444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
South Korea’s LNG bunkering market has witnessed significant growth in recent years. As one of the world’s largest importers of liquefied natural gas (LNG), South Korea has recognized the potential of LNG bunkering as a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional marine fuels. The country’s strategic location, thriving shipping industry, and government initiatives have contributed to the development of a robust LNG bunkering market.
Meaning
LNG bunkering refers to the process of supplying liquefied natural gas to ships for use as fuel. It involves transferring LNG from storage facilities or specialized bunkering vessels to ships, enabling them to reduce emissions and comply with environmental regulations. LNG bunkering offers several advantages over conventional marine fuels, including lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced air pollution, and improved energy efficiency.
Executive Summary
The South Korea LNG bunkering market is experiencing steady growth due to various factors. The country’s strong focus on reducing emissions and transitioning towards cleaner energy sources has led to increased demand for LNG as a marine fuel. The government’s support in the form of regulations, incentives, and infrastructure development has further boosted the market. Key industry players are investing in LNG bunkering infrastructure and forming partnerships to capitalize on the growing demand.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
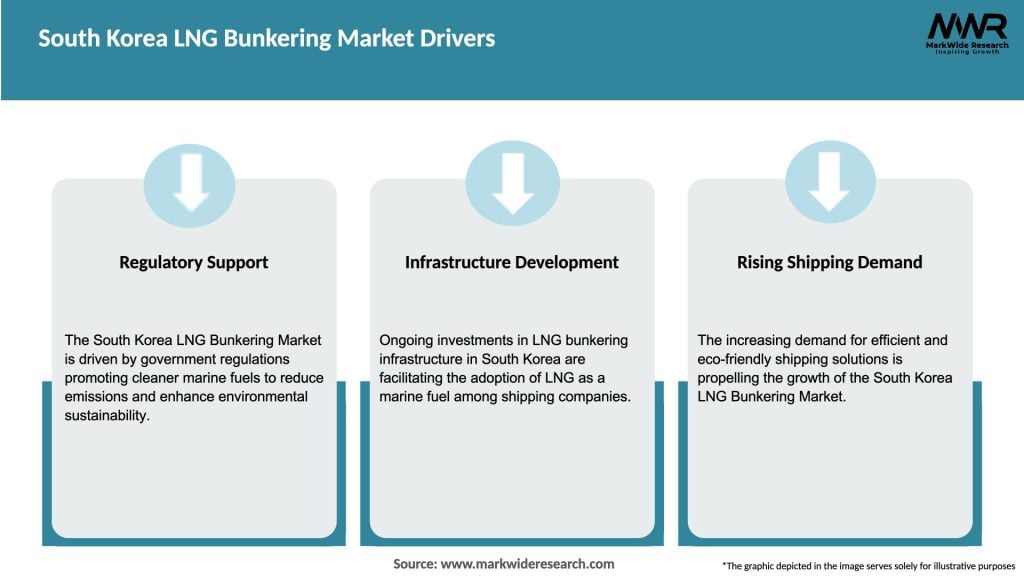
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities

Market Dynamics
The South Korea LNG bunkering market is characterized by dynamic trends and ongoing developments. The market dynamics are influenced by factors such as government policies, environmental regulations, technological advancements, and market competition. Continuous collaboration between industry stakeholders, proactive government support, and investments in infrastructure development will shape the future trajectory of the market.
Regional Analysis
South Korea’s strategic location in Northeast Asia positions it as a significant player in the LNG bunkering market. The country’s major ports, including Busan, Incheon, and Ulsan, serve as important maritime hubs. These ports are well-connected to international shipping routes, making them ideal locations for LNG bunkering infrastructure development. Furthermore, South Korea’s strong shipbuilding industry and established LNG supply chain contribute to the region’s growth potential.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The South Korea LNG bunkering market can be segmented based on the following criteria:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Industry participants and stakeholders involved in the South Korea LNG bunkering market can benefit in several ways:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a temporary impact on the South Korea LNG bunkering market. The global slowdown in shipping activities and disruptions in international trade during the pandemic resulted in reduced demand for LNG bunkering services. However, as the world recovers from the pandemic and shipping activities resume, the LNG bunkering market is expected to regain its growth trajectory.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The South Korea LNG bunkering market is expected to witness substantial growth in the coming years. The government’s commitment to reducing emissions, coupled with the country’s well-established LNG infrastructure and shipping network, provides a strong foundation for market expansion. Continued investments in infrastructure development, technological advancements, and collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders will drive the future growth and sustainability of the LNG bunkering market in South Korea.
Conclusion
The South Korea LNG bunkering market is poised for significant growth as the maritime industry increasingly adopts cleaner and more sustainable fuel options. The country’s commitment to environmental stewardship, coupled with robust LNG infrastructure and favorable government policies, creates a conducive environment for market development. Industry participants and stakeholders should leverage the opportunities presented by LNG bunkering, collaborate for infrastructure development, and stay abreast of technological advancements to position themselves for success in this evolving market.
What is LNG Bunkering?
LNG Bunkering refers to the process of supplying liquefied natural gas (LNG) as fuel to ships and vessels. This method is gaining traction due to its environmental benefits and compliance with international maritime regulations.
What are the key players in the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market?
Key players in the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market include Korea Gas Corporation, SK E&S, and Hyundai Heavy Industries, among others. These companies are actively involved in developing infrastructure and services for LNG bunkering.
What are the growth factors driving the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market?
The growth of the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market is driven by increasing demand for cleaner marine fuels, stricter emissions regulations, and the expansion of LNG infrastructure in major ports.
What challenges does the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market face?
Challenges in the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market include high initial investment costs for infrastructure, regulatory hurdles, and competition from alternative fuels such as hydrogen and ammonia.
What opportunities exist in the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market?
Opportunities in the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market include the potential for technological advancements in LNG fueling systems, partnerships with shipping companies, and the growing trend towards sustainable shipping practices.
What trends are shaping the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market?
Trends in the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market include the increasing adoption of dual-fuel engines, the development of small-scale LNG bunkering facilities, and a focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions in maritime operations.
South Korea LNG Bunkering Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Ship-to-Ship, Port-to-Port, Terminal Services, Barge Services |
| End User | Shipping Companies, Freight Operators, Offshore Vessels, Fishing Fleets |
| Technology | Liquefaction, Regasification, Storage Solutions, Fuel Management Systems |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Distributors, Online Platforms, Third-Party Providers |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the South Korea LNG Bunkering Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at