444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The spray drying in pharmaceutical market represents a critical segment within the global pharmaceutical manufacturing industry, encompassing advanced technologies and processes essential for drug formulation and production. This specialized market focuses on the application of spray drying techniques to transform liquid pharmaceutical formulations into dry powder forms, enabling enhanced stability, bioavailability, and shelf life of various drug compounds. Spray drying technology has emerged as a cornerstone process in pharmaceutical manufacturing, particularly for heat-sensitive compounds, biologics, and complex drug delivery systems.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth driven by increasing demand for advanced drug delivery systems, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and growing emphasis on personalized medicine. The pharmaceutical industry’s continuous evolution toward more sophisticated formulation techniques has positioned spray drying processes as indispensable tools for modern drug development. Current market trends show significant adoption rates of 12.3% annually across major pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, with particular strength in biologics and specialty drug segments.
Regional distribution reveals concentrated activity in North America and Europe, accounting for approximately 68% of global market share, while Asia-Pacific regions demonstrate the fastest growth trajectory. The market encompasses various stakeholder categories, including pharmaceutical manufacturers, contract research organizations, equipment suppliers, and technology providers, all contributing to a comprehensive ecosystem supporting advanced pharmaceutical production capabilities.
The spray drying in pharmaceutical market refers to the specialized industry segment focused on the application of spray drying technology for pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, involving the conversion of liquid drug formulations into dry powder forms through controlled evaporation and particle formation techniques.
Spray drying technology encompasses sophisticated equipment and processes designed to transform liquid pharmaceutical solutions, suspensions, or emulsions into fine powder particles through rapid moisture removal. This process involves atomizing liquid feed into fine droplets within a heated chamber, where controlled airflow facilitates rapid solvent evaporation, resulting in dried particles with specific characteristics tailored for pharmaceutical applications.
The technology’s significance extends beyond simple moisture removal, encompassing particle engineering capabilities that enable precise control over particle size distribution, morphology, density, and surface properties. These characteristics directly influence drug dissolution rates, bioavailability, stability, and overall therapeutic efficacy, making spray drying an essential tool for pharmaceutical formulation scientists and manufacturers seeking to optimize drug delivery systems.
Market leadership in the spray drying pharmaceutical sector is characterized by continuous technological advancement and increasing adoption across diverse therapeutic areas. The industry demonstrates strong growth momentum driven by expanding applications in biologics manufacturing, personalized medicine development, and advanced drug delivery system formulation. Key market drivers include rising demand for improved drug stability, enhanced bioavailability requirements, and growing emphasis on patient-centric formulation approaches.
Technology adoption rates show significant acceleration, with pharmaceutical companies increasingly integrating spray drying capabilities into their manufacturing processes. The market benefits from substantial investment in research and development activities, with innovation focus areas including continuous manufacturing integration, process analytical technology implementation, and sustainable manufacturing practices. Regulatory compliance remains a critical factor, with manufacturers investing heavily in quality systems and validation protocols to meet stringent pharmaceutical industry standards.
Competitive dynamics reveal a landscape characterized by both established equipment manufacturers and emerging technology providers, creating opportunities for innovation and market expansion. The industry’s evolution toward more sophisticated applications, including nanotechnology integration and complex drug delivery systems, positions spray drying as an increasingly valuable pharmaceutical manufacturing capability with substantial growth potential across multiple market segments.

Primary market insights reveal several critical trends shaping the spray drying pharmaceutical landscape:
Market penetration analysis indicates strong adoption across major pharmaceutical segments, with particularly robust growth in specialty pharmaceuticals and contract manufacturing organizations. The insights demonstrate clear market evolution toward more sophisticated applications and higher value-added services within the pharmaceutical manufacturing ecosystem.
Primary growth drivers propelling the spray drying pharmaceutical market include the increasing complexity of modern drug formulations and the growing demand for enhanced drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutical innovation continues to drive adoption as companies seek advanced manufacturing technologies capable of handling sensitive compounds, improving bioavailability, and enabling novel therapeutic approaches. The rise of biologics and biosimilars has created substantial demand for specialized processing technologies, with spray drying offering unique advantages for protein stabilization and formulation optimization.
Regulatory requirements serve as significant market drivers, with pharmaceutical companies investing in advanced manufacturing technologies to meet evolving quality standards and compliance expectations. The implementation of Quality by Design principles has increased demand for precise process control capabilities, positioning spray drying systems with advanced monitoring and control features as essential manufacturing tools. Patient safety considerations drive continuous improvement in manufacturing processes, with spray drying technology offering enhanced product consistency and quality assurance capabilities.
Economic factors including cost reduction pressures and efficiency improvement requirements motivate pharmaceutical manufacturers to adopt advanced processing technologies. Spray drying offers significant advantages in terms of product stability, shelf life extension, and manufacturing flexibility, contributing to overall operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The technology’s ability to enable continuous manufacturing processes aligns with industry trends toward more efficient and sustainable production methods.
Capital investment requirements represent a primary constraint for spray drying pharmaceutical market growth, as advanced systems require substantial initial investments and ongoing maintenance costs. Technical complexity associated with spray drying processes demands specialized expertise and extensive validation activities, creating barriers for smaller pharmaceutical companies and emerging market participants. The need for comprehensive process development and optimization can extend project timelines and increase development costs significantly.
Regulatory challenges pose ongoing constraints, with pharmaceutical spray drying operations subject to stringent validation requirements and extensive documentation protocols. The complexity of regulatory approval processes for new applications and process modifications can limit market expansion and innovation adoption rates. Quality control demands require sophisticated analytical capabilities and continuous monitoring systems, adding operational complexity and cost considerations for pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Technical limitations including heat sensitivity concerns for certain compounds and potential degradation risks during processing can restrict application scope for some pharmaceutical formulations. The technology’s suitability varies significantly based on specific drug characteristics and formulation requirements, limiting universal applicability across all pharmaceutical segments. Scale-up challenges from laboratory to commercial production can present technical and economic obstacles for pharmaceutical companies seeking to implement spray drying technologies.
Emerging opportunities in the spray drying pharmaceutical market center around expanding applications in personalized medicine and precision drug delivery systems. Nanotechnology integration presents significant growth potential, with spray drying techniques enabling the production of nanoparticle formulations with enhanced therapeutic properties and targeted delivery capabilities. The growing emphasis on patient-centric drug development creates opportunities for customized formulation approaches utilizing advanced spray drying technologies.
Geographic expansion opportunities exist in emerging pharmaceutical markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin American regions where pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities are rapidly developing. Contract manufacturing growth provides substantial opportunities for specialized service providers offering spray drying capabilities to pharmaceutical companies seeking outsourced manufacturing solutions. The trend toward continuous manufacturing presents opportunities for technology providers to develop integrated spray drying systems compatible with continuous production platforms.
Innovation opportunities include development of more energy-efficient systems, advanced process control technologies, and specialized applications for complex drug delivery systems. The increasing focus on sustainability in pharmaceutical manufacturing creates opportunities for environmentally conscious spray drying solutions. Digital transformation initiatives within the pharmaceutical industry present opportunities for smart manufacturing integration and data-driven process optimization capabilities.
Market dynamics in the spray drying pharmaceutical sector reflect a complex interplay of technological advancement, regulatory evolution, and changing pharmaceutical industry requirements. Supply chain considerations have gained increased importance, with pharmaceutical companies seeking reliable technology partners capable of providing comprehensive support throughout the product lifecycle. The market demonstrates strong resilience and adaptability, with manufacturers continuously evolving their capabilities to address emerging pharmaceutical challenges and opportunities.
Competitive pressures drive continuous innovation and improvement in spray drying technologies, with equipment manufacturers investing heavily in research and development to maintain market position. The dynamics reveal increasing collaboration between technology providers and pharmaceutical companies, fostering innovation and accelerating technology adoption. Market consolidation trends show strategic partnerships and acquisitions as companies seek to expand capabilities and market reach.
Technology evolution continues to reshape market dynamics, with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics integration becoming increasingly important for process optimization and quality assurance. The market shows strong responsiveness to pharmaceutical industry trends, with rapid adaptation to emerging requirements such as continuous manufacturing, personalized medicine, and sustainable production practices. Customer expectations continue to evolve, demanding more sophisticated solutions with enhanced performance characteristics and comprehensive support services.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for analyzing the spray drying pharmaceutical market incorporates multiple data collection and analysis approaches to ensure accuracy and reliability of market insights. Primary research activities include extensive interviews with industry experts, pharmaceutical manufacturers, equipment suppliers, and regulatory specialists to gather firsthand insights into market trends, challenges, and opportunities. The methodology encompasses structured surveys and questionnaires designed to capture quantitative data on market adoption rates, technology preferences, and investment patterns.
Secondary research components involve systematic analysis of industry publications, regulatory documents, patent filings, and company financial reports to establish comprehensive market understanding. The research approach includes examination of pharmaceutical industry databases, trade association reports, and academic research publications to validate findings and identify emerging trends. Market modeling techniques utilize statistical analysis and forecasting methodologies to project market growth patterns and identify key performance indicators.
Data validation processes ensure research accuracy through cross-referencing multiple sources and expert verification of key findings. The methodology incorporates regional analysis components to capture geographic variations in market dynamics and growth patterns. Quality assurance protocols include peer review processes and expert panel evaluations to maintain research integrity and reliability throughout the analysis process.
North American markets demonstrate strong leadership in spray drying pharmaceutical applications, with the United States accounting for approximately 45% of regional market share. The region benefits from advanced pharmaceutical manufacturing infrastructure, substantial research and development investments, and supportive regulatory frameworks that encourage technology adoption. Canadian pharmaceutical sectors show growing interest in spray drying technologies, particularly for biologics manufacturing and specialty drug production applications.
European markets exhibit sophisticated adoption patterns, with Germany, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom leading in technology implementation and innovation. The region’s emphasis on pharmaceutical excellence and quality manufacturing standards drives demand for advanced spray drying capabilities. Regulatory harmonization across European Union markets facilitates technology adoption and market expansion, with manufacturers benefiting from streamlined approval processes and consistent quality requirements.
Asia-Pacific regions represent the fastest-growing market segment, with China and India showing particularly strong growth trajectories of approximately 18.5% annually. The region’s expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and increasing focus on quality improvement drive technology adoption. Japanese pharmaceutical markets demonstrate advanced technology integration, while emerging markets in Southeast Asia present significant growth opportunities for spray drying technology providers seeking geographic expansion.
Market leadership in the spray drying pharmaceutical sector is characterized by a diverse ecosystem of established equipment manufacturers, specialized technology providers, and emerging innovation companies. The competitive landscape demonstrates strong innovation focus, with leading companies investing substantially in research and development to maintain technological advantages and expand application capabilities.
Key market participants include:
Competitive strategies focus on technology differentiation, comprehensive service offerings, and strategic partnerships with pharmaceutical companies. The landscape shows increasing emphasis on digital integration, process optimization capabilities, and regulatory compliance support as key competitive differentiators.
Technology-based segmentation reveals distinct market categories based on spray drying system configurations and capabilities:
Application-based segmentation demonstrates diverse utilization across pharmaceutical sectors:
End-user segmentation includes pharmaceutical manufacturers, contract research organizations, biotechnology companies, and academic research institutions, each with distinct requirements and adoption patterns.
Pharmaceutical formulation applications represent the largest market category, driven by increasing demand for enhanced drug delivery systems and improved bioavailability characteristics. This segment demonstrates strong growth in solid dosage form development, with spray drying enabling precise particle engineering for controlled release formulations. Innovation focus includes development of taste-masked formulations, pediatric-friendly dosage forms, and specialized delivery systems for challenging therapeutic compounds.
Biologics processing applications show the highest growth rates, with spray drying technology proving essential for protein stabilization and preservation. This category benefits from expanding biologics markets and increasing emphasis on biosimilar development. Technical advancement in this segment focuses on maintaining biological activity during processing and achieving optimal storage stability for sensitive biological compounds.
Contract manufacturing services represent a rapidly expanding category, with specialized service providers offering spray drying capabilities to pharmaceutical companies seeking outsourced manufacturing solutions. This segment demonstrates strong growth potential as pharmaceutical companies increasingly focus on core competencies while outsourcing specialized manufacturing processes. Service differentiation includes comprehensive process development support, regulatory compliance assistance, and flexible manufacturing capabilities for diverse pharmaceutical applications.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers benefit significantly from spray drying technology implementation through enhanced product quality, improved manufacturing efficiency, and expanded formulation capabilities. The technology enables precise control over particle characteristics, resulting in more consistent drug performance and enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Cost benefits include reduced manufacturing complexity, improved yield rates, and enhanced product stability leading to extended shelf life and reduced waste.
Contract research organizations gain competitive advantages through spray drying capabilities, enabling comprehensive formulation development services and accelerated drug development timelines. The technology provides flexibility for handling diverse pharmaceutical compounds and enables rapid prototyping and optimization of drug formulations. Service expansion opportunities include specialized applications for complex drug delivery systems and personalized medicine development.
Equipment suppliers benefit from growing market demand and opportunities for technology innovation and differentiation. The market provides substantial revenue potential through equipment sales, service contracts, and technology licensing arrangements. Strategic advantages include long-term customer relationships, recurring revenue streams from maintenance and support services, and opportunities for geographic expansion into emerging pharmaceutical markets.
Regulatory agencies benefit from improved pharmaceutical manufacturing standards and enhanced product quality assurance capabilities enabled by advanced spray drying technologies. The technology supports regulatory objectives for pharmaceutical safety, efficacy, and quality consistency.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital transformation trends are reshaping the spray drying pharmaceutical landscape, with manufacturers increasingly integrating advanced process control systems, real-time monitoring capabilities, and data analytics platforms. Industry 4.0 adoption includes implementation of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms for process optimization and predictive maintenance. The trend toward smart manufacturing enables enhanced quality control, reduced operational costs, and improved manufacturing efficiency across pharmaceutical spray drying operations.
Sustainability initiatives represent a growing trend, with pharmaceutical companies seeking energy-efficient spray drying solutions and environmentally conscious manufacturing processes. Green manufacturing practices include solvent recovery systems, waste reduction strategies, and renewable energy integration. The trend reflects increasing corporate responsibility commitments and regulatory pressure for sustainable pharmaceutical manufacturing practices.
Continuous manufacturing integration shows strong momentum, with pharmaceutical companies adopting continuous production platforms that incorporate spray drying as an integral process step. This trend enables enhanced quality control, reduced manufacturing costs, and improved production flexibility. Process intensification approaches focus on optimizing spray drying operations within continuous manufacturing frameworks, enabling more efficient and cost-effective pharmaceutical production.
Personalized medicine applications demonstrate growing importance, with spray drying technology adapting to support small-batch, patient-specific drug formulations. The trend includes development of flexible manufacturing systems capable of handling diverse formulation requirements and rapid changeover capabilities for different pharmaceutical products.
Recent technological advancements include development of advanced spray drying systems with enhanced particle engineering capabilities and improved process control features. Innovation highlights encompass integration of real-time particle size analysis, automated process optimization, and advanced material handling systems. The developments focus on improving product quality consistency, reducing manufacturing variability, and enabling more sophisticated pharmaceutical applications.
Strategic partnerships between equipment manufacturers and pharmaceutical companies have accelerated technology development and market adoption. Collaboration initiatives include joint research projects, technology validation studies, and co-development of specialized spray drying solutions for specific pharmaceutical applications. These partnerships facilitate knowledge transfer, reduce development risks, and accelerate time-to-market for innovative pharmaceutical formulations.
Regulatory developments include updated guidance documents for pharmaceutical spray drying operations and enhanced quality requirements for manufacturing processes. MarkWide Research analysis indicates increasing regulatory focus on process validation, quality by design implementation, and continuous improvement practices. The developments support industry evolution toward more sophisticated and reliable pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities.
Market expansion activities include geographic expansion of spray drying technology providers into emerging pharmaceutical markets and establishment of regional manufacturing and service capabilities. The developments reflect growing global demand for advanced pharmaceutical manufacturing technologies and increasing market opportunities in developing regions.
Strategic recommendations for pharmaceutical companies include evaluation of spray drying technology integration opportunities and assessment of potential competitive advantages through advanced manufacturing capabilities. Investment priorities should focus on technologies offering enhanced particle engineering capabilities, improved process control features, and compatibility with continuous manufacturing platforms. Companies should consider partnerships with experienced technology providers to accelerate implementation and reduce development risks.
Technology selection criteria should emphasize flexibility, scalability, and regulatory compliance capabilities to ensure long-term value and adaptability to evolving pharmaceutical requirements. MWR analysis suggests prioritizing systems with advanced monitoring and control features, comprehensive validation support, and proven track records in pharmaceutical applications. Due diligence should include thorough evaluation of supplier capabilities, service support, and technology roadmap alignment with company strategic objectives.
Market entry strategies for technology providers should focus on developing specialized expertise in high-growth application areas such as biologics processing and personalized medicine. Competitive differentiation opportunities include development of innovative process solutions, comprehensive service offerings, and strategic partnerships with pharmaceutical industry leaders. Geographic expansion should prioritize emerging markets with growing pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and supportive regulatory environments.
Risk management considerations include diversification of technology portfolios, development of robust supply chain relationships, and maintenance of strong regulatory compliance capabilities to address evolving industry requirements and market challenges.
Market projections indicate continued strong growth for the spray drying pharmaceutical sector, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing requirements and increasing adoption of advanced processing technologies. Growth trajectory analysis suggests sustained expansion at approximately 9.2% CAGR over the next five years, with particularly strong performance in biologics applications and emerging market segments. The outlook reflects increasing pharmaceutical industry sophistication and growing demand for enhanced drug delivery systems.
Technology evolution will likely focus on integration with digital manufacturing platforms, development of more energy-efficient systems, and advancement of specialized applications for complex pharmaceutical formulations. Innovation priorities include artificial intelligence integration, advanced process control capabilities, and sustainable manufacturing solutions. The future landscape will likely feature more sophisticated and automated spray drying systems with enhanced quality assurance capabilities.
Market expansion opportunities will continue to emerge in developing pharmaceutical markets, with increasing demand for advanced manufacturing technologies and quality improvement initiatives. MarkWide Research forecasts indicate substantial growth potential in Asia-Pacific regions, with market penetration rates expected to reach 75% by 2029. The expansion will be supported by increasing pharmaceutical manufacturing investments and regulatory framework development in emerging markets.
Industry transformation will likely accelerate adoption of continuous manufacturing approaches, personalized medicine applications, and sustainable production practices, positioning spray drying technology as an essential component of modern pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities.
The spray drying in pharmaceutical market represents a dynamic and essential segment of the global pharmaceutical manufacturing industry, characterized by continuous technological advancement and expanding application opportunities. The market demonstrates strong growth momentum driven by increasing pharmaceutical complexity, regulatory requirements, and demand for enhanced drug delivery systems. Key success factors include technology innovation, regulatory compliance, and strategic partnerships that enable comprehensive solutions for diverse pharmaceutical manufacturing requirements.
Market evolution continues toward more sophisticated applications, with particular strength in biologics processing, personalized medicine, and continuous manufacturing integration. The competitive landscape reflects healthy innovation dynamics and substantial investment in research and development activities. Future prospects remain highly favorable, with expanding global pharmaceutical markets, increasing quality requirements, and growing emphasis on advanced manufacturing technologies supporting sustained market growth and development opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders.
What is Spray Drying in Pharmaceutical?
Spray drying in pharmaceutical refers to a process that converts liquid solutions or suspensions into dry powder form by rapidly evaporating the solvent. This technique is widely used for producing fine particles of drugs, enhancing their solubility and bioavailability.
What are the key companies in the Spray Drying in Pharmaceutical Market?
Key companies in the spray drying in pharmaceutical market include GEA Group, SPX Flow, and Buchi Labortechnik, among others. These companies are known for their advanced spray drying technologies and equipment tailored for pharmaceutical applications.
What are the drivers of growth in the Spray Drying in Pharmaceutical Market?
The growth of the spray drying in pharmaceutical market is driven by the increasing demand for powdered formulations and the need for efficient drug delivery systems. Additionally, advancements in spray drying technology are enabling the production of high-quality pharmaceutical products.
What challenges does the Spray Drying in Pharmaceutical Market face?
Challenges in the spray drying in pharmaceutical market include the high operational costs associated with the technology and the need for precise control over process parameters. Furthermore, the scalability of spray drying processes can be a concern for large-scale production.
What opportunities exist in the Spray Drying in Pharmaceutical Market?
Opportunities in the spray drying in pharmaceutical market include the development of novel drug formulations and the increasing focus on personalized medicine. The growing trend towards biologics and biosimilars also presents significant potential for spray drying applications.
What trends are shaping the Spray Drying in Pharmaceutical Market?
Current trends in the spray drying in pharmaceutical market include the integration of automation and digital technologies to enhance process efficiency. Additionally, there is a rising interest in sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly solvents and reducing waste during production.
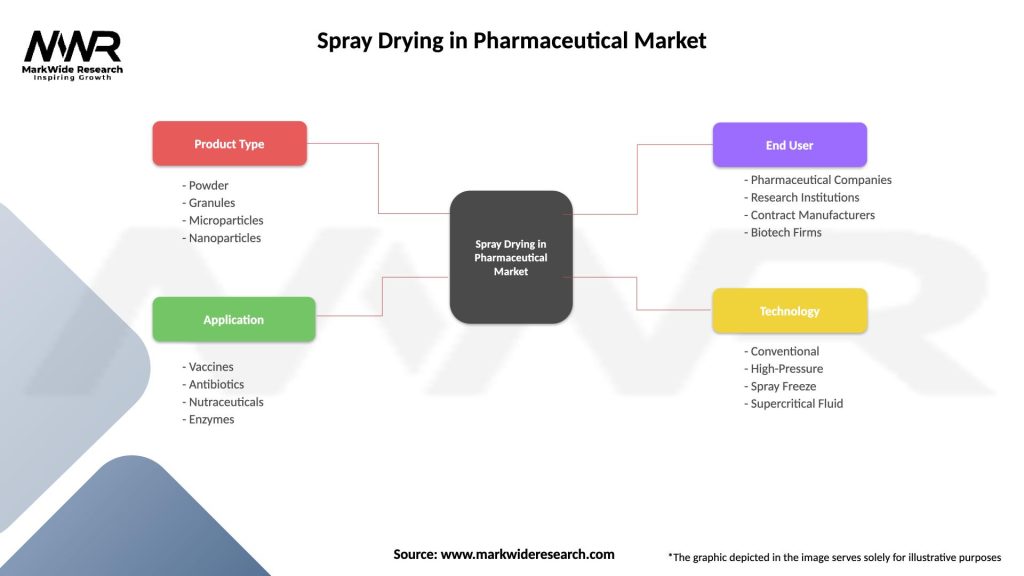
Spray Drying in Pharmaceutical Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Powder, Granules, Microparticles, Nanoparticles |
| Application | Vaccines, Antibiotics, Nutraceuticals, Enzymes |
| End User | Pharmaceutical Companies, Research Institutions, Contract Manufacturers, Biotech Firms |
| Technology | Conventional, High-Pressure, Spray Freeze, Supercritical Fluid |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Spray Drying in Pharmaceutical Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at