444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview: The surgical stapling energy device market encompasses a wide range of medical devices used in surgical procedures to create closures or connections within the body. These devices utilize energy sources such as electricity, ultrasonic waves, or radiofrequency to deliver precise and controlled energy to tissue, enabling the creation of secure and reliable surgical staples. The market for surgical stapling energy devices is driven by factors such as the increasing adoption of minimally invasive surgical techniques, advancements in surgical stapling technology, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases requiring surgical intervention.
Meaning: Surgical stapling energy devices are specialized instruments used by surgeons to create closures or connections in tissues during surgical procedures. These devices utilize various forms of energy, including electrical, ultrasonic, or radiofrequency energy, to generate heat and seal tissue, or to cut and divide tissue, enabling surgeons to perform precise and efficient surgical stapling procedures. Surgical stapling energy devices play a vital role in a wide range of surgical specialties, including general surgery, gynecology, urology, and thoracic surgery.
Executive Summary: The surgical stapling energy device market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for minimally invasive surgical techniques and the expanding applications of surgical stapling technology across diverse surgical specialties. Key market players are investing in research and development initiatives to enhance device performance, safety, and usability, as well as to develop innovative energy delivery systems. With the growing prevalence of chronic diseases and the rising demand for surgical interventions, the market for surgical stapling energy devices is poised for continued expansion in the foreseeable future.
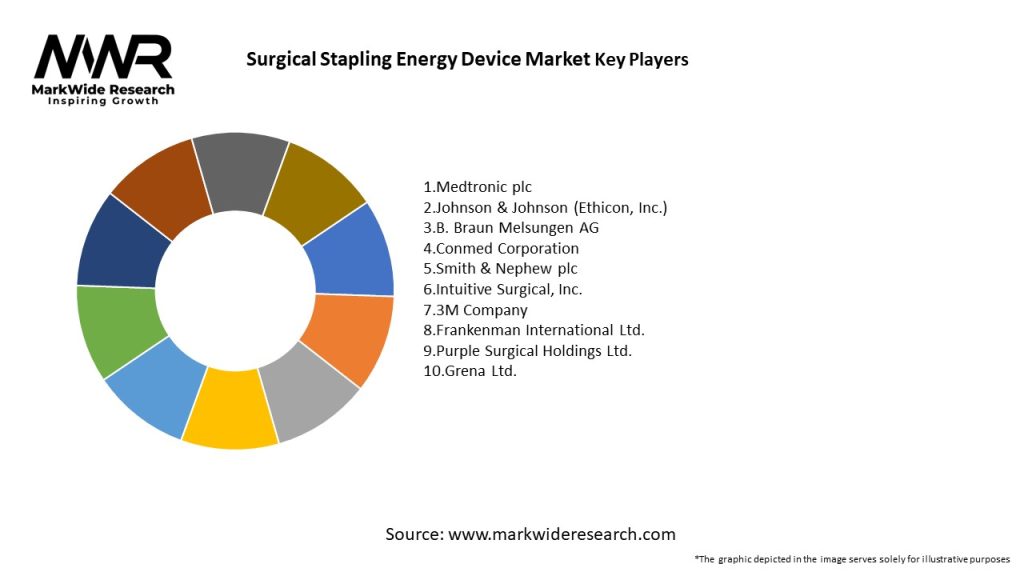
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics: The surgical stapling energy device market is characterized by dynamic interactions between technological innovation, clinical practice guidelines, regulatory requirements, and healthcare economics. Market players need to navigate these dynamics by leveraging strategic partnerships, innovation ecosystems, and value-based healthcare initiatives to drive adoption, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the overall efficiency of surgical stapling procedures.
Regional Analysis: The surgical stapling energy device market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as healthcare infrastructure, reimbursement policies, regulatory frameworks, and surgical practice patterns. North America and Europe lead the market due to the presence of established healthcare systems, high surgical volumes, and early adoption of advanced medical technologies. Emerging economies in Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East offer significant growth opportunities driven by rising healthcare expenditures, increasing demand for surgical interventions, and expanding access to minimally invasive surgical techniques.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
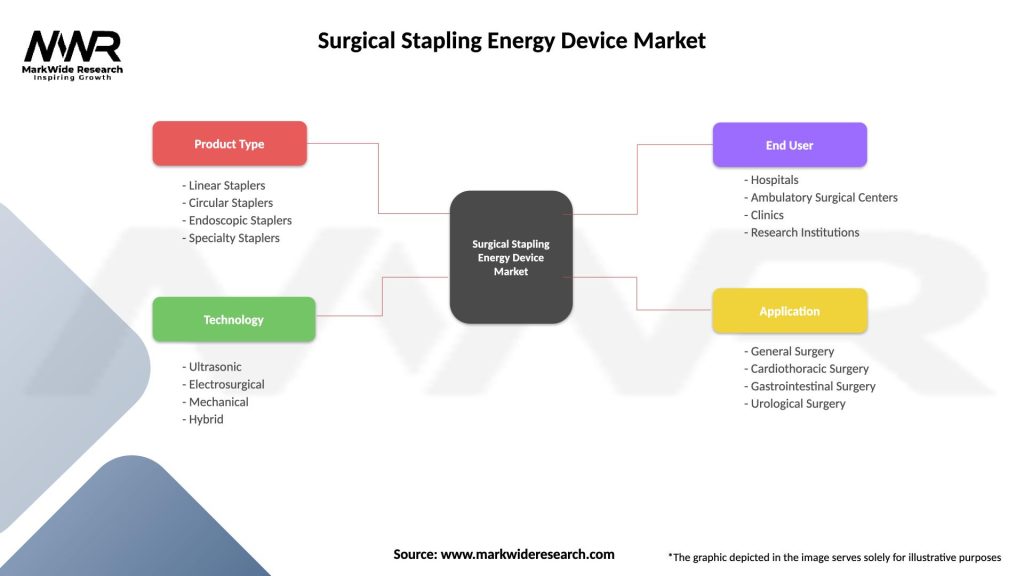
Segmentation: The surgical stapling energy device market can be segmented based on product type, energy source, application, end-user, and geographic region. Product types include powered staplers, manual staplers, linear cutters, and circular staplers. Energy sources encompass electrical, ultrasonic, radiofrequency, and hybrid energy technologies. Applications range from general surgery and gynecology to urology, thoracic surgery, and bariatric surgery. End-users include hospitals, ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs), specialty clinics, and academic medical centers.
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact: The Covid-19 pandemic has led to disruptions in surgical services, elective procedures, and healthcare supply chains, affecting the adoption and utilization of surgical stapling energy devices. However, the pandemic has also underscored the importance of innovation, collaboration, and resilience in healthcare delivery, driving investment in advanced surgical technologies, digital health solutions, and remote monitoring platforms for surgical patients.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook: The surgical stapling energy device market is poised for sustained growth and innovation driven by technological advancements, clinical evidence generation, and market expansion into emerging regions and surgical specialties. With the increasing demand for minimally invasive surgical techniques, patient-centered care models, and digital health solutions, there are opportunities to innovate, collaborate, and drive positive change in surgical practice, patient outcomes, and healthcare delivery.
Conclusion: The surgical stapling energy device market represents a dynamic and evolving segment of the global healthcare industry, offering innovative solutions for tissue closure, hemostasis, and anastomosis in surgical procedures across diverse medical specialties. With their precision, speed, and versatility, surgical stapling energy devices play a critical role in advancing surgical care, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing the overall efficiency and safety of surgical practice. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and evidence-based practice, stakeholders can drive continued growth, innovation, and excellence in surgical stapling technology and patient care in the 21st century.
What is Surgical Stapling Energy Device?
Surgical stapling energy devices are specialized instruments used in surgical procedures to join tissues together using staples, often enhanced with energy sources like ultrasound or electrical currents to improve efficiency and reduce tissue damage.
What are the key players in the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market?
Key players in the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market include Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson, and Ethicon, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market?
The growth of the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market is driven by the increasing number of surgical procedures, advancements in minimally invasive techniques, and the rising demand for efficient wound closure solutions.
What challenges does the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market face?
Challenges in the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market include high costs associated with advanced devices, potential complications from improper use, and stringent regulatory requirements that can delay product approvals.
What opportunities exist in the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market?
Opportunities in the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market include the development of innovative products that integrate smart technology, expansion into emerging markets, and increasing applications in various surgical specialties.
What trends are shaping the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market?
Trends in the Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market include the growing preference for robotic-assisted surgeries, the integration of advanced materials for better biocompatibility, and the focus on sustainability in manufacturing processes.
Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Linear Staplers, Circular Staplers, Endoscopic Staplers, Specialty Staplers |
| Technology | Ultrasonic, Electrosurgical, Mechanical, Hybrid |
| End User | Hospitals, Ambulatory Surgical Centers, Clinics, Research Institutions |
| Application | General Surgery, Cardiothoracic Surgery, Gastrointestinal Surgery, Urological Surgery |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Surgical Stapling Energy Device Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at