444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview: Subdermal needle electrodes are medical devices used in electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS) to assess the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. These electrodes consist of a thin, insulated needle that is inserted into the skin to record the electrical signals generated by muscle contractions or nerve impulses. The subdermal needle electrodes market is driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of neuromuscular disorders, technological advancements in electrode design, and growing demand for minimally invasive diagnostic procedures.
Meaning: Subdermal needle electrodes are specialized medical devices used in electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS) to evaluate the function of muscles and nerves. These electrodes are inserted beneath the skin to directly record the electrical activity of muscles or nerves, providing valuable diagnostic information for various neuromuscular conditions. Subdermal needle electrodes play a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of neuromuscular disorders, offering superior sensitivity and specificity compared to surface electrodes.
Executive Summary: The subdermal needle electrodes market is witnessing steady growth driven by the increasing incidence of neuromuscular disorders, advancements in electrode technology, and rising demand for non-invasive diagnostic tools. Key market players are focusing on developing innovative electrode designs, improving patient comfort, and enhancing signal quality to meet the evolving needs of healthcare providers and patients. With the growing application of EMG and NCS in neurology, rehabilitation, and sports medicine, the market for subdermal needle electrodes is expected to expand further in the coming years.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics: The subdermal needle electrodes market is characterized by rapid technological advancements, evolving regulatory landscapes, and changing patient preferences. Market players need to adapt to these dynamics by investing in research and development, expanding their product portfolios, and exploring new market opportunities to maintain a competitive edge.
Regional Analysis: North America dominates the subdermal needle electrodes market due to the presence of well-established healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditures, and a large patient population with neuromuscular disorders. Europe follows closely, driven by advancements in neurology and rehabilitation services. The Asia Pacific region is expected to witness significant growth, fueled by improving healthcare access and rising awareness about neurodiagnostic tests.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
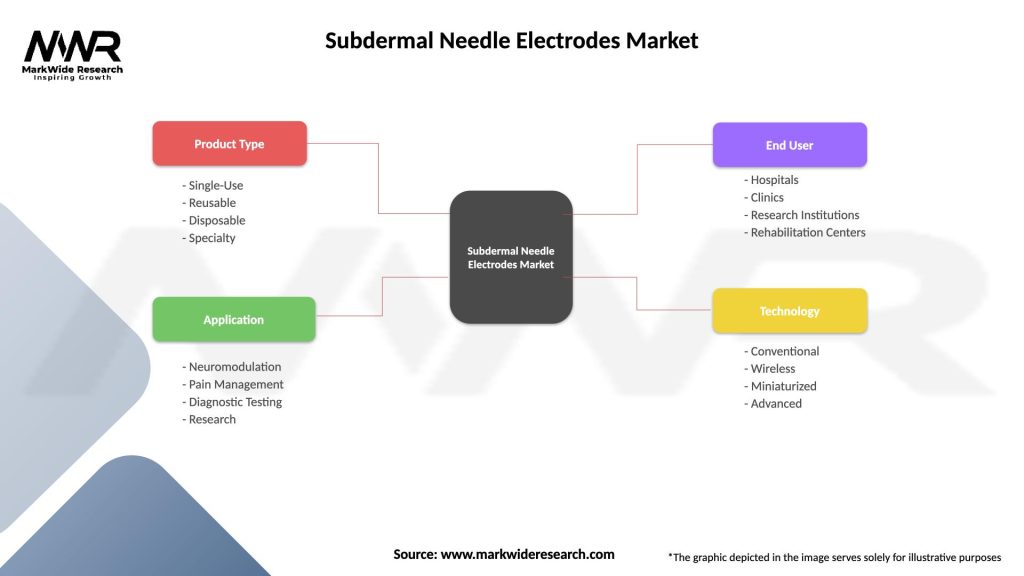
Segmentation: The subdermal needle electrodes market can be segmented based on type, application, end-user, and geography. Types of subdermal needle electrodes include monopolar and bipolar electrodes. Applications range from EMG and NCS to intraoperative monitoring and research studies. End-users encompass hospitals, neurology clinics, rehabilitation centers, and academic research institutions.
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact: The Covid-19 pandemic has led to disruptions in elective medical procedures, including neurodiagnostic tests using subdermal needle electrodes. However, the crisis has also highlighted the importance of telemedicine and remote monitoring technologies, creating new opportunities for market expansion in the post-pandemic era.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook: The subdermal needle electrodes market is expected to witness steady growth driven by the increasing prevalence of neuromuscular disorders, technological advancements, and growing patient demand for minimally invasive diagnostic procedures. Continued investment in research, innovation, and market expansion will be essential for market players to capitalize on emerging opportunities and address evolving patient needs.
Conclusion: Subdermal needle electrodes play a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of neuromuscular disorders, offering healthcare providers valuable insights into muscle and nerve function. With the advent of wireless technology, smart electrodes, and personalized medicine, the future of subdermal needle electrodes looks promising, paving the way for improved patient outcomes and enhanced neurodiagnostic capabilities. Stakeholders in the subdermal needle electrodes market are encouraged to embrace innovation, collaboration, and regulatory compliance to drive growth and innovation in this dynamic field.
What is Subdermal Needle Electrodes?
Subdermal needle electrodes are specialized devices used for various medical applications, including neuromodulation and pain management. They are designed to be inserted beneath the skin to deliver electrical stimulation to targeted areas.
What are the key players in the Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market?
Key players in the Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market include Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott Laboratories, among others. These companies are known for their innovative technologies and extensive product offerings in the field of medical devices.
What are the growth factors driving the Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market?
The Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market is driven by increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures, advancements in neurostimulation technologies, and a growing prevalence of chronic pain conditions. These factors contribute to the rising adoption of subdermal needle electrodes in clinical settings.
What challenges does the Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market face?
Challenges in the Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market include regulatory hurdles, high costs of advanced technologies, and potential complications associated with electrode implantation. These factors can hinder market growth and adoption rates.
What opportunities exist in the Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market?
Opportunities in the Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market include the development of new electrode designs, expansion into emerging markets, and increasing research on applications in mental health treatment. These trends may enhance market potential and innovation.
What trends are shaping the Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market?
Current trends in the Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market include the integration of smart technologies for real-time monitoring and feedback, as well as the growing focus on personalized medicine. These innovations are expected to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Single-Use, Reusable, Disposable, Specialty |
| Application | Neuromodulation, Pain Management, Diagnostic Testing, Research |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Research Institutions, Rehabilitation Centers |
| Technology | Conventional, Wireless, Miniaturized, Advanced |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Subdermal Needle Electrodes Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at