444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The South Korea Smart Grid Network Market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and the need for efficient and sustainable energy management systems. A smart grid network refers to an intelligent and interconnected system that integrates various technologies, such as sensors, communication networks, and advanced analytics, to optimize the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity.
Meaning
A smart grid network is a modernized electrical grid that utilizes digital technology to monitor and manage electricity flows efficiently. It enables real-time communication between power generation sources, transmission and distribution infrastructure, and consumers. The main goal of a smart grid network is to enhance the reliability, efficiency, and sustainability of the power system while empowering consumers to make informed decisions about their energy consumption.
Executive Summary
The South Korea Smart Grid Network Market is experiencing substantial growth due to the increasing demand for energy management solutions and the government’s initiatives to promote smart grid deployment. The market is witnessing the integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics, to optimize power generation, distribution, and consumption. Key players in the market are focusing on research and development activities to introduce innovative products and solutions.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
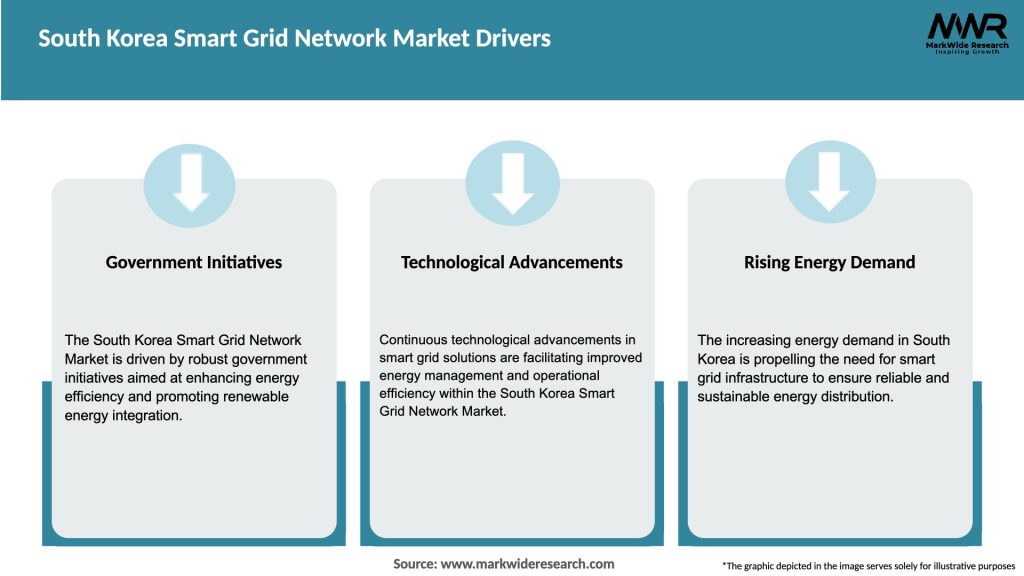
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities

Market Dynamics
The South Korea Smart Grid Network Market is characterized by intense competition and ongoing technological advancements. Market players are focusing on collaborations, partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product offerings. The market is witnessing a shift towards integrated solutions that combine various smart grid technologies to provide comprehensive energy management solutions.
Regional Analysis
The smart grid network market in South Korea is witnessing significant growth across various regions. The capital city, Seoul, is a key hub for smart grid deployments due to its dense population and high energy demand. Other major regions, including Busan, Incheon, and Gyeonggi Province, are also witnessing substantial investments in smart grid infrastructure. The government’s regional development plans and initiatives play a crucial role in driving smart grid adoption across different regions.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The South Korea Smart Grid Network Market can be segmented based on technology, component, and end-use industry. The technology segment includes advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), distribution automation, demand response, and grid optimization. The component segment comprises hardware, software, and services. The end-use industry segment encompasses residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had both short-term and long-term impacts on the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market. In the short term, the pandemic disrupted supply chains and slowed down the deployment of smart grid projects due to restrictions on movement and construction activities. However, the pandemic also highlighted the importance of resilient and efficient power systems, driving the need for smart grid networks that can support remote monitoring, automation, and demand response.
The long-term impact of the pandemic includes a greater emphasis on energy resilience, digitalization, and sustainability. The South Korean government’s focus on green recovery and sustainable development is expected to drive investments in smart grid infrastructure. The pandemic has also accelerated the adoption of remote working and online services, increasing the demand for reliable and efficient energy management systems.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market looks promising, with sustained growth expected in the coming years. The market is anticipated to witness significant investments in grid modernization, renewable energy integration, and energy storage systems. The increasing focus on sustainability, energy efficiency, and digitalization will drive the demand for smart grid technologies and solutions.
The adoption of emerging technologies, such as AI, IoT, and blockchain, will further enhance the capabilities of smart grid networks. The development of smart cities and the electrification of transportation will create additional opportunities for the integration of smart grid networks with various urban infrastructure components.
However, challenges related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and interoperability standards need to be addressed for seamless integration and widespread adoption of smart grid networks. Market players should continue to invest in research and development activities, collaborate with key stakeholders, and align their strategies with the government’s energy policies to capitalize on the evolving market opportunities.
Conclusion
The South Korea Smart Grid Network Market is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for efficient energy management, government initiatives, and technological advancements. Smart grid networks enable better monitoring, control, and optimization of the power grid, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources and empowering consumers to make informed decisions about their energy consumption.
While the market offers several opportunities, it also faces challenges such as high initial investment costs, data privacy concerns, and the lack of interoperability standards. However, with strategic collaborations, investments in research and development, and a focus on cybersecurity, market participants can overcome these challenges and drive the future growth of the smart grid network market in South Korea.
What is Smart Grid Network?
A Smart Grid Network refers to an advanced electrical grid that utilizes digital technology to monitor and manage the transport of electricity from all generation sources to meet the varying electricity demands of end users. It incorporates smart meters, renewable energy sources, and automated systems to enhance efficiency and reliability.
What are the key players in the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market?
Key players in the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market include Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO), LG Electronics, and Samsung SDI, among others. These companies are involved in various aspects of smart grid technology, including energy management systems and smart meter production.
What are the main drivers of the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market?
The main drivers of the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market include the increasing demand for energy efficiency, the integration of renewable energy sources, and government initiatives aimed at modernizing the energy infrastructure. These factors contribute to the growth of smart grid technologies.
What challenges does the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market face?
Challenges in the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market include high initial investment costs, cybersecurity concerns, and the need for regulatory frameworks to support new technologies. These factors can hinder the widespread adoption of smart grid solutions.
What opportunities exist in the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market?
Opportunities in the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market include advancements in energy storage technologies, the potential for electric vehicle integration, and the growing emphasis on sustainable energy practices. These trends can drive innovation and investment in smart grid solutions.
What trends are shaping the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market?
Trends shaping the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market include the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) applications in energy management, increased use of artificial intelligence for grid optimization, and the expansion of decentralized energy resources. These innovations are transforming how energy is produced and consumed.
South Korea Smart Grid Network Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Smart Meters, Advanced Sensors, Communication Networks, Energy Management Systems |
| End User | Utilities, Industrial Facilities, Commercial Buildings, Residential Users |
| Application | Demand Response, Grid Management, Renewable Integration, Energy Storage |
| Deployment | On-Premises, Cloud-Based, Hybrid, Edge Computing |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the South Korea Smart Grid Network Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at