444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The South Korea nuclear imaging devices market represents a rapidly expanding segment within the nation’s advanced healthcare technology landscape. This sophisticated market encompasses a comprehensive range of diagnostic imaging equipment including SPECT systems, PET scanners, gamma cameras, and hybrid imaging solutions that combine nuclear medicine with other imaging modalities. South Korea’s commitment to healthcare innovation and its aging population dynamics have positioned the country as a significant player in the nuclear imaging technology sector across the Asia-Pacific region.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth driven by increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, particularly cardiovascular conditions and various forms of cancer. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into nuclear imaging systems has enhanced diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency, contributing to market expansion at a compound annual growth rate of 6.2%. Healthcare institutions across South Korea are increasingly adopting advanced nuclear imaging solutions to meet rising patient demands and improve clinical outcomes.
Technological advancement remains a cornerstone of market development, with manufacturers focusing on developing more sensitive detectors, improved image resolution capabilities, and reduced radiation exposure protocols. The market benefits from South Korea’s robust healthcare infrastructure, government support for medical technology adoption, and the presence of leading global medical device manufacturers establishing regional operations.
The South Korea nuclear imaging devices market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of medical diagnostic equipment that utilizes radioactive tracers and sophisticated detection systems to create detailed images of internal body structures and physiological processes. These advanced imaging systems enable healthcare professionals to diagnose, monitor, and treat various medical conditions with unprecedented precision and accuracy.
Nuclear imaging technology encompasses multiple specialized devices including single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) systems, positron emission tomography (PET) scanners, gamma cameras, and innovative hybrid imaging platforms that combine nuclear medicine with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging capabilities. These sophisticated systems provide functional and metabolic information about organs and tissues, complementing anatomical imaging modalities.
Clinical applications span across multiple medical specialties including cardiology, oncology, neurology, and orthopedics. The technology enables early disease detection, treatment planning, therapy monitoring, and research applications that contribute to improved patient outcomes and healthcare delivery efficiency throughout South Korea’s medical system.
South Korea’s nuclear imaging devices market demonstrates exceptional growth potential driven by demographic shifts, technological innovations, and expanding clinical applications. The market encompasses a diverse portfolio of imaging solutions serving hospitals, diagnostic centers, research institutions, and specialized medical facilities across the country. Healthcare digitization and integration of advanced analytics have transformed traditional nuclear imaging workflows into comprehensive diagnostic platforms.
Key market drivers include the rapidly aging population, increasing cancer incidence rates, growing cardiovascular disease prevalence, and expanding healthcare infrastructure investments. Government initiatives supporting medical technology adoption and healthcare quality improvements have created favorable conditions for market expansion. The integration of AI-powered image analysis and cloud-based data management systems represents approximately 38% of new installations, indicating strong technology adoption trends.
Competitive landscape features both international medical device manufacturers and emerging domestic technology companies developing innovative nuclear imaging solutions. Market participants focus on developing cost-effective, high-performance systems that address specific clinical needs while maintaining compliance with stringent regulatory requirements and safety standards.
Strategic market analysis reveals several critical insights shaping the South Korea nuclear imaging devices landscape. The following key insights provide comprehensive understanding of market dynamics and growth opportunities:
Demographic transformation serves as the primary catalyst driving South Korea’s nuclear imaging devices market expansion. The country’s rapidly aging population creates increasing demand for diagnostic imaging services, particularly for age-related conditions including cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and various forms of cancer. Population aging trends indicate that approximately 28% of the population will be over 65 years old within the next decade, significantly impacting healthcare service requirements.
Disease prevalence patterns contribute substantially to market growth, with rising incidence rates of chronic conditions requiring regular monitoring and diagnostic imaging. Cancer rates, particularly lung, stomach, and liver cancers, continue increasing, driving demand for advanced PET-CT systems and specialized nuclear medicine procedures. Cardiovascular disease prevalence similarly supports market expansion through increased utilization of cardiac SPECT imaging and related diagnostic procedures.
Healthcare infrastructure investments by both government and private sectors create favorable conditions for technology adoption and market growth. National healthcare policies emphasizing early disease detection, preventive medicine, and quality improvement initiatives support procurement of advanced nuclear imaging equipment. Digital health transformation initiatives further accelerate adoption of integrated imaging solutions with advanced data analytics capabilities.
Technological advancement in nuclear imaging continues driving market demand through improved diagnostic capabilities, reduced examination times, and enhanced patient comfort. Innovations in detector technology, image reconstruction algorithms, and radiation dose optimization attract healthcare providers seeking to improve clinical outcomes while maintaining operational efficiency.
High capital investment requirements represent a significant barrier to market expansion, particularly for smaller healthcare facilities and regional medical centers. Advanced nuclear imaging systems require substantial upfront investments, ongoing maintenance costs, and specialized infrastructure modifications that can strain institutional budgets and limit adoption rates among cost-sensitive healthcare providers.
Regulatory complexity and compliance requirements create challenges for both manufacturers and healthcare institutions. Stringent safety regulations, radiation protection protocols, and quality assurance standards require significant resources for implementation and maintenance. Licensing procedures for radioactive materials and specialized personnel certification requirements add operational complexity and costs.
Technical expertise shortage poses ongoing challenges for market development, as nuclear imaging requires highly specialized technologists, medical physicists, and nuclear medicine physicians. Training programs and continuing education requirements create barriers to rapid technology adoption and limit the availability of qualified personnel across different regions.
Reimbursement limitations and healthcare cost containment pressures influence purchasing decisions and utilization patterns. Insurance coverage policies and government reimbursement rates for nuclear imaging procedures impact the financial viability of equipment investments and service expansion for healthcare providers.
Artificial intelligence integration presents substantial opportunities for market expansion and innovation. AI-powered image analysis, automated reporting systems, and predictive analytics capabilities offer significant value propositions for healthcare providers seeking to improve diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency. Machine learning algorithms for image reconstruction and interpretation represent emerging growth areas with adoption rates increasing by 42% annually.
Telemedicine integration and remote diagnostic capabilities create new market opportunities, particularly for serving rural and underserved populations. Cloud-based image sharing, remote consultation platforms, and mobile nuclear imaging solutions expand access to specialized diagnostic services while creating new revenue streams for healthcare providers and technology vendors.
Personalized medicine applications drive demand for advanced nuclear imaging capabilities supporting precision diagnostics and targeted therapy monitoring. Radiopharmaceutical development and companion diagnostic applications create opportunities for specialized imaging equipment and integrated diagnostic solutions.
Research and development activities in pharmaceutical companies, academic medical centers, and biotechnology firms generate demand for advanced nuclear imaging capabilities. Clinical trial support, drug development programs, and translational research applications represent growing market segments with specialized equipment requirements.
Competitive intensity within South Korea’s nuclear imaging devices market continues increasing as both established manufacturers and emerging technology companies compete for market share. Product differentiation focuses on advanced imaging capabilities, workflow optimization, dose reduction technologies, and integrated software solutions that enhance clinical value and operational efficiency.
Technology convergence trends drive market evolution through integration of nuclear imaging with other diagnostic modalities, artificial intelligence capabilities, and digital health platforms. Hybrid imaging systems combining nuclear medicine with CT, MRI, or ultrasound technologies represent approximately 55% of new equipment installations, indicating strong market preference for integrated solutions.
Supply chain dynamics influence market development through component availability, manufacturing capacity, and distribution networks. Global supply chain disruptions and semiconductor shortages have impacted equipment delivery timelines and pricing structures, creating opportunities for domestic manufacturers and alternative sourcing strategies.
Partnership strategies between equipment manufacturers, healthcare providers, and technology companies shape market development through collaborative innovation, shared risk models, and integrated service offerings. Strategic alliances focusing on research and development, clinical validation, and market access create competitive advantages and accelerate technology adoption.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into South Korea’s nuclear imaging devices market. Primary research activities include structured interviews with healthcare administrators, nuclear medicine physicians, medical device manufacturers, and regulatory officials to gather firsthand market intelligence and validate secondary research findings.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government healthcare statistics, medical device registration databases, clinical literature, and industry publications to establish market baselines and identify trends. Quantitative analysis utilizes statistical modeling techniques to project market growth patterns, segment performance, and competitive dynamics based on historical data and current market indicators.
Market segmentation analysis examines various dimensions including product categories, end-user segments, geographic regions, and application areas to provide granular insights into market structure and growth opportunities. Competitive landscape assessment evaluates manufacturer market positions, product portfolios, pricing strategies, and strategic initiatives through systematic analysis of public information and industry intelligence.
Data validation processes ensure research accuracy through triangulation of multiple information sources, expert review panels, and statistical verification methods. MarkWide Research methodology emphasizes rigorous quality control procedures and transparent analytical frameworks to deliver reliable market intelligence for strategic decision-making.
Seoul metropolitan area dominates South Korea’s nuclear imaging devices market, accounting for approximately 45% of total equipment installations due to concentration of major medical centers, research institutions, and specialized healthcare facilities. The capital region benefits from advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher patient volumes, and greater financial resources supporting technology adoption and equipment upgrades.
Busan and southeastern regions represent significant market opportunities driven by industrial development, population growth, and healthcare infrastructure expansion. Regional medical centers and university hospitals in these areas increasingly invest in advanced nuclear imaging capabilities to serve growing patient populations and support clinical research activities.
Daegu and central regions demonstrate steady market growth supported by government healthcare initiatives and regional development programs. Medical tourism activities and specialized treatment centers contribute to demand for advanced diagnostic imaging capabilities, creating opportunities for equipment manufacturers and service providers.
Rural and remote areas present emerging opportunities through telemedicine integration and mobile imaging solutions. Government initiatives supporting healthcare access improvement and regional medical center development drive demand for cost-effective nuclear imaging solutions adapted to smaller facility requirements and limited technical resources.
Market leadership in South Korea’s nuclear imaging devices sector features a combination of established global manufacturers and innovative domestic technology companies. The competitive environment emphasizes technological innovation, clinical value demonstration, and comprehensive service support to differentiate offerings and capture market share.
Product-based segmentation reveals diverse market structure reflecting varied clinical applications and institutional requirements. SPECT systems maintain strong market presence due to established clinical protocols and cost-effectiveness, while PET scanners demonstrate rapid growth driven by oncology applications and research activities.
By Technology:
By Application:
By End User:
SPECT systems category maintains substantial market presence through established clinical protocols and proven diagnostic capabilities. Cardiac SPECT imaging represents the largest application segment within this category, driven by high prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and established reimbursement patterns. Advanced SPECT-CT hybrid systems demonstrate growth rates of 8.5% as healthcare providers seek enhanced diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency.
PET scanner category experiences rapid expansion driven by increasing cancer incidence and expanding clinical applications. Oncology applications dominate PET utilization, with growing adoption for treatment planning, therapy monitoring, and clinical research activities. Integration of artificial intelligence and advanced image reconstruction algorithms enhances diagnostic capabilities and attracts healthcare provider investments.
Hybrid imaging category represents the fastest-growing market segment, combining nuclear medicine capabilities with anatomical imaging modalities. PET-CT systems lead this category through comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and established clinical workflows, while SPECT-CT systems provide cost-effective alternatives for specific clinical applications.
Gamma camera category serves specialized clinical applications including cardiac imaging, bone scans, and organ-specific procedures. Solid-state detector technology and compact system designs expand installation opportunities in smaller healthcare facilities and specialized clinics, creating new market segments and growth opportunities.
Healthcare providers benefit from advanced nuclear imaging capabilities through improved diagnostic accuracy, enhanced patient care quality, and expanded service offerings. Clinical outcomes improvement results from early disease detection, precise treatment planning, and effective therapy monitoring capabilities that nuclear imaging systems provide across multiple medical specialties.
Patients experience significant advantages including earlier disease detection, personalized treatment approaches, and reduced need for invasive diagnostic procedures. Radiation dose optimization in modern nuclear imaging systems minimizes patient exposure while maintaining diagnostic quality, addressing safety concerns and improving patient acceptance.
Medical device manufacturers capitalize on growing market demand through product innovation, technology differentiation, and strategic partnerships with healthcare providers. Service revenue opportunities from maintenance contracts, training programs, and software upgrades provide sustainable income streams beyond initial equipment sales.
Research institutions leverage advanced nuclear imaging capabilities for clinical trials, pharmaceutical development, and translational research activities. Academic medical centers benefit from enhanced research capabilities, improved clinical training programs, and strengthened partnerships with industry collaborators.
Government healthcare systems achieve improved population health outcomes through enhanced diagnostic capabilities, cost-effective disease management, and reduced long-term healthcare costs associated with early intervention and preventive care strategies.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Artificial intelligence integration represents the most significant trend transforming South Korea’s nuclear imaging devices market. Machine learning algorithms for image reconstruction, automated analysis, and predictive diagnostics enhance clinical capabilities while reducing interpretation time and improving diagnostic accuracy. Healthcare providers increasingly prioritize AI-enabled systems that offer workflow optimization and clinical decision support capabilities.
Hybrid imaging adoption continues accelerating as healthcare providers seek comprehensive diagnostic solutions combining functional and anatomical information. PET-CT and SPECT-CT systems demonstrate strong growth trends, with approximately 65% of new installations featuring hybrid capabilities that enhance diagnostic confidence and clinical utility across multiple applications.
Dose reduction technologies gain prominence as healthcare providers prioritize patient safety and regulatory compliance. Advanced detector technologies, optimized imaging protocols, and intelligent acquisition systems minimize radiation exposure while maintaining diagnostic quality, addressing growing concerns about cumulative radiation effects and patient safety.
Cloud-based solutions and digital health integration transform traditional nuclear imaging workflows through enhanced data management, remote access capabilities, and integrated electronic health record systems. Telemedicine compatibility and mobile imaging solutions expand service delivery options and improve access to specialized diagnostic capabilities.
Personalized medicine applications drive demand for advanced nuclear imaging capabilities supporting precision diagnostics and targeted therapy monitoring. Radiopharmaceutical development and companion diagnostic applications create new market opportunities and specialized equipment requirements.
Technology advancement initiatives by major manufacturers focus on developing next-generation nuclear imaging systems with enhanced sensitivity, improved resolution, and reduced examination times. Detector technology innovations including solid-state detectors and advanced photomultiplier systems improve image quality while reducing system complexity and maintenance requirements.
Strategic partnerships between equipment manufacturers and healthcare providers create collaborative innovation programs addressing specific clinical needs and market requirements. Research collaborations with academic medical centers and pharmaceutical companies accelerate technology development and clinical validation processes.
Regulatory developments including updated safety standards and quality assurance requirements influence product development strategies and market entry approaches. Government initiatives supporting medical technology adoption and healthcare infrastructure improvement create favorable conditions for market expansion and technology deployment.
Service model evolution toward comprehensive support offerings including maintenance contracts, training programs, and performance guarantees addresses healthcare provider concerns about technology complexity and operational costs. Subscription-based models and equipment-as-a-service offerings provide alternative procurement options for cost-sensitive healthcare institutions.
Market consolidation activities through mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances reshape competitive dynamics and create opportunities for enhanced product portfolios and expanded market reach. MarkWide Research analysis indicates increasing collaboration between traditional medical device manufacturers and emerging technology companies developing innovative nuclear imaging solutions.
Healthcare providers should prioritize nuclear imaging investments that offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, workflow optimization, and future-ready technology platforms. Hybrid imaging systems provide superior clinical value and long-term viability compared to single-modality solutions, justifying higher initial investments through enhanced diagnostic capabilities and operational efficiency.
Technology manufacturers must focus on developing cost-effective solutions that address specific clinical needs while maintaining advanced capabilities and regulatory compliance. AI integration and digital health compatibility represent essential features for competitive positioning and market success in the evolving healthcare technology landscape.
Investment strategies should emphasize comprehensive service offerings, training programs, and ongoing support capabilities that address healthcare provider concerns about technology complexity and operational requirements. Partnership approaches with healthcare institutions create opportunities for collaborative innovation and market development.
Regional expansion opportunities exist in underserved markets through mobile imaging solutions, telemedicine integration, and cost-optimized equipment designed for smaller healthcare facilities. Government healthcare initiatives supporting rural healthcare access create favorable conditions for market development and technology deployment.
Research and development investments should prioritize dose reduction technologies, AI-powered analytics, and personalized medicine applications that align with evolving clinical needs and regulatory requirements. Clinical validation and evidence generation support market acceptance and reimbursement approval processes.
Market trajectory for South Korea’s nuclear imaging devices sector indicates sustained growth driven by demographic trends, technology advancement, and expanding clinical applications. Long-term projections suggest continued market expansion at a compound annual growth rate of 6.8% through the next decade, supported by aging population dynamics and increasing healthcare technology adoption.
Technology evolution will focus on artificial intelligence integration, dose optimization, and personalized medicine applications that enhance clinical value and operational efficiency. Next-generation systems incorporating advanced detector technologies, machine learning algorithms, and cloud-based analytics will define competitive advantages and market leadership positions.
Clinical applications expansion into new therapeutic areas including immunotherapy monitoring, precision oncology, and neurodegenerative disease management will drive additional market growth and equipment specialization. Research applications in pharmaceutical development and clinical trials create sustained demand for advanced nuclear imaging capabilities.
Market structure evolution toward integrated healthcare solutions and comprehensive service models will reshape competitive dynamics and customer relationships. Digital health integration and telemedicine compatibility become essential features for market success and technology adoption.
MarkWide Research projections indicate that hybrid imaging systems will account for approximately 75% of new installations within five years, reflecting healthcare provider preferences for comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and workflow optimization. Investment in training programs and technical support infrastructure will become increasingly important for market participants seeking sustainable competitive advantages.
South Korea’s nuclear imaging devices market presents exceptional growth opportunities driven by favorable demographic trends, advancing healthcare technology, and expanding clinical applications. The market benefits from strong government support, sophisticated healthcare infrastructure, and increasing adoption of advanced diagnostic imaging solutions across diverse medical specialties.
Technology integration trends including artificial intelligence, hybrid imaging capabilities, and digital health compatibility will continue shaping market development and competitive dynamics. Healthcare providers increasingly prioritize comprehensive diagnostic solutions that offer enhanced clinical value, workflow optimization, and future-ready technology platforms.
Strategic success in this dynamic market requires focus on innovation, clinical value demonstration, and comprehensive service offerings that address healthcare provider needs and regulatory requirements. Market participants must balance advanced technology capabilities with cost-effectiveness and operational simplicity to achieve sustainable growth and market leadership positions in South Korea’s evolving nuclear imaging landscape.
What is Nuclear Imaging Devices?
Nuclear Imaging Devices are medical instruments used to visualize the function of organs and tissues in the body through the use of radioactive materials. These devices are essential in diagnosing various conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
What are the key players in the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market?
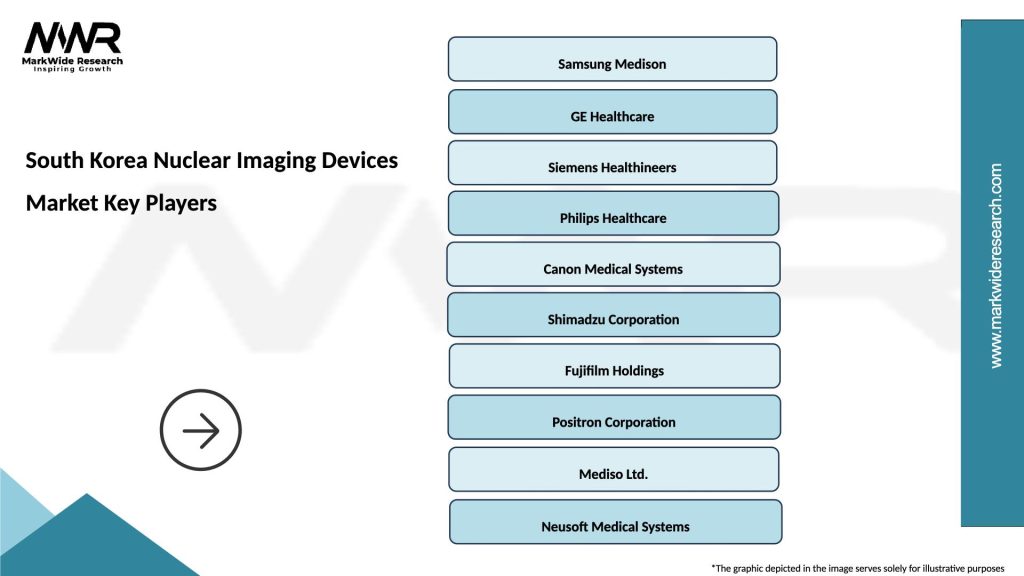
Key players in the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market include Siemens Healthineers, GE Healthcare, and Philips Healthcare, among others. These companies are known for their innovative technologies and comprehensive product offerings in nuclear imaging.
What are the growth factors driving the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market?
The growth of the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market is driven by an increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in imaging technologies, and a growing emphasis on early diagnosis and personalized medicine. Additionally, the rising geriatric population contributes to the demand for these devices.
What challenges does the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market face?
The South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market faces challenges such as high costs associated with nuclear imaging procedures and regulatory hurdles related to the use of radioactive materials. Furthermore, there is a need for skilled professionals to operate these complex devices.
What opportunities exist in the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market?
Opportunities in the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market include the development of advanced imaging technologies, such as hybrid imaging systems, and the expansion of applications in fields like oncology and cardiology. Additionally, increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure present further growth potential.
What trends are shaping the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market?
Trends shaping the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market include the integration of artificial intelligence in imaging analysis, the shift towards portable and compact imaging devices, and the growing focus on patient-centered care. These trends are enhancing diagnostic accuracy and improving patient outcomes.
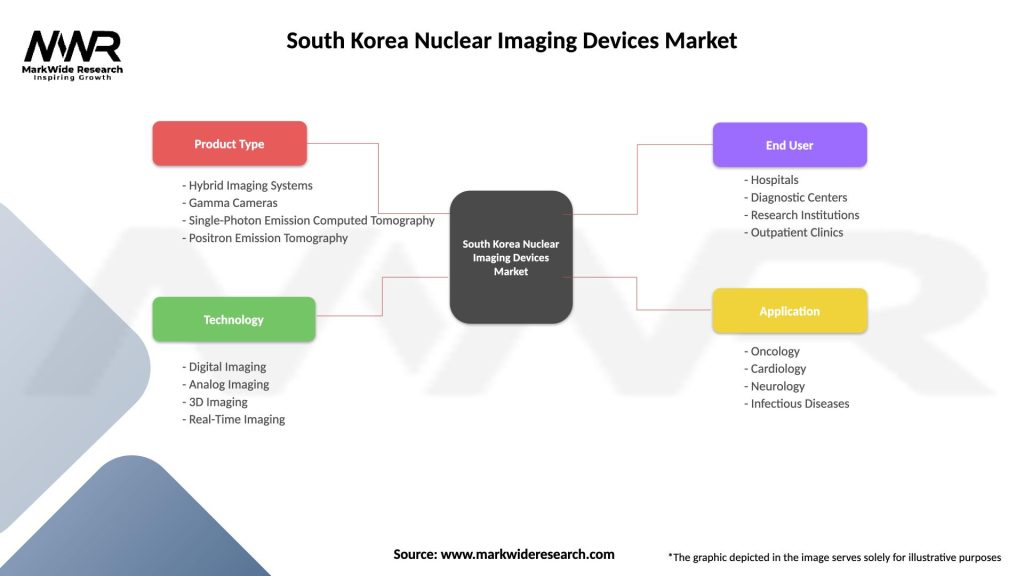
South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Hybrid Imaging Systems, Gamma Cameras, Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography, Positron Emission Tomography |
| Technology | Digital Imaging, Analog Imaging, 3D Imaging, Real-Time Imaging |
| End User | Hospitals, Diagnostic Centers, Research Institutions, Outpatient Clinics |
| Application | Oncology, Cardiology, Neurology, Infectious Diseases |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the South Korea Nuclear Imaging Devices Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at