444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The South Korea electric vehicle charging equipment market represents one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving sectors in the Asia-Pacific region’s sustainable transportation ecosystem. South Korea’s commitment to carbon neutrality by 2050 has positioned the nation as a global leader in electric vehicle infrastructure development, with the charging equipment market experiencing unprecedented growth driven by government initiatives, technological innovations, and increasing consumer adoption of electric vehicles.
Market dynamics indicate that South Korea’s electric vehicle charging infrastructure is expanding at a remarkable pace, with the country achieving 85% urban coverage for public charging stations and maintaining one of the highest charging station densities globally. The market encompasses various charging technologies, including Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging systems, with particular emphasis on ultra-fast charging solutions that can deliver 350kW charging capacity for next-generation electric vehicles.
Government support through the Korean New Deal and Green New Deal initiatives has accelerated market development, with substantial investments in charging infrastructure deployment across metropolitan areas, highways, and rural regions. The market benefits from strong domestic manufacturing capabilities, with leading Korean companies developing advanced charging technologies that compete globally while serving the rapidly expanding domestic electric vehicle market.
The South Korea electric vehicle charging equipment market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of hardware, software, and services designed to provide electrical energy to electric vehicles through various charging methodologies and power levels. This market encompasses the manufacturing, installation, operation, and maintenance of charging infrastructure that supports the country’s transition to sustainable transportation.
Charging equipment in this context includes AC charging stations for residential and commercial applications, DC fast chargers for public and highway installations, wireless charging systems for innovative applications, and smart charging solutions that integrate with grid management systems. The market also covers associated components such as charging cables, connectors, power electronics, communication systems, and energy management software that enable efficient and reliable charging operations.
Market scope extends beyond hardware to include charging network management platforms, payment processing systems, mobile applications for user interface, and grid integration technologies that support vehicle-to-grid capabilities. This comprehensive approach reflects South Korea’s holistic strategy for electric vehicle infrastructure development that prioritizes user experience, grid stability, and technological innovation.
South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment market stands as a testament to the nation’s technological prowess and environmental commitment, demonstrating exceptional growth trajectory supported by comprehensive government policies and robust private sector investment. The market has achieved significant milestones in charging infrastructure deployment, with rapid charging stations accounting for approximately 45% of total installations nationwide, reflecting the country’s focus on convenience and efficiency for electric vehicle users.
Key market characteristics include strong domestic manufacturing capabilities, advanced technology integration, and strategic partnerships between government entities, automotive manufacturers, and charging infrastructure providers. The market benefits from South Korea’s dense urban population and compact geography, which facilitate efficient charging network deployment and high utilization rates across installed infrastructure.
Technological innovation drives market differentiation, with Korean companies leading development in ultra-fast charging technologies, smart grid integration, and wireless charging solutions. The market’s growth is further supported by increasing electric vehicle adoption rates, which have reached 12% of new vehicle sales in major metropolitan areas, creating sustained demand for expanded charging infrastructure.
Strategic market insights reveal several critical factors shaping South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment landscape:
Government policy initiatives serve as the primary catalyst for South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment market expansion. The Korean New Deal allocates substantial resources for green infrastructure development, with specific targets for charging station deployment that create predictable demand for equipment manufacturers and service providers. Regulatory frameworks establish technical standards, safety requirements, and interoperability specifications that ensure market stability and consumer confidence.
Environmental consciousness among South Korean consumers drives increasing adoption of electric vehicles, creating corresponding demand for accessible and reliable charging infrastructure. The country’s commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 40% by 2030 necessitates rapid transportation electrification, positioning charging equipment as critical infrastructure for achieving national climate goals.
Technological advancement in battery technology and electric vehicle performance creates opportunities for charging equipment innovation. Improvements in charging speed, efficiency, and user interface design attract both individual consumers and fleet operators seeking optimal total cost of ownership for electric vehicle operations. Smart city initiatives integrate charging infrastructure with broader urban planning strategies, creating synergies with renewable energy systems and intelligent transportation networks.
High capital investment requirements for charging infrastructure deployment present significant barriers for market participants, particularly smaller companies seeking to establish charging networks. The substantial upfront costs associated with land acquisition, electrical infrastructure upgrades, and equipment installation create financial challenges that may limit market entry and expansion opportunities for some stakeholders.
Grid capacity constraints in certain regions pose technical challenges for large-scale charging infrastructure deployment. Existing electrical distribution systems may require substantial upgrades to support high-power charging stations, creating additional costs and potential delays in project implementation. Permitting processes for electrical infrastructure modifications can extend project timelines and increase development complexity.
Technology standardization challenges across different charging protocols and connector types create market fragmentation that may confuse consumers and increase infrastructure costs. While South Korea has made progress in establishing national standards, ongoing evolution in charging technologies requires continuous adaptation and potential equipment obsolescence concerns for investors and operators.
Export market potential represents a significant opportunity for South Korean charging equipment manufacturers, as global demand for electric vehicle infrastructure accelerates across developed and emerging markets. Korean companies’ technological expertise and manufacturing capabilities position them competitively for international expansion, particularly in markets with similar urban density and technological infrastructure characteristics.
Wireless charging technology development offers opportunities for market differentiation and premium positioning. South Korea’s advanced telecommunications infrastructure and technology sector expertise create favorable conditions for developing and deploying innovative wireless charging solutions for both stationary and dynamic charging applications. Smart charging integration with renewable energy systems presents opportunities for creating comprehensive energy management solutions that optimize grid stability and reduce operational costs.
Fleet electrification initiatives by logistics companies, delivery services, and public transportation operators create substantial market opportunities for specialized charging solutions. These applications often require customized charging infrastructure with specific power requirements, scheduling capabilities, and fleet management integration that command premium pricing and long-term service contracts.
Competitive dynamics in South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment market reflect a balance between established domestic players and international technology providers. Korean manufacturers leverage their understanding of local market requirements, regulatory environment, and consumer preferences to maintain strong market positions, while international companies contribute advanced technologies and global best practices to enhance overall market sophistication.
Supply chain considerations play an increasingly important role in market dynamics, with companies focusing on securing reliable sources for critical components such as power electronics, charging cables, and communication modules. The global semiconductor shortage has highlighted the importance of supply chain resilience, prompting market participants to develop more robust sourcing strategies and inventory management approaches.
Pricing pressures from government procurement processes and competitive bidding for large-scale infrastructure projects influence market dynamics, encouraging efficiency improvements and cost optimization throughout the value chain. However, the emphasis on quality, reliability, and advanced features helps maintain healthy margins for companies that can demonstrate superior technology and service capabilities.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment market. Primary research includes structured interviews with industry executives, government officials, charging infrastructure operators, and electric vehicle users to gather firsthand perspectives on market trends, challenges, and opportunities.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government publications, industry reports, company financial statements, and technical specifications to validate market data and identify emerging trends. MarkWide Research utilizes proprietary databases and analytical frameworks to synthesize information from multiple sources and develop comprehensive market intelligence that supports strategic decision-making.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing information from multiple sources, conducting expert interviews to verify findings, and applying statistical analysis techniques to ensure data accuracy and reliability. The research methodology emphasizes both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights to provide a complete understanding of market dynamics and future prospects.
Seoul metropolitan area dominates South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment market, accounting for approximately 55% of total installations due to high population density, strong government support, and concentrated electric vehicle adoption. The region benefits from advanced electrical infrastructure, favorable zoning regulations, and strong consumer purchasing power that supports premium charging solutions and innovative technology deployment.
Busan and surrounding regions represent the second-largest market segment, with growing charging infrastructure deployment driven by port logistics operations, industrial facilities, and urban development initiatives. The region’s focus on sustainable transportation solutions for cargo handling and urban mobility creates opportunities for specialized charging equipment designed for commercial and industrial applications.
Rural and highway corridors present emerging opportunities for charging infrastructure development, supported by government initiatives to ensure nationwide electric vehicle accessibility. These regions require different charging solutions optimized for longer-distance travel, with emphasis on ultra-fast charging capabilities and reliable operation in diverse environmental conditions. Regional distribution shows approximately 25% market share for secondary cities and 20% for rural areas, reflecting the ongoing expansion beyond major metropolitan centers.
Market leadership in South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment sector reflects a combination of domestic innovation and international collaboration:
By charging type, the South Korea electric vehicle charging equipment market demonstrates clear segmentation patterns:
By application sector, market segmentation reflects diverse use cases:
Residential charging equipment represents the largest market segment by volume, driven by increasing electric vehicle ownership and government incentives for home charging installation. This category emphasizes user-friendly operation, integration with home energy management systems, and cost-effective solutions that provide reliable overnight charging capabilities. Smart home integration features are becoming increasingly important, with 75% of new installations including connectivity features for remote monitoring and control.
Commercial charging solutions focus on maximizing utilization rates and providing positive user experiences for employees and customers. These systems often include advanced features such as load management, user authentication, and payment processing capabilities. Workplace charging programs show strong growth, with many companies installing charging infrastructure as employee benefits and corporate sustainability initiatives.
Public charging infrastructure emphasizes reliability, accessibility, and rapid charging capabilities to support long-distance travel and urban mobility needs. This category requires robust construction, weather resistance, and comprehensive maintenance support to ensure consistent availability. Highway charging corridors represent a critical component, with ultra-fast charging stations spaced at optimal intervals to eliminate range anxiety for electric vehicle users.
Equipment manufacturers benefit from South Korea’s strong domestic market demand, which provides a stable foundation for business growth and technology development. The market’s emphasis on quality and innovation creates opportunities for premium positioning and healthy profit margins, while government support reduces market development risks and provides predictable demand patterns.
Charging network operators gain advantages from South Korea’s high population density and concentrated urban development, which enable efficient network deployment and high utilization rates. The country’s advanced digital infrastructure supports sophisticated network management and user interface systems that enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Electric vehicle manufacturers benefit from comprehensive charging infrastructure that reduces consumer purchase barriers and supports market expansion. The availability of diverse charging options, from residential to ultra-fast highway charging, enables manufacturers to offer vehicles with varying range and charging capabilities to meet different consumer needs and price points.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Ultra-fast charging adoption represents the most significant trend shaping South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment market. The deployment of 350kW+ charging systems along major highways and in urban centers reflects consumer demand for charging experiences comparable to traditional fuel refilling times. This trend drives technological innovation in power electronics, cooling systems, and grid integration capabilities.
Smart charging integration with renewable energy systems and grid management platforms creates opportunities for optimized energy utilization and cost reduction. Vehicle-to-grid technology enables electric vehicles to serve as distributed energy storage resources, supporting grid stability and renewable energy integration while providing additional revenue streams for vehicle owners.
Wireless charging development gains momentum as South Korea leverages its advanced telecommunications and technology sectors to create innovative charging solutions. Dynamic wireless charging for highways and stationary wireless systems for parking applications represent emerging opportunities that could transform the charging experience and reduce infrastructure requirements.
Government policy evolution continues to shape market development through updated regulations, expanded incentive programs, and revised infrastructure deployment targets. Recent policy announcements include enhanced support for rural charging infrastructure and new technical standards for ultra-fast charging systems that ensure safety and interoperability across different vehicle models and charging networks.
Technology partnerships between Korean companies and international technology providers accelerate innovation and market development. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that collaborative agreements focusing on advanced charging technologies and grid integration solutions are becoming increasingly common as companies seek to combine local market knowledge with global technological expertise.
Infrastructure expansion projects by major charging network operators demonstrate market confidence and growth potential. Recent announcements include plans for nationwide ultra-fast charging networks and specialized charging solutions for commercial vehicle fleets, indicating sustained investment in market development and technology advancement.
Market participants should prioritize technology innovation and differentiation to maintain competitive advantages in South Korea’s rapidly evolving electric vehicle charging equipment market. Investment in research and development for next-generation charging technologies, including wireless systems and ultra-fast charging capabilities, will be critical for long-term market success and export opportunities.
Strategic partnerships with automotive manufacturers, utility companies, and technology providers can enhance market positioning and accelerate growth. Companies should focus on developing comprehensive solutions that address multiple aspects of the charging ecosystem, from hardware manufacturing to network management and user experience optimization.
International expansion strategies should leverage South Korea’s technological expertise and market experience to capture opportunities in global markets with similar characteristics. Export market development can provide additional revenue streams and reduce dependence on domestic market fluctuations while establishing Korean companies as global leaders in charging technology.
Long-term market prospects for South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment sector remain exceptionally positive, supported by sustained government commitment, technological innovation, and increasing consumer adoption of electric vehicles. Market expansion is expected to continue at a robust pace, with charging infrastructure deployment reaching comprehensive nationwide coverage by the end of the decade.
Technology evolution will drive market transformation, with wireless charging systems potentially achieving 25% market penetration for new installations by 2030. Smart charging capabilities will become standard features, enabling sophisticated energy management and grid integration that supports South Korea’s renewable energy transition and carbon neutrality goals.
Export opportunities will expand significantly as Korean companies establish themselves as global leaders in charging technology and infrastructure development. MWR projections indicate that Korean charging equipment exports could capture substantial market share in key international markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and emerging economies seeking advanced charging solutions for their electric vehicle infrastructure development programs.
South Korea’s electric vehicle charging equipment market represents a dynamic and rapidly expanding sector that exemplifies the nation’s commitment to sustainable transportation and technological innovation. The market’s strong foundation, built on comprehensive government support, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and sophisticated consumer demand, positions it for continued growth and global leadership in charging technology development.
Market success factors include the effective combination of policy support, private sector innovation, and consumer adoption that creates a virtuous cycle of growth and improvement. The emphasis on quality, reliability, and advanced features distinguishes the South Korean market and provides a competitive advantage for domestic companies seeking international expansion opportunities.
Future prospects remain highly favorable, with emerging technologies such as wireless charging, ultra-fast charging systems, and smart grid integration creating new opportunities for market participants. The market’s evolution from basic charging infrastructure to comprehensive energy management solutions reflects South Korea’s broader transformation toward a sustainable and technologically advanced transportation ecosystem that serves as a model for global markets pursuing similar objectives.
What is Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment?
Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment refers to the devices and infrastructure used to charge electric vehicles, including home chargers, public charging stations, and fast chargers. These systems are essential for supporting the growing adoption of electric vehicles in various sectors.
What are the key players in the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market?
Key players in the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market include companies like Hyundai Motor Company, LG Electronics, and Samsung SDI, which are actively involved in the development and deployment of charging solutions, among others.
What are the main drivers of the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market?
The main drivers of the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market include the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, government incentives for EV infrastructure, and advancements in charging technology. These factors contribute to a growing demand for efficient and accessible charging solutions.
What challenges does the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market face?
Challenges in the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market include the high initial costs of installation, the need for extensive infrastructure development, and concerns over charging speed and accessibility. These issues can hinder the rapid expansion of charging networks.
What opportunities exist in the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market?
Opportunities in the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market include the potential for innovation in charging technologies, the expansion of renewable energy integration, and the development of smart charging solutions. These trends can enhance the efficiency and sustainability of charging infrastructure.
What trends are shaping the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market?
Trends shaping the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market include the rise of ultra-fast charging stations, the integration of IoT technology for better user experience, and the increasing focus on sustainability in charging solutions. These trends are driving the evolution of the market.
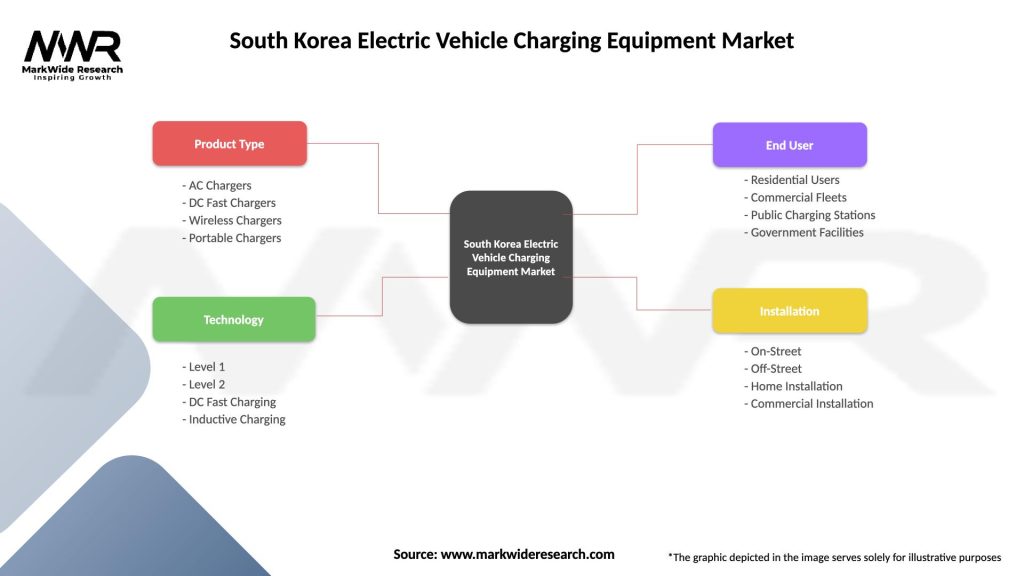
South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | AC Chargers, DC Fast Chargers, Wireless Chargers, Portable Chargers |
| Technology | Level 1, Level 2, DC Fast Charging, Inductive Charging |
| End User | Residential Users, Commercial Fleets, Public Charging Stations, Government Facilities |
| Installation | On-Street, Off-Street, Home Installation, Commercial Installation |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the South Korea Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at