444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Spain prenatal monitoring devices market represents a rapidly evolving segment of the healthcare technology industry, driven by increasing awareness of maternal and fetal health, technological advancements, and government initiatives supporting prenatal care. Prenatal monitoring devices encompass a comprehensive range of medical equipment designed to track fetal development, maternal health parameters, and pregnancy progression throughout the gestational period.
Market dynamics in Spain reflect a growing emphasis on preventive healthcare and early detection of pregnancy complications. The market has experienced substantial growth, with adoption rates increasing by approximately 12.5% annually as healthcare providers integrate advanced monitoring technologies into routine prenatal care protocols. Digital transformation in healthcare has accelerated the deployment of sophisticated monitoring systems across Spanish hospitals, clinics, and home care settings.
Healthcare infrastructure improvements and increased healthcare spending have positioned Spain as a significant market for prenatal monitoring technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence, wireless connectivity, and portable monitoring solutions has enhanced the accessibility and effectiveness of prenatal care, contributing to improved maternal and fetal outcomes across the country.
The Spain prenatal monitoring devices market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of medical devices, technologies, and solutions specifically designed to monitor, assess, and track the health and development of both mother and fetus during pregnancy. These sophisticated systems encompass various monitoring modalities including fetal heart rate monitoring, uterine contraction assessment, maternal vital signs tracking, and advanced imaging technologies.
Prenatal monitoring devices serve as critical tools for healthcare professionals to detect potential complications early, ensure optimal pregnancy outcomes, and provide continuous surveillance of maternal and fetal well-being. The market includes both hospital-grade equipment for clinical settings and portable devices designed for home monitoring, enabling comprehensive care throughout the pregnancy journey.
Technology integration has transformed traditional prenatal monitoring into sophisticated, data-driven healthcare solutions that provide real-time insights, predictive analytics, and seamless connectivity between patients and healthcare providers, fundamentally changing how prenatal care is delivered and managed in Spain.
Spain’s prenatal monitoring devices market demonstrates robust growth potential driven by demographic trends, technological innovation, and evolving healthcare delivery models. The market encompasses a diverse portfolio of monitoring solutions ranging from traditional cardiotocography systems to advanced wearable devices and telemedicine platforms.
Key market drivers include rising birth rates among certain demographics, increased maternal age requiring enhanced monitoring, and growing awareness of prenatal health importance. Government healthcare policies supporting maternal health initiatives have contributed to market expansion, with public healthcare system investments driving approximately 35% of total market demand.
Technological advancement remains a primary catalyst for market evolution, with artificial intelligence integration, cloud-based data management, and mobile health applications transforming traditional monitoring approaches. The shift toward personalized medicine and patient-centric care models has accelerated adoption of innovative monitoring solutions across Spanish healthcare facilities.
Market segmentation reveals strong demand across multiple categories, with fetal monitoring devices representing the largest segment, followed by maternal monitoring systems and integrated monitoring platforms. Regional distribution shows concentrated demand in major metropolitan areas while rural healthcare facilities increasingly adopt portable and telemedicine-enabled solutions.
Strategic market analysis reveals several critical insights shaping the Spain prenatal monitoring devices landscape:
Demographic trends significantly influence the Spain prenatal monitoring devices market, with changing population dynamics creating sustained demand for advanced monitoring solutions. Maternal age increases have resulted in higher-risk pregnancies requiring enhanced monitoring protocols, driving adoption of sophisticated prenatal monitoring technologies across healthcare facilities.
Government healthcare initiatives supporting maternal and child health programs have created favorable market conditions for prenatal monitoring device manufacturers. Public healthcare system investments in modern medical equipment and technology infrastructure have facilitated widespread adoption of advanced monitoring solutions, with government funding contributing to approximately 40% of equipment procurement in public hospitals.
Technological innovation continues to drive market expansion as manufacturers develop increasingly sophisticated monitoring capabilities. Integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning algorithms, and predictive analytics has enhanced the clinical value of prenatal monitoring systems, enabling early detection of complications and improved patient outcomes.
Healthcare digitization initiatives across Spain have accelerated demand for connected monitoring devices capable of seamless integration with electronic health records and hospital information systems. The push toward interoperable healthcare technologies has created opportunities for innovative monitoring solutions that enhance care coordination and clinical decision-making.
High implementation costs represent a significant barrier to market expansion, particularly for smaller healthcare facilities with limited capital budgets. Advanced prenatal monitoring systems require substantial initial investments, ongoing maintenance costs, and staff training expenses that can strain healthcare facility resources and delay adoption decisions.
Regulatory complexity associated with medical device approval and compliance creates challenges for market participants. European Union medical device regulations require extensive documentation, clinical validation, and ongoing compliance monitoring, which can extend product development timelines and increase market entry costs for manufacturers.
Technical integration challenges pose obstacles for healthcare facilities seeking to implement new monitoring systems. Legacy infrastructure compatibility, data migration requirements, and workflow integration complexities can complicate deployment processes and require significant technical expertise and resources.
Healthcare professional training requirements represent an ongoing challenge as advanced monitoring technologies demand specialized knowledge and skills. The need for comprehensive training programs and ongoing education can slow adoption rates and increase implementation costs for healthcare organizations.
Telemedicine expansion presents substantial opportunities for prenatal monitoring device manufacturers as healthcare delivery models evolve toward remote care solutions. COVID-19 pandemic impacts have accelerated telemedicine adoption, creating demand for home-based monitoring devices that enable continuous prenatal care while minimizing hospital visits.
Artificial intelligence integration offers significant potential for market growth as healthcare providers seek predictive monitoring capabilities. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of prenatal monitoring data to identify patterns, predict complications, and optimize treatment protocols, creating value-added opportunities for technology providers.
Wearable technology advancement opens new market segments as consumer acceptance of health monitoring devices increases. Pregnancy-specific wearables that monitor fetal heart rate, maternal activity, and other vital parameters represent emerging opportunities for companies developing consumer-oriented prenatal monitoring solutions.
Rural healthcare expansion creates opportunities for portable and mobile monitoring solutions that can extend prenatal care access to underserved areas. Mobile health units equipped with advanced monitoring devices can provide specialized prenatal care in remote regions, addressing healthcare accessibility challenges while expanding market reach.
Supply chain dynamics in the Spain prenatal monitoring devices market reflect a complex ecosystem involving international manufacturers, local distributors, and healthcare end-users. Global supply chain disruptions have highlighted the importance of diversified sourcing strategies and local manufacturing capabilities to ensure consistent product availability and competitive pricing.
Competitive pressures drive continuous innovation as manufacturers strive to differentiate their offerings through advanced features, improved usability, and enhanced clinical outcomes. Market consolidation trends have resulted in strategic partnerships and acquisitions as companies seek to expand their technology portfolios and market presence.
Healthcare policy changes significantly impact market dynamics, with reimbursement policies, quality standards, and safety regulations influencing product development priorities and market access strategies. Value-based healthcare initiatives emphasize clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness, driving demand for monitoring solutions that demonstrate measurable benefits.
Technology convergence has created dynamic market conditions as traditional medical device boundaries blur with consumer electronics, software platforms, and data analytics services. This convergence has attracted new market entrants while challenging established players to adapt their business models and technology strategies.
Comprehensive market research methodology employed for analyzing the Spain prenatal monitoring devices market incorporates multiple data collection and analysis approaches to ensure accuracy and reliability. Primary research activities include structured interviews with healthcare professionals, medical device manufacturers, distributors, and key opinion leaders across the prenatal care ecosystem.
Secondary research encompasses extensive analysis of industry reports, government healthcare statistics, regulatory filings, and academic publications related to prenatal monitoring technologies and maternal healthcare trends. Market data validation involves cross-referencing multiple sources and employing triangulation techniques to verify findings and ensure data integrity.
Quantitative analysis utilizes statistical modeling techniques to project market trends, growth rates, and segmentation patterns based on historical data and current market indicators. Qualitative assessment incorporates expert opinions, industry insights, and stakeholder perspectives to provide context and depth to quantitative findings.
Data collection protocols adhere to strict quality standards and ethical guidelines, ensuring participant confidentiality and data security throughout the research process. Regular methodology reviews and updates ensure research approaches remain current with evolving market conditions and industry best practices.
Madrid region dominates the Spain prenatal monitoring devices market, accounting for approximately 28% of total market share due to its concentration of major hospitals, research institutions, and healthcare technology companies. Healthcare infrastructure in Madrid supports advanced prenatal monitoring capabilities with significant investments in medical technology and specialized maternal care facilities.
Catalonia region represents the second-largest market segment, with Barcelona serving as a major hub for medical device distribution and healthcare innovation. Regional healthcare policies supporting maternal health initiatives have driven adoption of advanced monitoring technologies across public and private healthcare facilities.
Andalusia region demonstrates strong growth potential with expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing birth rates in major metropolitan areas. Government investments in rural healthcare access have created opportunities for portable and mobile prenatal monitoring solutions to serve underserved communities.
Valencia and Basque regions show steady market development with growing demand for integrated monitoring systems that support both hospital-based and home care applications. Regional healthcare networks are increasingly adopting telemedicine-enabled monitoring solutions to improve care coordination and patient access.
Market leadership in the Spain prenatal monitoring devices sector is characterized by a mix of international medical device manufacturers and specialized technology companies. Competitive dynamics reflect ongoing innovation, strategic partnerships, and market expansion efforts across multiple product categories and customer segments.
By Product Type:
By Technology:
By End User:
Fetal monitoring devices represent the largest market category, driven by clinical requirements for continuous fetal surveillance during labor and high-risk pregnancies. Cardiotocography systems maintain strong demand despite emerging wireless alternatives, with hospitals prioritizing proven reliability and clinical validation over newer technologies.
Maternal monitoring systems show increasing adoption as healthcare providers recognize the importance of comprehensive maternal health assessment throughout pregnancy. Integrated monitoring platforms that combine maternal and fetal monitoring capabilities are gaining preference due to workflow efficiency and cost optimization benefits.
Portable monitoring devices experience rapid growth as patient preferences shift toward home-based care options and healthcare providers seek to reduce hospital readmissions. Wearable prenatal monitors represent an emerging category with significant potential, though clinical validation and regulatory approval remain key challenges.
Ultrasound systems maintain steady demand for routine prenatal screening and diagnostic applications, with advanced imaging capabilities and 3D/4D technologies driving premium segment growth. Point-of-care ultrasound devices are increasingly adopted in primary care settings to improve prenatal care access and early detection capabilities.
Healthcare providers benefit from enhanced clinical decision-making capabilities through advanced monitoring technologies that provide real-time data, predictive analytics, and comprehensive patient assessment tools. Improved patient outcomes result from early detection of complications, continuous monitoring capabilities, and evidence-based care protocols supported by sophisticated monitoring systems.
Patients and families experience improved care quality through continuous monitoring, reduced hospital visits, and enhanced communication with healthcare providers. Home monitoring options provide convenience and comfort while maintaining clinical oversight, particularly beneficial for high-risk pregnancies requiring frequent assessment.
Medical device manufacturers gain access to growing market opportunities driven by demographic trends, technology advancement, and healthcare digitization initiatives. Innovation partnerships with healthcare providers enable product development aligned with clinical needs and market requirements.
Healthcare systems achieve operational efficiency improvements through streamlined workflows, reduced manual monitoring requirements, and enhanced data management capabilities. Cost optimization results from improved resource utilization, reduced complications, and enhanced care coordination across prenatal care networks.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Artificial intelligence integration represents a transformative trend in prenatal monitoring, with machine learning algorithms enabling predictive analysis of fetal distress, preterm labor risk, and other pregnancy complications. AI-powered monitoring systems demonstrate improved accuracy in detecting subtle changes in fetal heart rate patterns and maternal health indicators.
Wireless connectivity has become standard in modern prenatal monitoring devices, enabling patient mobility, reduced infection risk, and seamless data transmission to electronic health records. Bluetooth and Wi-Fi capabilities facilitate real-time monitoring while allowing patients greater comfort and freedom of movement during labor and delivery.
Home monitoring expansion reflects changing patient preferences and healthcare delivery models, with portable devices enabling continuous prenatal surveillance outside hospital settings. Remote monitoring platforms allow healthcare providers to track high-risk pregnancies while reducing hospital visits and healthcare costs.
Data analytics advancement enables comprehensive analysis of prenatal monitoring data to identify trends, predict outcomes, and optimize care protocols. Big data applications support population health management and evidence-based practice development in prenatal care delivery.
Regulatory harmonization efforts across European Union markets have streamlined medical device approval processes while maintaining safety and efficacy standards. MDR compliance requirements have driven innovation in device design, clinical validation, and post-market surveillance capabilities.
Strategic partnerships between medical device manufacturers and healthcare technology companies have accelerated development of integrated monitoring solutions. Collaboration initiatives focus on combining hardware expertise with software innovation to create comprehensive prenatal care platforms.
Clinical research advancement has validated the effectiveness of advanced monitoring technologies in improving pregnancy outcomes and reducing complications. Evidence-based studies support adoption of innovative monitoring approaches and guide clinical practice guidelines development.
Investment activity in prenatal monitoring technology startups has increased, with venture capital funding supporting development of next-generation monitoring solutions. Innovation accelerators and healthcare technology incubators are fostering development of disruptive prenatal monitoring technologies.
MarkWide Research analysis indicates that market participants should prioritize development of integrated monitoring platforms that combine multiple monitoring modalities with advanced analytics capabilities. Healthcare providers increasingly prefer comprehensive solutions that streamline workflows and provide holistic patient assessment tools.
Investment focus should emphasize wireless connectivity, artificial intelligence integration, and telemedicine compatibility to align with evolving healthcare delivery models. Product development strategies must consider both clinical effectiveness and user experience to ensure successful market adoption.
Market entry strategies should leverage partnerships with established healthcare distributors and clinical validation through pilot programs with leading Spanish hospitals. Regulatory compliance planning must account for evolving European medical device regulations and post-market surveillance requirements.
Geographic expansion opportunities exist in underserved rural markets through portable and mobile monitoring solutions that address healthcare access challenges. Value proposition development should emphasize clinical outcomes, cost-effectiveness, and operational efficiency benefits for healthcare providers.
Market growth trajectory for Spain’s prenatal monitoring devices sector remains positive, driven by demographic trends, technology advancement, and healthcare digitization initiatives. MarkWide Research projects continued expansion with growth rates expected to reach 8.2% annually over the next five years, supported by increasing adoption of advanced monitoring technologies.
Technology evolution will continue transforming prenatal monitoring capabilities, with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics becoming standard features in next-generation monitoring systems. Integration trends will drive development of comprehensive platforms that combine monitoring, diagnostics, and care management capabilities.
Healthcare delivery transformation toward value-based care models will emphasize monitoring solutions that demonstrate measurable improvements in patient outcomes and cost-effectiveness. Telemedicine integration will become increasingly important as healthcare providers expand remote care capabilities and patient access options.
Market consolidation may occur as larger medical device companies acquire innovative technology startups to enhance their prenatal monitoring portfolios. Competitive dynamics will favor companies that successfully combine clinical effectiveness, technological innovation, and cost optimization in their monitoring solutions.
Spain’s prenatal monitoring devices market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation, driven by favorable demographic trends, advancing technology capabilities, and evolving healthcare delivery models. Market dynamics reflect strong demand for sophisticated monitoring solutions that enhance clinical outcomes while improving patient experience and operational efficiency.
Technology advancement continues to reshape the prenatal monitoring landscape, with artificial intelligence, wireless connectivity, and telemedicine integration creating new possibilities for comprehensive prenatal care delivery. Healthcare providers increasingly recognize the value of advanced monitoring systems in improving pregnancy outcomes and reducing complications.
Strategic success in this market requires understanding of clinical needs, regulatory requirements, and technology trends that influence adoption decisions. Market participants must balance innovation with proven clinical effectiveness while addressing cost considerations and integration challenges faced by healthcare providers.
Future market development will be characterized by continued technology convergence, expanded home monitoring capabilities, and enhanced data analytics applications that support evidence-based prenatal care practices. The Spain prenatal monitoring devices market is positioned for sustained growth as healthcare stakeholders prioritize maternal and fetal health outcomes through advanced monitoring technologies.
What is Prenatal Monitoring Devices?
Prenatal monitoring devices are medical tools used to track the health and development of a fetus during pregnancy. These devices include ultrasound machines, fetal monitors, and wearable technology that provide real-time data on fetal heart rate and maternal health.
What are the key players in the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market?
Key players in the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market include Philips Healthcare, GE Healthcare, and Siemens Healthineers, among others. These companies are known for their innovative technologies and comprehensive product offerings in prenatal care.
What are the growth factors driving the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market?
The growth of the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market is driven by increasing awareness of maternal and fetal health, advancements in medical technology, and a rise in the number of pregnancies. Additionally, government initiatives promoting prenatal care contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market face?
The Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market faces challenges such as high costs of advanced monitoring devices and regulatory hurdles in medical device approval. Additionally, the need for skilled professionals to operate these devices can limit their accessibility.
What opportunities exist in the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market?
Opportunities in the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market include the development of telemedicine solutions for remote monitoring and the integration of artificial intelligence in prenatal care. These innovations can enhance patient outcomes and expand access to prenatal services.
What trends are shaping the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market?
Trends shaping the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market include the increasing adoption of wearable monitoring devices and the use of mobile health applications. These trends reflect a shift towards more personalized and accessible prenatal care solutions.
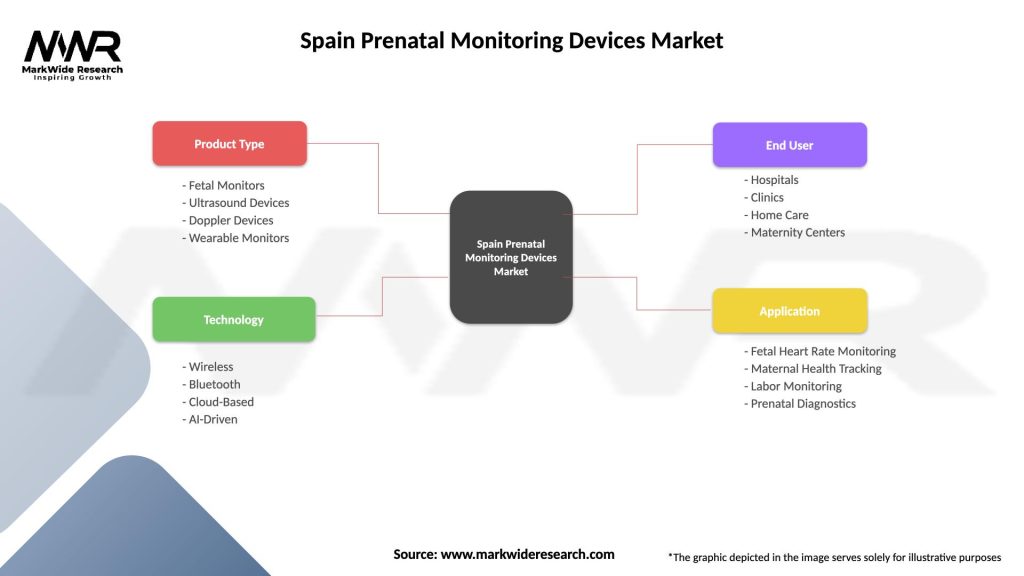
Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Fetal Monitors, Ultrasound Devices, Doppler Devices, Wearable Monitors |
| Technology | Wireless, Bluetooth, Cloud-Based, AI-Driven |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Home Care, Maternity Centers |
| Application | Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring, Maternal Health Tracking, Labor Monitoring, Prenatal Diagnostics |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Spain Prenatal Monitoring Devices Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at