444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
T cell transfer therapy, also known as adoptive T cell therapy, is a promising approach to cancer treatment that harnesses the power of the body’s own immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. This innovative therapy involves isolating T cells from a patient’s blood, genetically modifying or activating them to recognize and attack cancer cells, and then reintroducing them into the patient’s body. T cell transfer therapy has shown remarkable efficacy in treating certain types of cancer and holds great promise for revolutionizing cancer treatment.
Meaning
T cell transfer therapy is a form of immunotherapy that involves the isolation, modification, and infusion of T cells into a patient’s body to target and destroy cancer cells. T cells, a type of white blood cell, play a crucial role in the immune system’s ability to recognize and eliminate abnormal or infected cells. By enhancing the activity of T cells against cancer cells, T cell transfer therapy offers a targeted and personalized approach to cancer treatment with the potential for long-lasting responses and minimal side effects.
Executive Summary
The T cell transfer therapy market is witnessing rapid growth and innovation as researchers and biopharmaceutical companies explore the therapeutic potential of harnessing the immune system to fight cancer. Recent advances in T cell engineering, genetic editing techniques, and manufacturing technologies have paved the way for the development of next-generation T cell therapies with improved efficacy, safety, and scalability. With ongoing clinical trials and regulatory approvals, T cell transfer therapy is poised to transform the landscape of cancer treatment.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The T cell transfer therapy market is characterized by dynamic interactions between scientific advancements, clinical developments, regulatory considerations, and market forces. Key stakeholders, including biopharmaceutical companies, academic research institutions, regulatory agencies, healthcare providers, and patients, play integral roles in shaping the market landscape and driving innovation in T cell therapy.
Regional Analysis
The T cell transfer therapy market exhibits regional variations in terms of research activity, clinical adoption, regulatory frameworks, and healthcare infrastructure. Developed regions such as North America and Europe lead in terms of clinical trials, investment, and regulatory approvals for T cell therapies, while emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America offer untapped opportunities for market expansion and collaboration.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in T Cell Transfer Therapy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
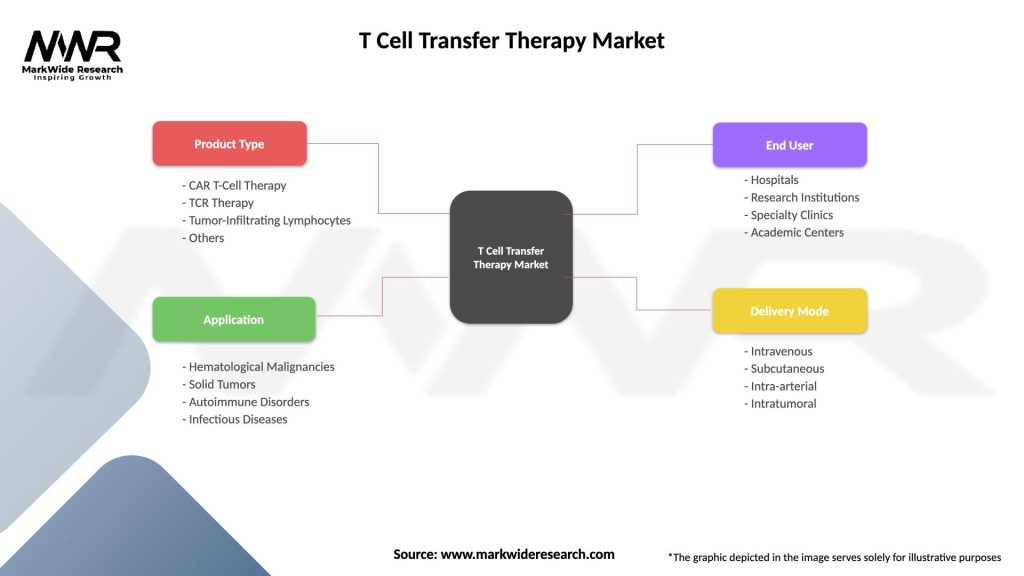
Segmentation
The T cell transfer therapy market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Segmentation provides insights into the diverse applications and opportunities within the T cell transfer therapy market, enabling stakeholders to tailor their strategies and offerings to specific clinical needs and market dynamics.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had mixed effects on the T cell transfer therapy market. While the pandemic initially disrupted clinical trials, manufacturing, and patient access to T cell therapies, the increased focus on immunotherapy and vaccine development has accelerated research and investment in T cell-based approaches for cancer treatment and infectious diseases.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The T cell transfer therapy market is poised for significant growth and innovation, driven by advances in technology, expanding clinical evidence, and increasing investment and regulatory support. With ongoing research and development, the continued optimization of manufacturing processes, and the exploration of novel therapeutic targets and combinations, T cell therapy has the potential to become a cornerstone of cancer treatment and a transformative force in medicine.
Conclusion
T cell transfer therapy represents a revolutionary approach to cancer treatment that harnesses the body’s own immune system to target and eliminate cancer cells. With remarkable clinical successes, ongoing innovation, and increasing investment and regulatory support, T cell therapy is poised to transform the landscape of cancer treatment and improve outcomes for patients worldwide. By addressing key challenges, seizing opportunities for collaboration and innovation, and staying abreast of emerging trends, stakeholders in the T cell therapy market can drive progress towards realizing the full therapeutic potential of this groundbreaking technology.
What is T Cell Transfer Therapy?
T Cell Transfer Therapy is an innovative treatment approach that involves the extraction and modification of T cells to enhance their ability to target and destroy cancer cells. This therapy is primarily used in the treatment of various cancers, including leukemia and lymphoma.
What are the key companies in the T Cell Transfer Therapy Market?
Key companies in the T Cell Transfer Therapy Market include Novartis, Gilead Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Kite Pharma, among others.
What are the drivers of growth in the T Cell Transfer Therapy Market?
The growth of the T Cell Transfer Therapy Market is driven by increasing cancer prevalence, advancements in cell therapy technologies, and a growing focus on personalized medicine. Additionally, supportive regulatory frameworks are facilitating the development and approval of new therapies.
What challenges does the T Cell Transfer Therapy Market face?
The T Cell Transfer Therapy Market faces challenges such as high treatment costs, complex manufacturing processes, and potential side effects associated with therapies. These factors can limit patient access and adoption rates.
What opportunities exist in the T Cell Transfer Therapy Market?
Opportunities in the T Cell Transfer Therapy Market include the expansion of clinical applications beyond hematological cancers, ongoing research into combination therapies, and the development of more efficient manufacturing techniques. These advancements could enhance treatment accessibility and effectiveness.
What trends are shaping the T Cell Transfer Therapy Market?
Trends in the T Cell Transfer Therapy Market include the rise of off-the-shelf therapies, increased collaboration between biotech firms and research institutions, and the integration of artificial intelligence in treatment development. These trends are expected to accelerate innovation and improve patient outcomes.
T Cell Transfer Therapy Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | CAR T-Cell Therapy, TCR Therapy, Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes, Others |
| Application | Hematological Malignancies, Solid Tumors, Autoimmune Disorders, Infectious Diseases |
| End User | Hospitals, Research Institutions, Specialty Clinics, Academic Centers |
| Delivery Mode | Intravenous, Subcutaneous, Intra-arterial, Intratumoral |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in T Cell Transfer Therapy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at