444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The space wheel market represents an innovative approach to long-duration human spaceflight and space habitat construction. Space wheels, also known as space stations or habitats, are rotating structures designed to simulate gravity through centripetal force, providing a more comfortable and sustainable living environment for astronauts during extended missions.
Meaning
Space wheels are large rotating structures that utilize centrifugal force to simulate gravity, creating a more familiar and habitable environment for astronauts living and working in space. These structures enable long-duration space missions, space tourism, and future space colonization efforts by addressing the physiological and psychological challenges associated with microgravity environments.
Executive Summary
The space wheel market is characterized by growing interest in space exploration, advancements in space habitat technology, and increasing investments from government agencies and private companies. Space wheels offer unique opportunities for scientific research, commercial activities, and human spaceflight missions, driving innovation and collaboration within the space industry.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The space wheel market operates within a dynamic ecosystem shaped by technological innovation, market trends, regulatory developments, and geopolitical factors. Collaboration, partnerships, and strategic alliances among government agencies, commercial entities, and international partners play a crucial role in driving innovation and accelerating the pace of space habitat development.
Regional Analysis
The space wheel market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as government space policies, industrial capabilities, market demand, and international partnerships. Key regions such as North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East are significant contributors to the global space industry, with established space agencies, aerospace companies, and commercial space ventures.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Space Wheel Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The space wheel market can be segmented based on factors such as habitat type, mission duration, destination, and end-user. Segmentation enables market players to target specific market segments, customize their offerings, and address the unique requirements of different customer groups within the space industry.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a limited impact on the space wheel market, with disruptions in supply chains, delays in project timelines, and changes in workforce operations. However, the pandemic has also highlighted the importance of space exploration, scientific research, and international collaboration in addressing global challenges and advancing human knowledge and technology.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The space wheel market is poised for significant growth and innovation, driven by increasing demand for long-duration space missions, commercial space activities, and space tourism experiences. Technological advancements, market trends, and regulatory reforms will shape the future trajectory of the market, creating new opportunities and challenges for industry participants and stakeholders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the space wheel market represents a dynamic and evolving segment of the space industry, offering unique opportunities for scientific research, commercial activities, and human spaceflight missions. Despite technical challenges, cost constraints, and regulatory hurdles, space wheel developers and operators are poised to capitalize on emerging market trends and opportunities, driving innovation, collaboration, and sustainable growth within the space industry. By investing in technology development, diversifying revenue streams, and fostering collaboration, space wheel stakeholders can unlock the full potential of space exploration and human habitation beyond Earth orbit.
What is Space Wheel?
Space Wheel refers to a type of technology or device designed for use in space exploration and transportation, often involving innovative designs for propulsion or structural support in a zero-gravity environment.
What are the key players in the Space Wheel Market?
Key players in the Space Wheel Market include companies like SpaceX, Boeing, and Lockheed Martin, which are involved in developing advanced aerospace technologies and systems, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Space Wheel Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Space Wheel Market include increasing investments in space exploration, advancements in aerospace technology, and the rising demand for satellite deployment and space tourism.
What challenges does the Space Wheel Market face?
The Space Wheel Market faces challenges such as high development costs, regulatory hurdles, and the technical complexities associated with operating in space environments.
What opportunities exist in the Space Wheel Market?
Opportunities in the Space Wheel Market include the potential for commercial space travel, partnerships with government space agencies, and innovations in reusable spacecraft technology.
What trends are shaping the Space Wheel Market?
Trends shaping the Space Wheel Market include the increasing focus on sustainability in space missions, the development of hybrid propulsion systems, and the growing interest in public-private partnerships for space exploration.
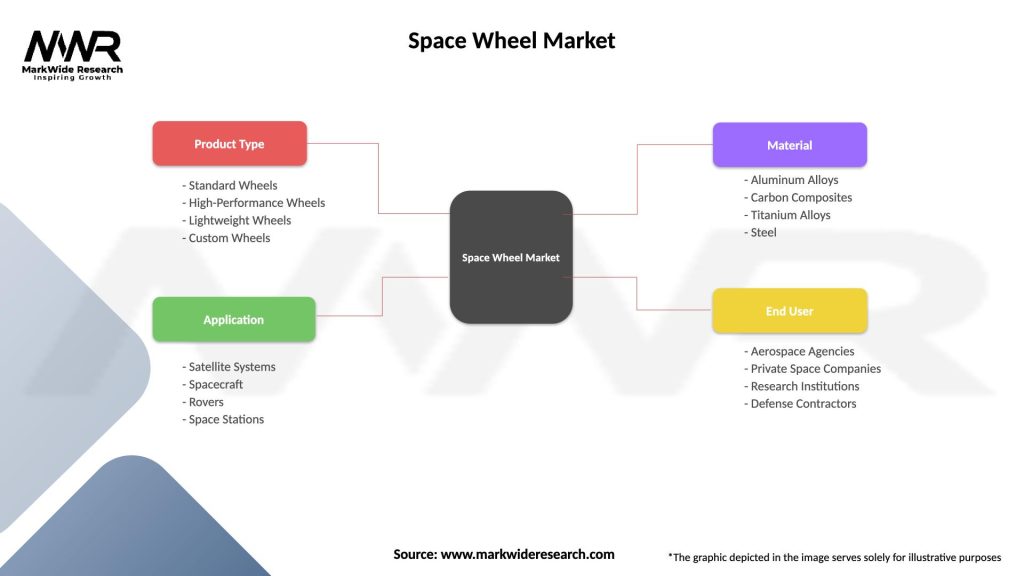
Space Wheel Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Standard Wheels, High-Performance Wheels, Lightweight Wheels, Custom Wheels |
| Application | Satellite Systems, Spacecraft, Rovers, Space Stations |
| Material | Aluminum Alloys, Carbon Composites, Titanium Alloys, Steel |
| End User | Aerospace Agencies, Private Space Companies, Research Institutions, Defense Contractors |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Space Wheel Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at