444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The street vendors market represents a vibrant and essential component of urban economies worldwide, providing convenient access to a variety of goods and services in public spaces. Street vendors operate in diverse locations such as sidewalks, markets, parks, and festivals, offering a wide range of products including food, beverages, clothing, accessories, crafts, and souvenirs. This informal sector plays a significant role in meeting consumer needs, fostering entrepreneurship, and contributing to local economies by creating employment opportunities and generating revenue.
Meaning
Street vendors are individuals or small businesses that sell goods or services in public spaces, typically without a fixed location or formal storefront. Street vending is characterized by its flexibility, low barriers to entry, and direct interaction with customers in high-traffic areas. Vendors may specialize in specific products or offer a diverse range of items, catering to local residents, tourists, and passersby. Street vending serves as a vital source of income for entrepreneurs, particularly in urban areas where access to traditional employment opportunities may be limited.
Executive Summary
The street vendors market is a dynamic and resilient sector that plays a vital role in urban economies worldwide. Street vendors offer convenience, affordability, and diversity, attracting consumers seeking quick and accessible goods and services. Despite facing challenges such as regulatory hurdles, competition, and fluctuating demand, street vendors demonstrate adaptability and innovation in responding to changing market conditions. Key trends shaping the market include the rise of food trucks and mobile vendors, digital payment adoption, and collaborative efforts to address socio-economic issues facing vendors. Overall, the street vendors market presents opportunities for entrepreneurship, community engagement, and inclusive economic development.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The street vendors market operates within a dynamic ecosystem shaped by socio-economic, cultural, and regulatory factors. Market dynamics such as urbanization trends, consumer preferences, regulatory frameworks, and technological advancements influence vendors’ business strategies, market entry barriers, and opportunities for growth. Understanding these dynamics is essential for vendors to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and sustain viable businesses in competitive urban environments.
Regional Analysis
The street vendors market exhibits regional variations in terms of regulatory frameworks, cultural norms, consumer preferences, and market dynamics. Let’s explore some key regions:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Street Vendors Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

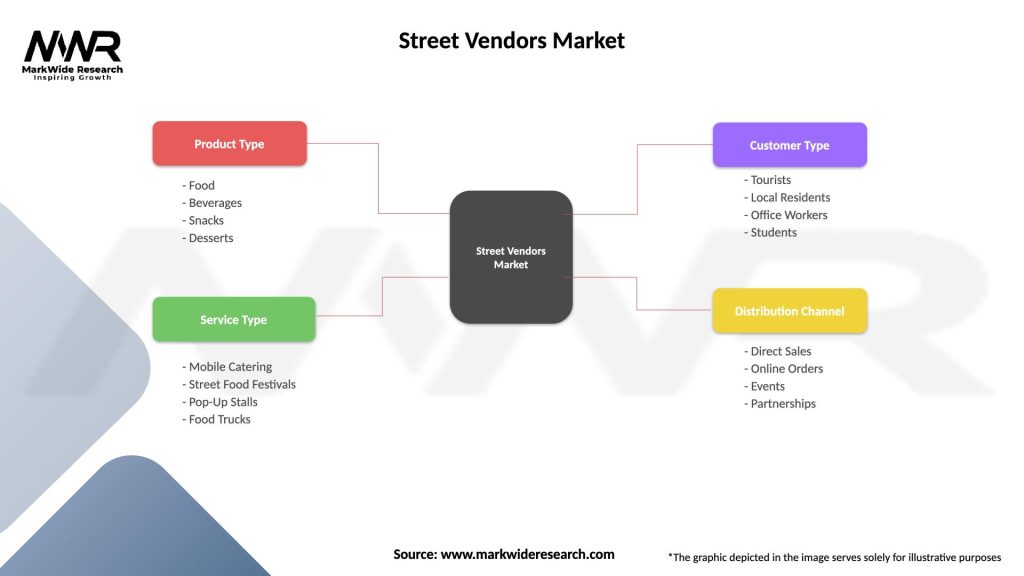
Segmentation
The street vendors market can be segmented based on various factors such as:
Segmentation enables vendors to target specific customer segments, tailor their product offerings, and optimize their marketing strategies to meet diverse consumer needs and preferences.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The street vendors market offers several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis of the street vendors market reveals the following:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had profound effects on the street vendors market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the street vendors market is influenced by trends such as urbanization, digitalization, sustainability, and socio-economic inequalities. While regulatory challenges, gentrification pressures, and pandemic-related disruptions pose risks to street vendors’ livelihoods, opportunities exist for innovation, collaboration, and advocacy to shape more inclusive and resilient urban environments. By leveraging technology, embracing sustainability, and strengthening community networks, street vendors can adapt to changing market conditions, expand their businesses, and continue to contribute to vibrant and diverse street cultures worldwide.
Conclusion
The street vendors market is a vital and dynamic sector within urban economies, providing convenient access to a diverse array of goods and services while fostering entrepreneurship and community engagement. Despite facing regulatory hurdles, competition from formal retail establishments, and socio-economic vulnerabilities, street vendors demonstrate resilience, adaptability, and innovation in responding to changing market dynamics.
The future of the street vendors market holds promise for inclusive economic development, cultural preservation, and social cohesion, provided that policymakers, urban planners, and society at large recognize and support the vital contributions of street vendors to urban life and prosperity. By fostering an enabling environment that balances regulatory oversight with vendors’ livelihoods, cities can harness the economic potential and cultural richness of street vending to create more equitable, vibrant, and resilient urban communities for all.
What is Street Vendors?
Street vendors are individuals or small businesses that sell goods or services in public spaces, often without a permanent storefront. They typically offer a variety of products, including food, beverages, and handmade crafts, catering to local consumers and tourists alike.
Who are the key players in the Street Vendors Market?
Key players in the Street Vendors Market include local entrepreneurs, food truck operators, and small-scale artisans. Notable examples are vendors selling street food, handmade jewelry, and local crafts, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Street Vendors Market?
The growth of the Street Vendors Market is driven by urbanization, increasing consumer demand for convenient and affordable food options, and the rise of food tourism. Additionally, the flexibility and low startup costs associated with street vending attract many entrepreneurs.
What challenges do street vendors face in the Street Vendors Market?
Street vendors often face challenges such as regulatory hurdles, competition from established businesses, and issues related to health and safety compliance. Additionally, they may encounter difficulties in securing stable locations for their operations.
What opportunities exist in the Street Vendors Market for new entrants?
Opportunities in the Street Vendors Market include the growing trend of gourmet street food, the potential for niche markets such as vegan or organic offerings, and the use of social media for marketing. These factors can help new vendors attract a diverse customer base.
What trends are shaping the Street Vendors Market?
Trends in the Street Vendors Market include the increasing popularity of food trucks, the integration of technology for payment solutions, and a focus on sustainability through eco-friendly packaging. These trends reflect changing consumer preferences and the evolving landscape of urban dining.
Street Vendors Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Food, Beverages, Snacks, Desserts |
| Service Type | Mobile Catering, Street Food Festivals, Pop-Up Stalls, Food Trucks |
| Customer Type | Tourists, Local Residents, Office Workers, Students |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Online Orders, Events, Partnerships |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Street Vendors Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at