444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
Maize, commonly known as corn, is one of the most vital staple crops in South America. It holds immense economic, cultural, and nutritional significance for the region. South American countries, with their diverse climates and agricultural practices, contribute significantly to the global maize market. This comprehensive report provides a detailed analysis of the South American maize market, covering key insights, market dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, industry trends, and the impact of Covid-19.
Meaning
Maize, scientifically known as Zea mays, is a cereal grain that originated in Mesoamerica and was introduced to South America during the European colonization. It serves as a primary food source for both human consumption and livestock feed. Additionally, maize-derived products have industrial applications in biofuels, starch, and other bio-based materials.
Executive Summary:
The South American maize market has experienced steady growth over the years, driven by increasing demand from various industries, including food and beverage, animal feed, and ethanol production. The region’s rich agricultural landscape, favorable climatic conditions, and advancing farming techniques contribute to robust maize cultivation. Despite facing challenges like climate variability and disease outbreaks, the market shows resilience and continues to offer lucrative opportunities for stakeholders.
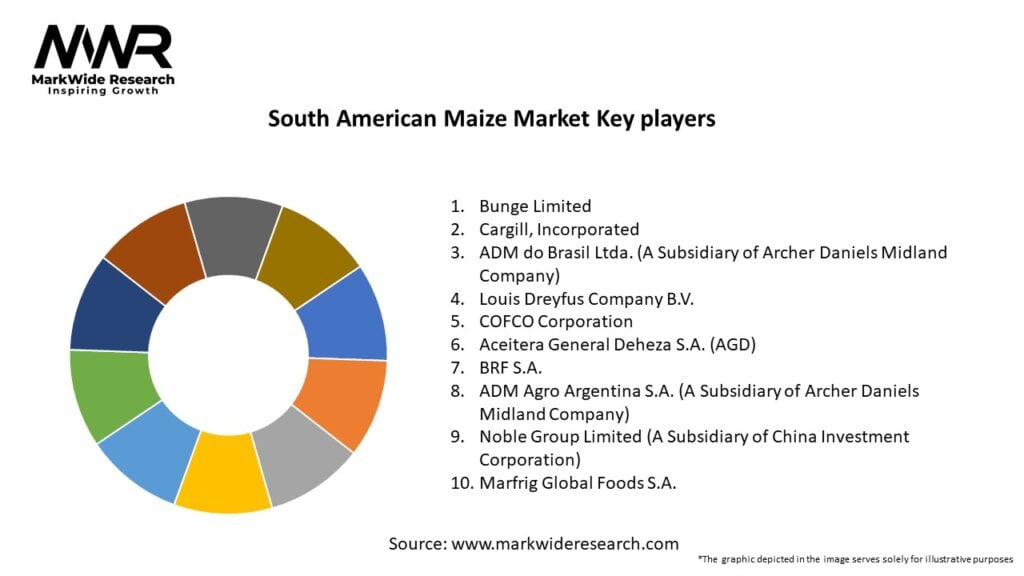
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of the South American Maize Market:
Increasing Demand for Maize-Based Products: The growing consumption of maize-based products, such as cornmeal, tortillas, and snacks, in both domestic and international markets is driving demand.
Biofuel Production: South America is a significant producer of ethanol derived from maize, with Brazil at the forefront of biofuel production, further boosting the region’s maize demand.
Livestock Industry Growth: Maize is a major ingredient in animal feed, and the expanding livestock sector in South America, particularly in Brazil and Argentina, is increasing maize consumption.
Favorable Climate and Agricultural Practices: South America’s climate is conducive to large-scale maize cultivation, and advances in farming techniques, such as precision agriculture, are improving yields and reducing crop risks.
Rising Export Demand: The demand for South American maize in global markets, including China, the European Union, and other emerging markets, is driving the region’s export growth.
Market Restraints
Despite the positive growth trajectory, the South American Maize Market faces several challenges:
Volatility in Global Commodity Prices: The market is sensitive to fluctuations in global maize prices, which can impact profitability for farmers and producers in South America.
Climate Change Risks: Extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, are increasingly affecting maize production in South America. Climate change poses a significant threat to crop yields and food security in the region.
Dependence on Global Trade Agreements: South America’s maize market is heavily influenced by international trade agreements, and any changes in tariffs or trade barriers can negatively impact exports.
Pests and Diseases: The region is vulnerable to pests and diseases that can affect maize yields, necessitating investment in pest control and crop protection methods.
Market Opportunities
The South American Maize Market presents several growth opportunities:
Technological Advancements: The adoption of modern farming technologies, such as drones, IoT devices, and GM maize varieties, offers opportunities for improving yields, reducing costs, and enhancing crop resilience.
Expansion of Biofuel Production: Increased demand for renewable energy sources provides a significant opportunity for South American maize producers to expand their role in biofuel production, particularly ethanol.
Diversification of Export Markets: As global demand for maize continues to grow, South America has opportunities to expand its exports to new markets, including emerging economies in Africa and Asia.
Sustainability Practices: With rising global awareness of sustainability, South American farmers can adopt eco-friendly agricultural practices, such as conservation tillage and crop rotation, to increase market appeal and improve environmental outcomes.
Market Dynamics
The South American Maize Market is shaped by the following dynamics:
Economic Importance: Maize is a key economic driver in South America, supporting agriculture, food industries, and the biofuel sector.
Government Policies and Subsidies: Government policies and subsidies in countries like Brazil and Argentina, aimed at supporting maize production, play a critical role in ensuring market stability and encouraging investment in the sector.
Global Supply Chains: South American maize is a critical component of global agricultural supply chains, especially in terms of exports to large markets like China and the European Union.
Consumer Preferences: Changing dietary habits and increasing awareness of the nutritional benefits of maize-based foods are contributing to the growing demand for maize in both regional and international markets.
Regional Analysis
The South American Maize Market is dominated by key countries with large-scale production capabilities:
Brazil: As the largest producer of maize in South America, Brazil plays a leading role in both regional and global maize markets. The country’s vast agricultural landscape and favorable climate make it a major exporter, particularly to China and the European Union.
Argentina: Argentina is another major player in the South American maize market, with its strong agricultural sector and high-quality maize production. The country is also a significant exporter of maize to international markets.
Paraguay: Paraguay has experienced growth in its maize production due to favorable growing conditions and increasing demand from both domestic and export markets.
Other South American Countries: Other countries such as Bolivia, Uruguay, and Colombia are also involved in maize production, contributing to regional trade and export markets.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the South American Maize Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
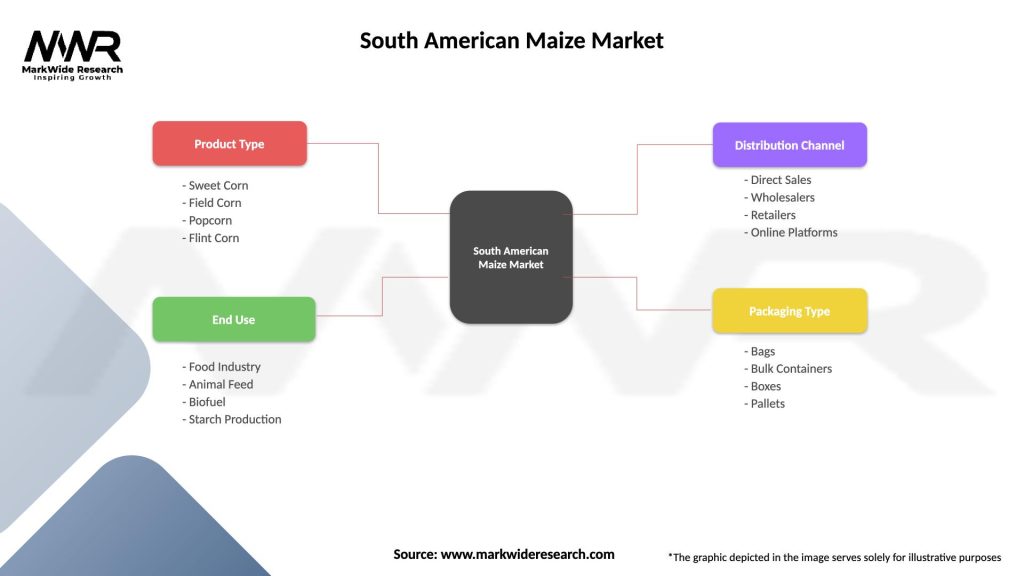
The South American Maize Market can be segmented based on the following factors:
Type of Maize: Yellow Maize, White Maize, and Other Varieties.
End-Use Application: Food and Beverage, Animal Feed, Biofuel Production, Industrial Use.
Distribution Channel: Direct Sales, Export, Processing Companies.
Geography: Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, and Other South American Countries.
Category-wise Insights
Each category of maize production offers distinct applications and benefits:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Export Opportunities: With global demand for maize growing, South American producers can leverage the region’s agricultural advantages to expand export markets.
Technological Advancements: Adoption of new farming technologies can increase productivity, enhance sustainability, and improve market competitiveness.
Sustainability Focus: Industry stakeholders can benefit from adopting environmentally friendly practices that align with global sustainability trends and meet consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Biofuel Demand: The rising global demand for renewable energy sources, particularly biofuels, is driving increased use of maize for ethanol production.
Adoption of GM Crops: The use of genetically modified maize varieties to improve yield and pest resistance is a growing trend in the region.
Sustainability Focus: Increasing emphasis on sustainable farming practices and reducing the environmental impact of maize production is a key trend in the market.
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the South American Maize Market. While disruptions in global supply chains initially affected exports, the agricultural sector has largely recovered, with demand for maize-based food and biofuels remaining strong. The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of food security and efficient agricultural practices in the region.
Key Industry Developments
Product Innovations: Companies are innovating in maize-based biofuels and food products to cater to growing global demand.
Strategic Partnerships: Partnerships between agricultural cooperatives, food processors, and biofuel companies are strengthening the maize supply chain in South America.
Analyst Suggestions
Diversify Export Markets: South American producers should continue to expand their export markets, particularly in emerging economies in Asia and Africa.
Invest in Sustainable Practices: Stakeholders should invest in sustainable farming techniques to future-proof the maize market in South America against climate change risks.
Future Outlook:
The South American maize market is expected to witness continued growth, driven by population growth, increasing demand from various industries, and expanding international trade. However, to sustain this growth, industry players must remain adaptable to changing market dynamics and invest in innovative practices.
Conclusion:
The South American maize market plays a pivotal role in the region’s agricultural and economic landscape. With increasing demand from diverse industries and export opportunities, the market presents promising prospects for stakeholders. By addressing challenges like climate variability and price volatility, and capitalizing on emerging trends, the South American maize industry can secure a thriving future. Industry participants and policymakers must work collaboratively to ensure sustainable and resilient growth in this vital sector.
What is Maize?
Maize, also known as corn, is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico. It is a staple food in many South American countries and is used for various applications, including animal feed, food products, and biofuels.
What are the key players in the South American Maize Market?
Key players in the South American Maize Market include companies like Bunge Limited, Cargill, and Archer Daniels Midland Company. These companies are involved in various aspects of maize production, processing, and distribution, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the South American Maize Market?
The South American Maize Market is driven by factors such as increasing demand for animal feed, rising biofuel production, and the growing popularity of maize-based food products. Additionally, favorable climatic conditions in certain regions contribute to higher maize yields.
What challenges does the South American Maize Market face?
The South American Maize Market faces challenges such as climate change impacts, pest infestations, and fluctuating market prices. These factors can affect production stability and profitability for farmers and producers.
What opportunities exist in the South American Maize Market?
Opportunities in the South American Maize Market include the expansion of export markets, advancements in agricultural technology, and the development of genetically modified maize varieties. These factors can enhance productivity and meet global demand.
What trends are shaping the South American Maize Market?
Trends in the South American Maize Market include a shift towards sustainable farming practices, increased investment in biotechnology, and the growing use of maize in renewable energy production. These trends are influencing how maize is cultivated and utilized.
South American Maize Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Sweet Corn, Field Corn, Popcorn, Flint Corn |
| End Use | Food Industry, Animal Feed, Biofuel, Starch Production |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Wholesalers, Retailers, Online Platforms |
| Packaging Type | Bags, Bulk Containers, Boxes, Pallets |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the South American Maize Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at