444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The South Korea residential real estate market represents one of Asia’s most dynamic and rapidly evolving property sectors, characterized by significant urbanization trends and technological innovation. Market dynamics in South Korea reflect a complex interplay of demographic shifts, government policies, and economic factors that continue to shape housing demand and supply patterns across major metropolitan areas.
Seoul metropolitan area dominates the residential landscape, accounting for approximately 48% of total housing transactions nationwide. The market demonstrates remarkable resilience despite periodic regulatory interventions, with apartment complexes representing the preferred housing format for urban residents. Digital transformation has revolutionized property transactions, with online platforms facilitating 72% of initial property searches among potential buyers.
Government initiatives continue to influence market trajectories through various housing supply programs and regulatory frameworks designed to address affordability concerns. The market exhibits strong regional variations, with Busan, Daegu, and Incheon emerging as significant secondary markets offering diverse investment opportunities for both domestic and international stakeholders.
The South Korea residential real estate market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of residential property transactions, development, and investment activities encompassing apartments, houses, and other dwelling units across the Korean peninsula. This market encompasses both primary and secondary property sales, rental transactions, and new construction developments that serve the housing needs of South Korea’s population.
Residential real estate in South Korea includes various property types ranging from high-rise apartment complexes and traditional houses to modern townhouses and luxury condominiums. The market operates through established channels including real estate agencies, online platforms, and direct transactions between parties, supported by comprehensive legal frameworks and financing mechanisms.
Market participants include individual homeowners, property investors, construction companies, real estate developers, financial institutions, and government agencies that collectively contribute to the sector’s growth and stability through their diverse roles and interactions.
South Korea’s residential real estate sector continues to demonstrate robust performance despite various economic and regulatory challenges, with apartment sales maintaining their position as the dominant transaction category. The market benefits from strong demographic fundamentals, including urbanization trends and household formation patterns that support sustained housing demand.
Technology adoption has accelerated significantly, with PropTech solutions gaining 65% adoption rates among real estate professionals and property management companies. Smart home features and energy-efficient building systems increasingly influence buyer preferences, particularly among younger demographics seeking modern living solutions.
Regional diversification presents notable opportunities as secondary cities experience renewed interest from both residents and investors seeking alternatives to Seoul’s premium pricing. Government housing policies continue to shape market dynamics through supply-side interventions and demand management measures designed to promote market stability.
Market insights reveal several critical trends shaping South Korea’s residential real estate landscape:
Primary market drivers propelling South Korea’s residential real estate sector include sustained urbanization trends and evolving lifestyle preferences among Korean households. Economic stability and favorable employment conditions in major metropolitan areas continue to support housing demand, particularly in technology and service sectors that attract young professionals.
Government infrastructure investments significantly impact residential market dynamics through improved transportation networks, educational facilities, and commercial developments that enhance neighborhood attractiveness. Low interest rate environments have historically supported property financing accessibility, enabling broader homeownership participation across various income segments.
Demographic transitions including household size reduction and lifestyle changes drive demand for smaller, more efficient living spaces equipped with modern amenities. Foreign investment interest in Korean real estate, particularly from neighboring Asian countries, provides additional market momentum and capital inflows that support development activities.
Technology integration serves as a crucial driver, with smart building systems and digital property management solutions becoming standard expectations rather than premium features, influencing both new construction and renovation markets.
Regulatory constraints represent significant challenges for South Korea’s residential real estate market, with government cooling measures periodically implemented to address affordability concerns and market speculation. Loan-to-value ratio restrictions and debt-to-income requirements limit financing accessibility for certain buyer segments, particularly first-time homeowners.
Supply limitations in prime urban locations create persistent challenges, with land scarcity and zoning restrictions constraining new development opportunities in Seoul and other major cities. Construction cost inflation affects project viability and ultimately impacts housing affordability for end consumers.
Economic uncertainties including global market volatility and trade tensions can influence investor confidence and property transaction volumes. Demographic challenges such as declining birth rates and population aging may impact long-term housing demand patterns in certain regions.
Environmental regulations and building code requirements increase development complexity and costs, while tax policy changes can significantly affect investment returns and market participation rates among various stakeholder groups.
Emerging opportunities in South Korea’s residential real estate market center around sustainable development and smart city initiatives that align with government environmental goals and technological advancement priorities. Green building certifications and energy-efficient housing solutions present significant growth potential as environmental consciousness increases among consumers.
Secondary city development offers substantial opportunities as government policies promote balanced regional growth and infrastructure improvements enhance connectivity between major urban centers. Busan, Daegu, and Gwangju demonstrate particular promise for residential development and investment activities.
PropTech innovation creates opportunities for technology companies and real estate firms to develop integrated solutions addressing property management, transaction facilitation, and resident services. Co-living concepts and flexible housing solutions cater to changing lifestyle preferences among younger demographics and urban professionals.
International investment opportunities continue expanding as South Korea’s real estate market gains recognition for stability and growth potential. Real estate crowdfunding and fractional ownership models democratize property investment access and create new market segments for innovative financial products.
Market dynamics in South Korea’s residential real estate sector reflect complex interactions between supply and demand factors, regulatory frameworks, and economic conditions. Cyclical patterns emerge from government policy adjustments, with cooling measures typically followed by periods of market stabilization and gradual recovery.
Price volatility varies significantly across regions, with Seoul metropolitan area experiencing more pronounced fluctuations compared to secondary markets. Transaction volumes demonstrate seasonal patterns influenced by traditional moving periods and tax calendar considerations that affect buyer and seller timing decisions.
Supply-demand imbalances persist in premium locations, driving continued interest in urban redevelopment projects and high-density residential developments. Market liquidity remains robust despite periodic regulatory interventions, supported by strong domestic demand and established financing mechanisms.
Innovation adoption rates accelerate across the sector, with digital platforms achieving 78% market penetration among real estate professionals. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that technology integration continues reshaping traditional real estate practices and customer expectations throughout the transaction process.
Research methodology for analyzing South Korea’s residential real estate market employs comprehensive data collection approaches combining quantitative analysis and qualitative insights from industry stakeholders. Primary research includes structured interviews with real estate developers, property agents, financial institutions, and government officials involved in housing policy formulation.
Secondary data sources encompass government housing statistics, real estate transaction databases, construction permits, and demographic surveys that provide foundational market intelligence. Market surveys conducted among property buyers, sellers, and renters offer valuable insights into consumer preferences, decision-making factors, and satisfaction levels.
Analytical frameworks incorporate statistical modeling techniques, trend analysis, and comparative studies across different regions and property segments. Data validation processes ensure accuracy and reliability through cross-referencing multiple sources and expert verification of key findings and market projections.
Forecasting models utilize historical data patterns, economic indicators, and policy impact assessments to project future market trends and identify potential growth opportunities and challenges facing the residential real estate sector.
Regional analysis reveals distinct characteristics across South Korea’s residential real estate markets, with Seoul metropolitan area maintaining its position as the dominant market representing approximately 52% of total residential transactions. Gangnam, Seocho, and Songpa districts continue attracting premium buyers seeking luxury residential options and investment opportunities.
Busan metropolitan area emerges as the second-largest residential market, benefiting from port city advantages and government initiatives promoting regional development. Coastal residential projects and urban regeneration programs drive market activity, with transaction volumes growing at 6.2% annually over recent periods.
Incheon region demonstrates strong growth potential due to proximity to Seoul and Incheon International Airport, attracting both domestic and international residents. New town developments and transportation infrastructure improvements support residential market expansion and property value appreciation.
Daegu and Gwangju represent emerging opportunities with affordable housing options and quality of life improvements attracting residents from more expensive metropolitan areas. Regional market share for these cities has increased by 8.5% as buyers seek alternatives to Seoul’s premium pricing environment.
Competitive landscape in South Korea’s residential real estate market features diverse participants ranging from large construction conglomerates to specialized property developers and real estate service providers. Major players maintain significant market presence through integrated business models encompassing development, construction, and property management services.
Market competition intensifies through technological innovation, customer service excellence, and sustainable development practices that differentiate companies in an increasingly sophisticated marketplace.
Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct categories within South Korea’s residential real estate sector based on property types, price ranges, and target demographics. Primary segmentation divides the market into apartments, houses, and alternative housing formats that serve different consumer needs and preferences.
By Property Type:
By Price Range:
Category-wise insights demonstrate that apartment complexes dominate South Korea’s residential market, accounting for approximately 75% of urban housing transactions. Modern apartment buildings incorporate advanced security systems, community facilities, and smart home technologies that appeal to contemporary lifestyle preferences.
Luxury residential segment shows resilience despite economic uncertainties, with high-net-worth individuals continuing to invest in premium properties as wealth preservation strategies. Penthouse units and exclusive residential towers maintain strong demand in prime Seoul locations, supported by limited supply and prestigious positioning.
Affordable housing category benefits from government support programs including public rental housing and shared equity schemes designed to improve homeownership accessibility. First-time buyer programs demonstrate 23% participation growth as young professionals seek entry into property ownership markets.
Smart home integration becomes increasingly important across all categories, with IoT-enabled apartments commanding premium pricing and faster sales cycles. Energy-efficient features and sustainable building materials influence buyer decisions across price segments, reflecting growing environmental consciousness among Korean consumers.
Industry participants in South Korea’s residential real estate market enjoy numerous advantages from the sector’s growth and modernization trends. Property developers benefit from strong domestic demand, government infrastructure investments, and technological advancement opportunities that enhance project viability and profitability.
Real estate agents gain from digital platform integration that expands their market reach and improves transaction efficiency. PropTech adoption enables agents to serve more clients effectively while providing enhanced services including virtual property tours, digital documentation, and automated market analysis tools.
Financial institutions participate in market growth through mortgage lending, real estate investment products, and property-backed securities that diversify their portfolios. Construction companies benefit from steady project pipelines and opportunities to incorporate innovative building technologies and sustainable construction practices.
Investors access diverse opportunities ranging from direct property ownership to REITs and crowdfunding platforms that democratize real estate investment participation. Government stakeholders achieve policy objectives through market mechanisms that promote balanced regional development and housing affordability improvements.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Key trends shaping South Korea’s residential real estate market include accelerating digital transformation and sustainable development practices that redefine industry standards and consumer expectations. Virtual reality property tours and AI-powered market analysis tools become standard offerings among progressive real estate companies.
Co-living spaces and flexible housing solutions gain popularity among younger demographics seeking affordable urban living options with community amenities. Micro-apartments and studio units address changing household compositions and lifestyle preferences in dense urban environments.
Smart building integration extends beyond basic automation to include predictive maintenance systems, energy optimization platforms, and resident service applications that enhance living experiences. Blockchain technology emerges in property transactions, offering improved security and transparency in documentation processes.
Suburban renaissance occurs as remote work trends and quality of life considerations drive interest in residential areas outside major city centers. Mixed-use developments combining residential, commercial, and recreational facilities become preferred formats for new community planning initiatives.
Recent industry developments highlight significant changes in South Korea’s residential real estate landscape, with government policy adjustments and technological innovations driving market evolution. New town development projects in satellite cities demonstrate government commitment to balanced regional growth and housing supply expansion.
PropTech companies secure substantial funding for platform development and market expansion, with Zigbang and Dabang leading digital transformation initiatives. Artificial intelligence integration in property valuation and market analysis improves accuracy and efficiency for both professionals and consumers.
Sustainable construction standards become mandatory for new residential developments, promoting green building certifications and energy-efficient design principles. Modular construction techniques gain adoption as developers seek cost-effective and time-efficient building methods for large-scale projects.
International partnerships between Korean developers and foreign companies facilitate knowledge transfer and capital investment in residential projects. Real estate crowdfunding platforms launch successfully, democratizing property investment access and creating new funding sources for development projects.
Industry analysts recommend that residential real estate stakeholders focus on technology adoption and sustainable development practices to maintain competitive advantages in evolving market conditions. Diversification strategies across regions and property types can help mitigate risks associated with market concentration and regulatory changes.
Developers should prioritize smart building features and energy-efficient systems that align with consumer preferences and government environmental objectives. Flexible design concepts that accommodate changing lifestyle needs and demographic trends will likely command premium pricing and faster sales cycles.
Real estate professionals must embrace digital platforms and data analytics tools to enhance service delivery and maintain relevance in increasingly competitive markets. Customer experience optimization through technology integration and personalized services becomes crucial for business success.
Investors should consider secondary market opportunities and emerging residential formats that offer attractive returns while supporting portfolio diversification objectives. MWR analysis suggests that sustainable investment approaches will increasingly influence property valuations and long-term performance outcomes.
Future outlook for South Korea’s residential real estate market remains positive despite near-term challenges, with demographic trends and technological advancement creating new opportunities for growth and innovation. Market projections indicate continued expansion in secondary cities as infrastructure improvements and government incentives attract residents and investors.
Smart city initiatives will likely accelerate residential market transformation, with IoT integration and sustainable building practices becoming standard requirements rather than premium features. PropTech adoption rates are expected to reach 85% market penetration within the next five years, fundamentally changing how properties are marketed, sold, and managed.
Regulatory environment may stabilize as government policies balance market growth objectives with affordability concerns and financial stability requirements. International investment interest will likely continue growing, particularly from Asian investors seeking stable real estate opportunities in developed markets.
MarkWide Research projections suggest that sustainable residential developments will capture increasing market share as environmental consciousness influences buyer decisions and government regulations promote green building standards. Innovation adoption across the sector will drive efficiency improvements and enhanced customer experiences throughout the property lifecycle.
South Korea’s residential real estate market demonstrates remarkable resilience and adaptability in navigating complex economic and regulatory environments while maintaining strong fundamentals that support long-term growth prospects. Technology integration and sustainable development practices emerge as key differentiators that will shape future market dynamics and competitive positioning.
Market opportunities abound in secondary cities, innovative housing formats, and PropTech solutions that address evolving consumer needs and preferences. Stakeholder collaboration between government, developers, and technology providers will be essential for addressing affordability challenges while promoting market growth and innovation.
Strategic focus on regional diversification, sustainability, and digital transformation will enable market participants to capitalize on emerging trends while building resilience against potential challenges. The South Korea residential real estate market is well-positioned to continue its growth trajectory while adapting to changing demographic patterns and technological advancement opportunities that define the future of urban living.
What is South Korea Residential Real Estate?
South Korea Residential Real Estate refers to the market segment that encompasses properties intended for living, including apartments, houses, and condominiums. This sector is influenced by various factors such as urbanization, population density, and government policies.
What are the key players in the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market?
Key players in the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market include major developers like Samsung C&T, Hyundai Engineering & Construction, and Daewoo Engineering & Construction, among others. These companies are involved in various aspects of residential property development and management.
What are the main drivers of the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market?
The main drivers of the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market include increasing urbanization, a growing middle class, and favorable government policies aimed at promoting home ownership. Additionally, low interest rates have also contributed to the market’s growth.
What challenges does the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market face?
The South Korea Residential Real Estate Market faces challenges such as high property prices, regulatory constraints, and a potential oversupply in certain areas. These factors can impact affordability and accessibility for potential homebuyers.
What opportunities exist in the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market?
Opportunities in the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market include the development of smart homes and eco-friendly buildings, as well as the potential for investment in rental properties due to increasing demand for housing. Additionally, urban regeneration projects present further growth avenues.
What trends are shaping the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market?
Trends shaping the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market include a shift towards smaller living spaces, increased demand for mixed-use developments, and a focus on sustainability in construction practices. These trends reflect changing consumer preferences and environmental considerations.
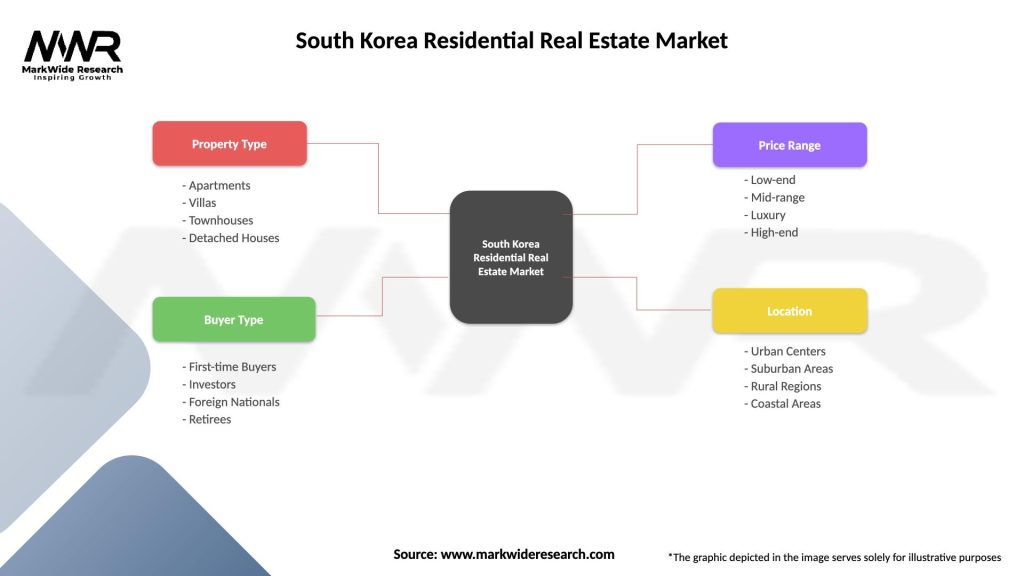
South Korea Residential Real Estate Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Property Type | Apartments, Villas, Townhouses, Detached Houses |
| Buyer Type | First-time Buyers, Investors, Foreign Nationals, Retirees |
| Price Range | Low-end, Mid-range, Luxury, High-end |
| Location | Urban Centers, Suburban Areas, Rural Regions, Coastal Areas |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the South Korea Residential Real Estate Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at