships.
Homebuyers benefit from diverse property options, competitive financing alternatives, and technology-enabled search and transaction processes. The market provides opportunities for wealth building through homeownership while offering lifestyle benefits including stability, community engagement, and personal expression through property ownership.
Sellers enjoy favorable market conditions in most regions with competitive buyer demand, rapid sales processes, and strong price appreciation. Technology platforms expand marketing reach while professional services ensure optimal pricing and transaction management.
Real Estate Professionals benefit from sustained transaction volume, technology tools that enhance productivity, and diverse service opportunities across multiple market segments. Professional development resources and industry support systems help agents and brokers adapt to changing market conditions.
Investors access diverse investment opportunities including rental properties, fix-and-flip projects, and new development ventures. The residential real estate market provides portfolio diversification, inflation hedging, and long-term wealth building potential through multiple investment strategies.
Lenders participate in a large and stable market with diverse borrower profiles and property types. Mortgage lending provides consistent revenue streams while serving essential community needs for homeownership financing.
Communities benefit from property tax revenue, economic development, and neighborhood stability that residential real estate development provides. Housing markets support local employment in construction, real estate services, and related industries.
Developers find opportunities across multiple market segments including new construction, renovation projects, and community development initiatives. Market demand supports various development strategies from affordable housing to luxury communities.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Remote Work Impact: The widespread adoption of remote and hybrid work arrangements fundamentally alters housing location preferences, with buyers seeking larger homes in more affordable markets outside traditional employment centers. This trend drives population migration patterns and creates new market opportunities in previously secondary markets.
Technology Integration: Digital transformation accelerates across all market segments with virtual tours, online transactions, artificial intelligence-powered property recommendations, and blockchain-based title processes becoming standard market features. MWR research indicates that technology adoption rates have increased by 65% since the pandemic began.
Sustainability Focus: Environmental consciousness drives demand for energy-efficient homes, solar installations, and sustainable building materials. Green building certifications and climate resilience features increasingly influence buyer decisions and property values.
Generational Preferences: Millennial and Generation Z buyers demonstrate distinct preferences for smart home technology, flexible spaces, and community amenities that differ significantly from previous generations. These preferences shape new construction design and renovation priorities.
Investment Diversification: Individual and institutional investors increasingly view residential real estate as essential portfolio components, driving demand for single-family rental properties and alternative investment structures including real estate investment trusts and crowdfunding platforms.
Urban-Suburban Shift: Population movement from urban cores to suburban and exurban areas accelerates, driven by space needs, affordability considerations, and lifestyle preferences. This shift creates new development opportunities while challenging urban market dynamics.
Regulatory Evolution: State and local governments implement zoning reforms, affordable housing mandates, and development incentives to address housing supply shortages. These regulatory changes create new opportunities while requiring market participants to adapt to evolving compliance requirements.
Financing Innovation: Lenders introduce new mortgage products including alternative credit scoring, down payment assistance programs, and shared equity arrangements to address affordability challenges. These innovations expand homeownership opportunities while managing risk exposure.
Construction Technology: Advanced construction methods including modular building, 3D printing, and prefabrication technologies promise to reduce costs and construction timelines. These innovations address labor shortages while improving construction quality and efficiency.
PropTech Advancement: Technology companies continue developing solutions for property management, transaction processing, market analysis, and customer service. These developments improve market efficiency while creating new business models and service opportunities.
ESG Integration: Environmental, social, and governance considerations increasingly influence investment decisions, development practices, and property management approaches. ESG focus drives demand for sustainable building practices and community-focused development projects.
Market Consolidation: Mergers and acquisitions among real estate companies, technology platforms, and service providers reshape competitive dynamics while creating larger, more capable market participants with enhanced service offerings.
Market Participants should prioritize technology adoption and digital capability development to remain competitive in an increasingly technology-driven market environment. Investment in customer relationship management systems, digital marketing platforms, and data analytics capabilities will be essential for long-term success.
Buyers should consider expanding geographic search areas to identify opportunities in emerging markets with strong growth potential and better affordability. Pre-approval for financing and readiness to act quickly will be crucial in competitive market conditions.
Sellers should leverage current market conditions while preparing properties to appeal to technology-savvy buyers who expect high-quality digital marketing and virtual tour capabilities. Professional staging and photography remain important for optimal market positioning.
Investors should diversify across geographic markets and property types to manage risk while capitalizing on demographic trends driving rental demand. Focus on markets with strong job growth, population increases, and favorable regulatory environments.
Developers should incorporate sustainable building practices, technology integration, and flexible design features that appeal to evolving buyer preferences. Attention to community amenities and walkability will be increasingly important for market success.
Policymakers should focus on zoning reform, streamlined permitting processes, and affordable housing incentives to address supply constraints while maintaining market stability. Public-private partnerships can help deliver housing solutions that serve community needs.
Long-term growth prospects for the United States residential real estate market remain positive, supported by favorable demographic trends, continued household formation, and the fundamental need for housing across diverse market segments. MarkWide Research projections indicate sustained market growth driven by millennial homebuying activity and ongoing population growth in key metropolitan areas.
Technology transformation will continue reshaping market operations with artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and blockchain technologies becoming standard market infrastructure. These technological advances will improve efficiency, reduce transaction costs, and enhance customer experiences across all market segments.
Geographic diversification trends will persist as remote work capabilities and lifestyle preferences drive population migration to more affordable markets with attractive amenities. This migration will create growth opportunities in secondary and tertiary markets while potentially moderating growth in traditional high-cost areas.
Sustainability integration will become increasingly important as climate concerns, energy costs, and regulatory requirements drive demand for environmentally responsible housing options. Properties with green features and climate resilience will command premium values and attract environmentally conscious buyers.
Market maturation in some regions may lead to more moderate appreciation rates while emerging markets continue experiencing robust growth. This geographic variation will create diverse investment opportunities and require market participants to adapt strategies to local conditions.
Regulatory evolution will likely focus on addressing affordability challenges through zoning reforms, development incentives, and innovative financing programs. These policy changes will create new opportunities while requiring market adaptation to evolving regulatory frameworks.
The United States residential real estate market demonstrates remarkable resilience and adaptability in the face of evolving economic conditions, demographic shifts, and technological transformation. Despite challenges including affordability constraints and supply limitations, the market continues providing essential housing solutions while serving as a cornerstone of American wealth building and economic stability.
Market fundamentals remain strong with sustained demand driven by demographic trends, employment growth, and lifestyle preferences that favor homeownership. Technology integration has revolutionized market operations while creating new opportunities for efficiency improvements and enhanced customer experiences across all market segments.
Future success in this dynamic market will require adaptability, technology adoption, and strategic focus on emerging opportunities in geographic markets, property types, and service delivery models. Market participants who embrace innovation while maintaining focus on customer needs will be best positioned for long-term success in this essential and evolving market sector.
What is Residential Real Estate?
Residential real estate refers to properties designed for people to live in, including single-family homes, apartments, and condominiums. This sector plays a crucial role in the housing market and overall economy.
What are the key players in the United States Residential Real Estate Market?
Key players in the United States Residential Real Estate Market include major real estate firms such as Keller Williams, RE/MAX, and Coldwell Banker, which facilitate property transactions and provide market insights, among others.
What are the main drivers of the United States Residential Real Estate Market?
The main drivers of the United States Residential Real Estate Market include low mortgage interest rates, increasing demand for housing, and demographic shifts such as millennials entering the home-buying market. These factors contribute to market growth and activity.
What challenges does the United States Residential Real Estate Market face?
Challenges in the United States Residential Real Estate Market include rising home prices, limited housing inventory, and regulatory hurdles that can complicate transactions. These issues can impact affordability and accessibility for potential buyers.
What opportunities exist in the United States Residential Real Estate Market?
Opportunities in the United States Residential Real Estate Market include the growth of smart home technology, increased interest in sustainable building practices, and the potential for urban revitalization projects. These trends can attract new investments and buyers.
What trends are shaping the United States Residential Real Estate Market?
Trends shaping the United States Residential Real Estate Market include the rise of remote work influencing housing preferences, increased demand for suburban properties, and a focus on eco-friendly homes. These trends reflect changing consumer behaviors and priorities.
the United States Residential Real Estate Market
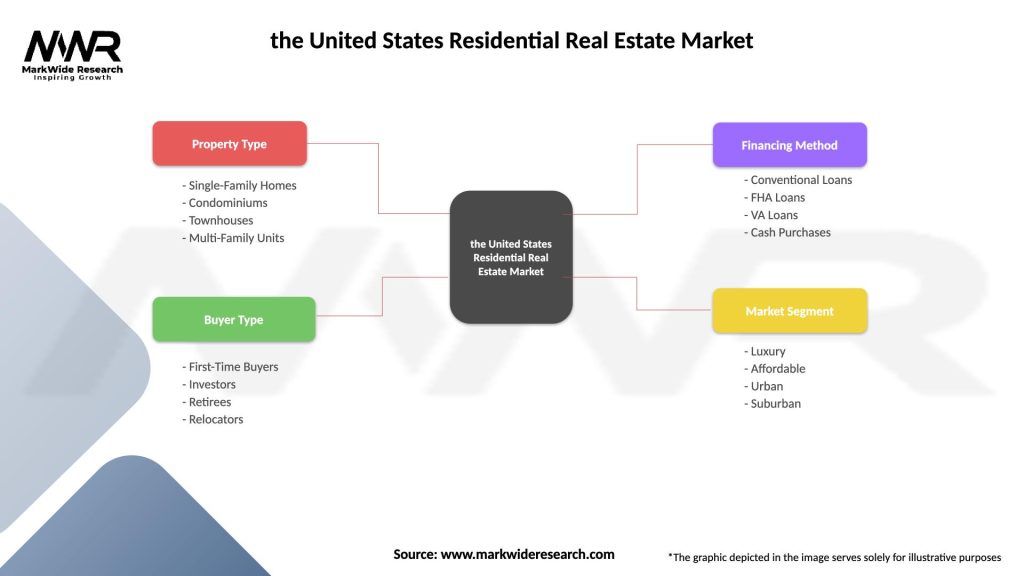
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Property Type | Single-Family Homes, Condominiums, Townhouses, Multi-Family Units |
| Buyer Type | First-Time Buyers, Investors, Retirees, Relocators |
| Financing Method | Conventional Loans, FHA Loans, VA Loans, Cash Purchases |
| Market Segment | Luxury, Affordable, Urban, Suburban |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the the United States Residential Real Estate Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at