444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education in the K-12 market has gained significant attention in recent years. It aims to provide students with a strong foundation in these key disciplines, preparing them for future careers in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. This educational approach focuses on promoting critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and innovation among students from kindergarten to grade 12.
Meaning
STEM education in the K-12 market refers to the integration of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics into the curriculum for students at the primary and secondary levels. It emphasizes the importance of these subjects in shaping the next generation’s skills and knowledge base. By incorporating STEM principles, educational institutions aim to equip students with the necessary tools to excel in a technology-driven world.
Executive Summary
The K-12 STEM education market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for a well-rounded education that prepares students for future job opportunities. The emphasis on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics has become crucial as the global economy becomes more reliant on technological advancements and innovation. This executive summary provides an overview of the key market insights, drivers, restraints, opportunities, and trends that are shaping the STEM education landscape in K-12 schools.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The K-12 STEM education market is driven by the interplay of various factors, including government policies, industry partnerships, technological advancements, and changing societal needs. The demand for a skilled workforce, economic competitiveness, and the imperative to prepare students for future challenges are key driving forces. However, limited teacher training, infrastructure constraints, and the complexity associated with STEM subjects present challenges to market growth. Opportunities arise from government initiatives, industry collaborations, online learning platforms, and investments in teacher professional development.
Regional Analysis
The adoption and implementation of STEM education in the K-12 market vary across regions. Developed countries, such as the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and Germany, have made significant progress in integrating STEM principles into their educational systems. These countries have established policies, funding mechanisms, and public-private partnerships to support STEM education initiatives. Developing regions, including Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are also witnessing an increasing focus on STEM education, driven by the need to cultivate a skilled workforce and drive economic growth.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the STEM Education In K-12 Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
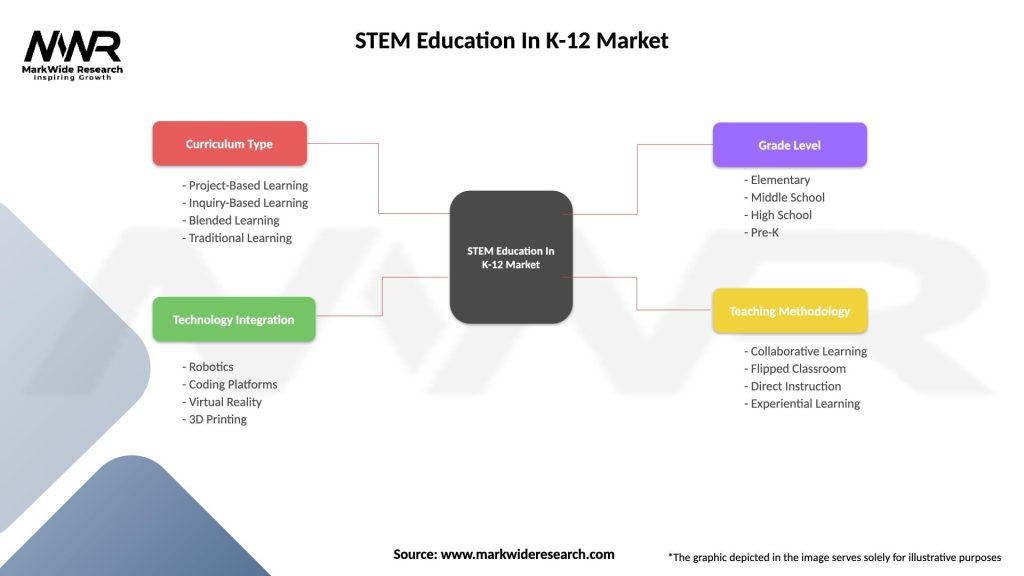
The K-12 STEM education market can be segmented based on grade level, component, and delivery mode. Grade-level segmentation includes kindergarten, primary school (grades 1-5), middle school (grades 6-8), and high school (grades 9-12). The components of STEM education encompass science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Delivery modes may include traditional classroom-based learning, online platforms, blended learning models, and hands-on experiential programs.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the K-12 STEM education market. School closures and the shift to remote learning have necessitated the adoption of online platforms and digital resources to deliver STEM education. Virtual classrooms, online simulations, and educational apps have helped maintain continuity in STEM learning. However, the pandemic has also highlighted the disparities in access to technology and internet connectivity, exacerbating inequalities in STEM education.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of STEM education in the K-12 market looks promising, driven by the increasing recognition of the importance of STEM skills in the global economy. Governments, educational institutions, and industry stakeholders are expected to continue investing in STEM education initiatives, addressing challenges such as teacher training, infrastructure development, and diversity in participation. The integration of technology, interdisciplinary approaches, and project-based learning will shape the future of STEM education, preparing students for the demands of a rapidly evolving world.
Conclusion
STEM education in the K-12 market is a critical component of preparing students for the challenges and opportunities of the future. It provides a comprehensive approach to education, emphasizing science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. The market is driven by the increasing demand for STEM professionals, economic competitiveness, and the need to bridge the skills gap. While challenges exist, such as limited teacher training and infrastructure constraints, the market presents significant opportunities through government initiatives, industry partnerships, online learning platforms, and investments in teacher professional development. With the right investments, collaborations, and a focus on inclusivity, STEM education in the K-12 market will continue to evolve, equipping students with the skills and knowledge necessary for success in a technology-driven world.
What is STEM Education in K-12?
STEM Education in K-12 refers to an educational approach that integrates science, technology, engineering, and mathematics into the curriculum. This method aims to enhance critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and prepare students for future careers in these fields.
What are the key companies in the STEM Education in K-12 market?
Key companies in the STEM Education in K-12 market include LEGO Education, Discovery Education, and Pearson. These organizations provide resources, curricula, and tools designed to enhance STEM learning experiences, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the STEM Education in K-12 market?
The main drivers of growth in the STEM Education in K-12 market include the increasing demand for skilled workers in STEM fields, the integration of technology in classrooms, and the emphasis on critical thinking and problem-solving skills in education.
What challenges does the STEM Education in K-12 market face?
Challenges in the STEM Education in K-12 market include a lack of trained educators, insufficient funding for STEM programs, and disparities in access to quality resources among different school districts.
What opportunities exist for the future of STEM Education in K-12?
Opportunities for the future of STEM Education in K-12 include the expansion of online learning platforms, increased collaboration between schools and industry, and the development of innovative teaching methods that engage students in hands-on learning.
What trends are shaping the STEM Education in K-12 market?
Trends shaping the STEM Education in K-12 market include the rise of project-based learning, the incorporation of coding and robotics into the curriculum, and a growing focus on interdisciplinary approaches that connect STEM subjects with the arts and humanities.
STEM Education In K-12 Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Curriculum Type | Project-Based Learning, Inquiry-Based Learning, Blended Learning, Traditional Learning |
| Technology Integration | Robotics, Coding Platforms, Virtual Reality, 3D Printing |
| Grade Level | Elementary, Middle School, High School, Pre-K |
| Teaching Methodology | Collaborative Learning, Flipped Classroom, Direct Instruction, Experiential Learning |
Leading Companies in the STEM Education In K-12 Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at