444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The telemedicine market is experiencing a significant growth trajectory, driven by the increasing adoption of advanced communication technologies and the need for convenient healthcare services. Telemedicine, also known as telehealth, refers to the remote diagnosis and treatment of patients using telecommunication tools and digital platforms. This innovative approach has revolutionized healthcare delivery by enabling patients to access medical services remotely, eliminating geographical barriers, and improving overall healthcare outcomes.
Meaning
Telemedicine encompasses a wide range of healthcare services, including remote consultations, real-time monitoring, electronic health records (EHR) management, and tele-surgery. It involves the use of various communication technologies such as video conferencing, mobile apps, and wearable devices to connect patients and healthcare providers. This virtual interaction enables healthcare professionals to assess, diagnose, and treat patients from a distance, enhancing accessibility and convenience for both patients and providers.
Executive Summary
The telemedicine market has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years, fueled by the convergence of technology advancements, increasing healthcare costs, and the growing demand for accessible healthcare services. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, as social distancing measures and lockdown restrictions limited in-person healthcare visits. This surge in demand has prompted healthcare organizations, technology companies, and policymakers to invest in telemedicine infrastructure and regulations to support its widespread implementation.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
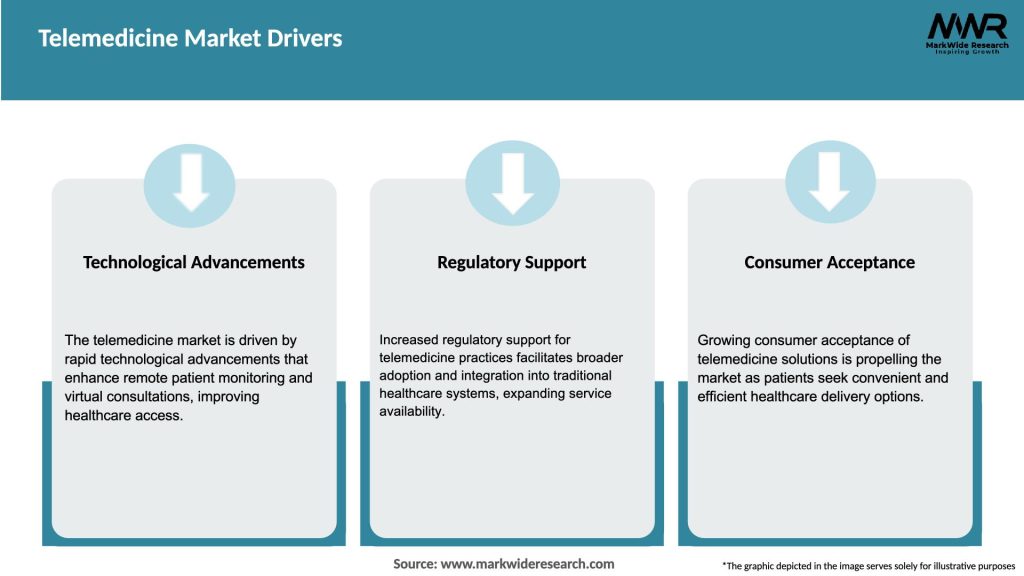
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The telemedicine market is characterized by intense competition among technology companies, healthcare providers, and telecommunication service providers. Collaborations and partnerships between these stakeholders are becoming increasingly common to leverage each other’s expertise and expand market reach. Additionally, mergers and acquisitions are prevalent in the telemedicine sector as companies seek to enhance their technological capabilities and diversify their service offerings.
Regional Analysis
The telemedicine market exhibits significant regional variations due to variations in healthcare infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and technology penetration. North America and Europe have been at the forefront of telemedicine adoption, driven by advanced healthcare systems, supportive regulations, and high internet penetration. The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing rapid growth due to the increasing demand for healthcare services, improving internet connectivity, and rising healthcare investments.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Telemedicine Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
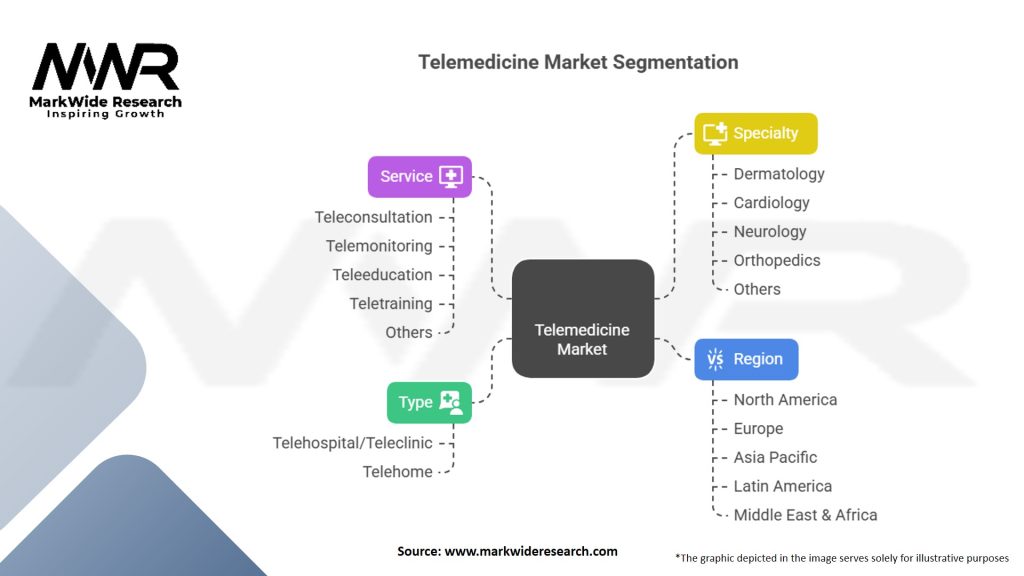
Segmentation
The telemedicine market can be segmented based on the type of service, mode of communication, and end-user.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telemedicine globally. Lockdowns, social distancing measures, and overwhelmed healthcare systems necessitated the use of telemedicine as a means to deliver essential healthcare services. The pandemic served as a catalyst for regulatory changes, reimbursement expansion, and increased public acceptance of telemedicine as a viable alternative to in-person healthcare visits.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the telemedicine market looks promising, with continued growth expected. Advancements in technology, increased awareness and acceptance of telemedicine, and favorable regulatory environments are likely to drive market expansion. The integration of telemedicine with AI, big data analytics, and remote monitoring technologies will further enhance its capabilities and contribute to improved healthcare outcomes. However, addressing infrastructure challenges, privacy concerns, and regulatory complexities will be crucial for realizing the full potential of telemedicine.
Conclusion
Telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare delivery, revolutionizing the way patients access medical services. The market is driven by the need for accessible healthcare, cost-effectiveness, and technological advancements. Telemedicine offers numerous benefits, including enhanced healthcare access, cost savings, improved patient outcomes, and operational efficiency. Despite challenges and limitations, the future of telemedicine appears promising, with continued growth and innovation on the horizon.
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine refers to the use of telecommunications technology to provide medical care and services remotely. It encompasses a variety of applications, including virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and telehealth services.
What are the key players in the Telemedicine Market?
Key players in the Telemedicine Market include Teladoc Health, Amwell, MDLive, and Doxy.me, among others. These companies offer various telehealth solutions, ranging from video consultations to remote monitoring tools.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Telemedicine Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Telemedicine Market include the increasing demand for remote healthcare services, advancements in telecommunications technology, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases that require ongoing management.
What challenges does the Telemedicine Market face?
The Telemedicine Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, concerns over data privacy and security, and the need for reliable internet access in rural areas. These factors can hinder the widespread adoption of telehealth services.
What opportunities exist in the Telemedicine Market?
Opportunities in the Telemedicine Market include the expansion of services into underserved areas, the integration of artificial intelligence for better diagnostics, and the growing acceptance of telehealth by both patients and healthcare providers.
What trends are shaping the Telemedicine Market?
Trends shaping the Telemedicine Market include the rise of mobile health applications, increased investment in telehealth technologies, and a shift towards value-based care models that emphasize patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Telemedicine Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Telehospital/Teleclinic, Telehome |
| Service | Teleconsultation, Telemonitoring, Teleeducation, Teletraining, Others |
| Specialty | Dermatology, Cardiology, Neurology, Orthopedics, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Telemedicine Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at