444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview:
The space food market represents a niche segment within the broader food industry, catering specifically to the unique needs and challenges of astronauts and space travelers. This market has evolved significantly since the early days of space exploration, with advancements in food science, packaging technology, and nutrition research driving innovation and expansion.
Meaning:
Space food refers to specially formulated and packaged food products designed for consumption by astronauts during space missions. These foods undergo rigorous testing and development to ensure they meet the nutritional requirements, safety standards, and operational constraints of space travel. Space food must be lightweight, compact, shelf-stable, and easy to prepare and consume in microgravity conditions.
Executive Summary:
The space food market continues to grow steadily, fueled by increasing investments in space exploration, commercial space travel, and long-duration missions to the International Space Station (ISS) and beyond. Key players in the space industry, as well as food manufacturers and research institutions, are collaborating to develop innovative solutions for sustaining human life in space and enabling long-term space habitation.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics:
The space food market operates within a dynamic ecosystem shaped by technological innovation, market demand, regulatory developments, and geopolitical factors. Key trends driving market dynamics include:
Regional Analysis:
The space food market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as technological capabilities, government priorities, and commercial interests in space exploration. Key regions driving market growth and innovation include:
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in the Space Food Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
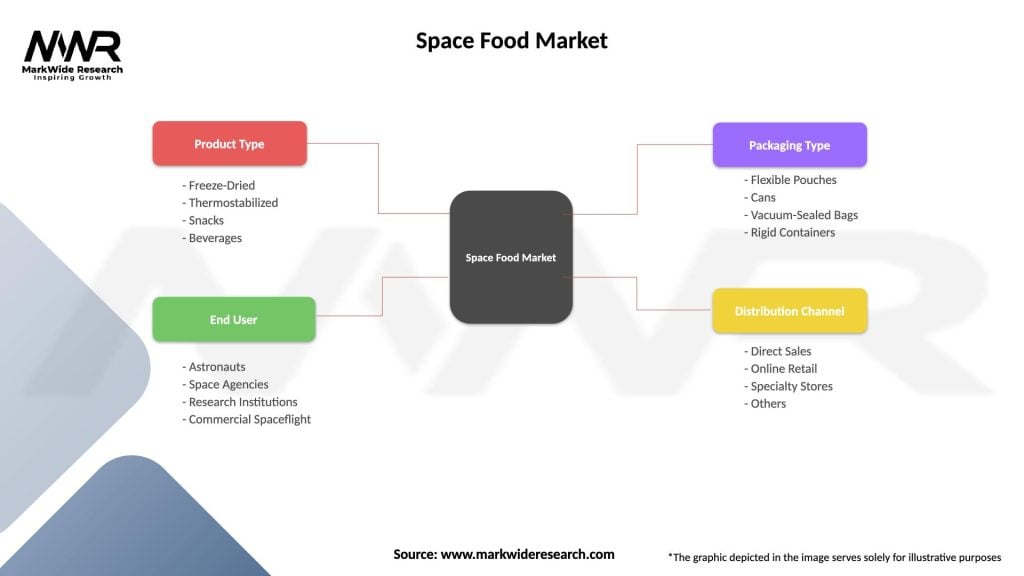
Segmentation:
The space food market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
A SWOT analysis provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the space food market:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact:
The Covid-19 pandemic has limited direct impact on the space food market, as space missions and space tourism activities have continued with appropriate safety protocols and precautions in place. However, pandemic-related disruptions to supply chains, manufacturing operations, and global economies may affect market dynamics, investment trends, and consumer behavior in the medium to long term.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook:
The future outlook for the space food market is promising, driven by increasing investments in space exploration, technological innovation, and commercialization of space activities. Continued collaboration, research, and public-private partnerships will advance space food science, expand market opportunities, and enable sustainable food systems for long-duration human space missions and future space settlements.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the space food market represents a unique and evolving segment of the food industry, catering to the nutritional needs, culinary preferences, and operational constraints of astronauts and space travelers. Advances in food technology, sustainable agriculture, and culinary innovation are shaping the future of space food, driving market growth, and expanding opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders in the global space economy.
What is Space Food?
Space food refers to the specialized food products designed for consumption in space environments, ensuring nutritional value and safety for astronauts during missions. It includes a variety of items such as freeze-dried meals, snacks, and beverages that can withstand the unique conditions of space travel.
What are the key players in the Space Food Market?
Key players in the Space Food Market include companies like NASA, SpaceX, and Blue Origin, which develop and supply food for space missions. Other notable companies involved in this sector are Orbital Foods and Astrobotic, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Space Food Market?
The Space Food Market is driven by the increasing number of space missions, advancements in food technology, and the growing interest in long-duration space travel. Additionally, the rise of private space exploration companies is contributing to the demand for innovative food solutions.
What challenges does the Space Food Market face?
Challenges in the Space Food Market include the need for food to have a long shelf life, the complexity of packaging for microgravity, and ensuring that meals meet the nutritional needs of astronauts. Additionally, the high cost of research and development can be a barrier.
What opportunities exist in the Space Food Market?
Opportunities in the Space Food Market include the potential for developing new food technologies that enhance taste and nutrition, as well as the possibility of catering to future space tourism. There is also a growing interest in sustainable food production methods for space missions.
What trends are emerging in the Space Food Market?
Emerging trends in the Space Food Market include the use of plant-based ingredients, advancements in food preservation techniques, and the incorporation of 3D printing technology for meal preparation. These innovations aim to improve the overall dining experience for astronauts.
Space Food Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Freeze-Dried, Thermostabilized, Snacks, Beverages |
| End User | Astronauts, Space Agencies, Research Institutions, Commercial Spaceflight |
| Packaging Type | Flexible Pouches, Cans, Vacuum-Sealed Bags, Rigid Containers |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Online Retail, Specialty Stores, Others |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Space Food Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at