444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview:
South Korea’s freight forwarding market is a key player in the nation’s logistics landscape, facilitating the movement of goods domestically and internationally. With a strong emphasis on technology, efficient transportation networks, and global trade partnerships, South Korea’s freight forwarding industry is positioned for growth.
Meaning:
Freight forwarding in South Korea involves the coordination and management of the transportation of goods through various modes, including air, sea, road, and rail. As a crucial element of the supply chain, freight forwarders in South Korea contribute to the nation’s export-oriented economy by ensuring the timely and secure delivery of goods.
Executive Summary:
South Korea’s freight forwarding market stands out for its technological prowess, strategic geographic location, and integration into global trade networks. The industry has witnessed steady growth, driven by advancements in manufacturing, trade liberalization, and a commitment to innovation. However, challenges such as geopolitical tensions and global economic uncertainties require a resilient and adaptive approach.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics:
South Korea’s freight forwarding market operates in a dynamic environment influenced by technological advancements, global economic trends, and geopolitical considerations. Staying agile, innovative, and responsive to market dynamics is crucial for sustained success.
Regional Analysis:
Regional variations within South Korea’s freight forwarding market are influenced by factors such as industrial clusters, transportation infrastructure, and proximity to major ports. The capital city, Seoul, serves as a central hub, while Busan, with its major port, plays a key role in international trade.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading companies South Korea Freight forwarding Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
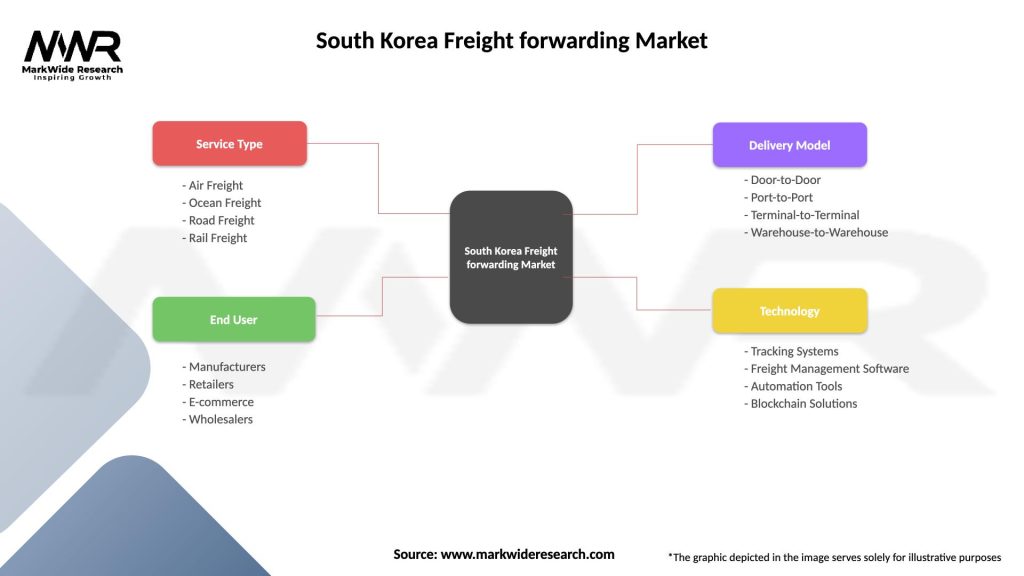
Segmentation:
Segmentation in South Korea’s freight forwarding market can be based on transportation modes (air, sea, road, rail), industry verticals (electronics, automotive, pharmaceuticals), and specialized services (cold chain logistics, express delivery, project cargo).
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact:
The COVID-19 pandemic had a notable impact on South Korea’s freight forwarding market, with disruptions in global trade, fluctuations in demand for specific goods, and the need for resilient and adaptable logistics solutions. The industry demonstrated resilience through technology adoption and collaborative measures.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook:
South Korea’s freight forwarding market is poised for continued growth, driven by its technological strengths, global trade connectivity, and commitment to innovation. Adapting to market trends, addressing geopolitical challenges, and embracing sustainable practices will be key factors shaping the industry’s future success.
Conclusion:
As a vital component of South Korea’s logistics ecosystem, the freight forwarding market plays a pivotal role in supporting the nation’s export-oriented economy. Navigating the complexities of global trade, technology adoption, and market dynamics requires a strategic and collaborative approach. By staying at the forefront of technological advancements, fostering talent development, and embracing sustainable practices, companies operating in South Korea’s freight forwarding market can position themselves for long-term success and contribute to the resilience of the nation’s supply chain.
What is Freight forwarding?
Freight forwarding refers to the process of organizing the shipment of goods from one place to another, often involving multiple carriers and logistics services. It encompasses various activities such as transportation, warehousing, and customs clearance.
What are the key players in the South Korea Freight forwarding Market?
Key players in the South Korea Freight forwarding Market include companies like CJ Logistics, Hanjin Transportation, and Hyundai Glovis, which provide comprehensive logistics solutions and freight services, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the South Korea Freight forwarding Market?
The main drivers of growth in the South Korea Freight forwarding Market include the increasing demand for e-commerce logistics, the expansion of international trade, and advancements in supply chain technology that enhance efficiency.
What challenges does the South Korea Freight forwarding Market face?
Challenges in the South Korea Freight forwarding Market include regulatory complexities, fluctuating fuel prices, and the need for sustainable practices in logistics operations.
What opportunities exist in the South Korea Freight forwarding Market?
Opportunities in the South Korea Freight forwarding Market include the growth of cross-border e-commerce, the adoption of digital freight platforms, and the increasing focus on green logistics solutions.
What trends are shaping the South Korea Freight forwarding Market?
Trends shaping the South Korea Freight forwarding Market include the rise of automation in logistics, the integration of artificial intelligence for route optimization, and the growing emphasis on real-time tracking and transparency in shipments.
South Korea Freight forwarding Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Air Freight, Ocean Freight, Road Freight, Rail Freight |
| End User | Manufacturers, Retailers, E-commerce, Wholesalers |
| Delivery Model | Door-to-Door, Port-to-Port, Terminal-to-Terminal, Warehouse-to-Warehouse |
| Technology | Tracking Systems, Freight Management Software, Automation Tools, Blockchain Solutions |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies South Korea Freight forwarding Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at