444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The South America membrane water and wastewater treatment market represents a rapidly expanding sector driven by increasing environmental regulations, water scarcity concerns, and growing industrial demand for advanced filtration technologies. This market encompasses various membrane technologies including reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, microfiltration, and nanofiltration systems designed to address the region’s diverse water treatment challenges.
Regional dynamics indicate that South America is experiencing significant growth in membrane-based treatment solutions, with countries like Brazil, Argentina, Chile, and Colombia leading adoption rates. The market is characterized by increasing investments in water infrastructure, stringent environmental policies, and rising awareness about water quality standards across municipal, industrial, and residential sectors.
Technology advancement continues to drive market expansion, with membrane systems offering superior efficiency rates of approximately 95-99% contaminant removal compared to conventional treatment methods. The region’s unique geographical challenges, including varying water quality conditions and diverse industrial requirements, create substantial opportunities for specialized membrane solutions.
Market penetration across South America shows promising growth trajectories, particularly in urban areas where water treatment infrastructure modernization is prioritized. The integration of smart technologies and automated monitoring systems is enhancing operational efficiency while reducing maintenance costs for end-users.
The South America membrane water and wastewater treatment market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of membrane-based filtration technologies, systems, and services designed to purify water and treat wastewater across residential, commercial, and industrial applications throughout South American countries.
Membrane technology utilizes semi-permeable barriers to separate contaminants, dissolved solids, and impurities from water through various filtration mechanisms. These systems employ physical and chemical processes to achieve high-quality water output suitable for drinking, industrial processes, or safe environmental discharge.
Treatment applications encompass municipal water treatment plants, industrial wastewater processing, desalination facilities, and distributed water treatment systems. The market includes membrane modules, complete treatment systems, replacement components, and associated maintenance services.
Regional scope covers major South American markets including Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Peru, Venezuela, Ecuador, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana, each presenting unique water treatment challenges and regulatory requirements.
Market dynamics in South America’s membrane water and wastewater treatment sector demonstrate robust expansion driven by environmental sustainability initiatives and infrastructure modernization programs. The region’s diverse industrial base, including mining, oil and gas, food processing, and manufacturing sectors, creates substantial demand for advanced water treatment solutions.
Key growth drivers include increasing water scarcity concerns, stricter environmental regulations, and rising industrial water consumption requiring efficient treatment and recycling systems. Government initiatives promoting sustainable water management practices are accelerating market adoption rates across multiple sectors.
Technology trends show significant advancement in membrane materials, system automation, and energy efficiency improvements. Smart monitoring systems and predictive maintenance capabilities are becoming standard features, enhancing operational reliability and reducing total cost of ownership.
Competitive landscape features both international technology providers and regional system integrators working to address local market requirements. Strategic partnerships between global membrane manufacturers and local engineering companies are facilitating market penetration and technology transfer.
Future prospects indicate sustained growth potential driven by ongoing urbanization, industrial expansion, and increasing environmental awareness. The market is expected to benefit from continued infrastructure investments and technological innovations improving system performance and cost-effectiveness.
Primary market insights reveal several critical factors shaping the South America membrane water and wastewater treatment landscape:
Environmental regulations serve as primary market drivers, with South American governments implementing stricter water quality standards and discharge requirements. These regulatory frameworks mandate advanced treatment technologies capable of meeting stringent environmental protection criteria.
Water scarcity concerns across the region are accelerating adoption of membrane-based treatment and recycling systems. Countries experiencing drought conditions and competing water demands are prioritizing efficient treatment technologies that maximize water recovery rates.
Industrial expansion in key sectors including mining, petrochemicals, food processing, and manufacturing creates substantial demand for specialized water treatment solutions. These industries require reliable treatment systems to manage process water, cooling water, and wastewater discharge requirements.
Urbanization trends throughout South America are straining existing water infrastructure, necessitating advanced treatment technologies to serve growing populations. Municipal authorities are investing in membrane systems to ensure reliable water supply and effective wastewater management.
Technology advancement continues improving membrane performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Innovations in membrane materials, system design, and automation are making advanced treatment solutions more accessible to diverse market segments.
Economic development across the region is generating increased water consumption and wastewater production, requiring scalable treatment solutions. Growing industrial activity and improved living standards are driving demand for higher water quality standards.
High capital costs associated with membrane system installation and infrastructure development present significant barriers, particularly for smaller municipalities and industrial facilities with limited budgets. Initial investment requirements can be substantial compared to conventional treatment alternatives.
Technical complexity of membrane systems requires specialized expertise for design, installation, and maintenance operations. Limited availability of trained technicians and engineers in certain regions can constrain market growth and system performance.
Energy consumption requirements for membrane systems, particularly reverse osmosis applications, can result in significant operational costs. High-pressure pumping systems and associated energy demands may limit adoption in areas with expensive or unreliable electricity supply.
Membrane fouling and replacement costs create ongoing operational challenges requiring regular maintenance and periodic membrane replacement. These factors contribute to total cost of ownership considerations that may deter some potential users.
Economic volatility in certain South American countries can impact infrastructure investment decisions and project financing availability. Currency fluctuations and economic uncertainty may delay or cancel planned water treatment projects.
Competition from alternatives including conventional treatment technologies and emerging solutions may limit membrane system adoption in price-sensitive applications where performance requirements are less stringent.
Infrastructure modernization programs across South America present substantial opportunities for membrane technology providers. Aging water treatment facilities require upgrades to meet current performance and regulatory standards, creating demand for advanced membrane solutions.
Industrial water recycling initiatives offer significant growth potential as companies seek to reduce water consumption and environmental impact. Membrane systems enable efficient water recovery and reuse across various industrial processes.
Desalination projects along South America’s extensive coastline represent emerging opportunities, particularly in water-stressed regions. Membrane-based desalination technology can provide reliable freshwater supply for municipal and industrial applications.
Decentralized treatment solutions are gaining traction in remote areas and smaller communities where centralized infrastructure is impractical. Modular membrane systems offer scalable treatment capabilities suitable for distributed applications.
Smart water management integration creates opportunities for advanced monitoring and control systems. IoT-enabled membrane systems with predictive maintenance capabilities appeal to operators seeking operational efficiency improvements.
Public-private partnerships facilitate large-scale infrastructure projects combining public sector requirements with private sector expertise and financing. These arrangements can accelerate membrane technology deployment across the region.
Supply chain dynamics in the South America membrane market involve complex interactions between international technology providers, regional distributors, and local system integrators. Global membrane manufacturers are establishing regional partnerships to improve market access and customer support capabilities.
Demand patterns vary significantly across countries and applications, with industrial sectors typically showing more consistent demand compared to municipal markets that may be subject to political and budgetary constraints. Seasonal variations in water availability also influence treatment system utilization rates.
Pricing dynamics reflect competitive pressures between established international suppliers and emerging regional providers. Technology commoditization in certain membrane categories is driving price competition while specialized applications maintain premium pricing structures.
Innovation cycles continue advancing membrane technology performance and reducing operational costs. Research and development investments focus on improving membrane selectivity, durability, and energy efficiency while reducing manufacturing costs.
Regulatory dynamics show increasing harmonization of water quality standards across South American countries, facilitating regional market development. However, implementation timelines and enforcement mechanisms vary significantly between jurisdictions.
Investment dynamics demonstrate growing interest from international development banks and private investors in water infrastructure projects. According to MarkWide Research analysis, infrastructure financing availability is improving across multiple South American markets.
Primary research methodology encompasses comprehensive interviews with industry stakeholders including membrane manufacturers, system integrators, end-users, and regulatory authorities across major South American markets. Direct engagement with market participants provides insights into current trends, challenges, and future requirements.
Secondary research involves extensive analysis of industry reports, government publications, trade association data, and company financial statements. This approach ensures comprehensive coverage of market dynamics and competitive landscape developments.
Data collection procedures utilize multiple sources including industry surveys, expert interviews, trade show participation, and facility visits. Information validation through cross-referencing ensures accuracy and reliability of market intelligence.
Market sizing methodology employs bottom-up and top-down approaches to validate market scope and growth projections. Regional analysis considers country-specific factors including regulatory requirements, economic conditions, and infrastructure development plans.
Competitive analysis examines market share distribution, technology positioning, and strategic initiatives across key industry participants. Company profiling includes assessment of capabilities, geographic presence, and growth strategies.
Trend analysis identifies emerging technologies, regulatory developments, and market opportunities through systematic monitoring of industry developments and stakeholder feedback. Forward-looking assessments consider potential market disruptions and growth catalysts.
Brazil dominates the South American membrane water and wastewater treatment market, representing approximately 50% of regional activity driven by large industrial base, extensive urban infrastructure, and progressive environmental regulations. Major cities including São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Brasília are implementing advanced membrane systems for municipal water treatment.
Argentina maintains the second-largest market position with significant industrial applications in food processing, petrochemicals, and mining sectors. Buenos Aires and surrounding metropolitan areas are prioritizing water infrastructure modernization using membrane technologies.
Chile demonstrates strong growth potential, particularly in mining applications where water scarcity and environmental regulations drive demand for efficient treatment and recycling systems. The country’s extensive coastline also presents desalination opportunities.
Colombia shows increasing market activity driven by oil and gas industry requirements and urban infrastructure development. Government initiatives promoting water access and quality improvements are supporting membrane technology adoption.
Peru’s market is characterized by mining industry demand and growing municipal treatment requirements. Lima and other major cities are investing in advanced water treatment infrastructure to serve expanding populations.
Other regional markets including Venezuela, Ecuador, Uruguay, and Paraguay present emerging opportunities despite varying economic and political conditions. Each country offers unique applications and growth potential for membrane technology providers.
Market leadership in South America’s membrane water and wastewater treatment sector involves both international technology providers and regional specialists competing across various application segments and geographic markets.
Competitive strategies focus on technology innovation, local partnerships, and comprehensive service offerings. Companies are establishing regional manufacturing and service capabilities to better serve South American markets while reducing costs and delivery times.
Market positioning varies by company, with some focusing on premium technology solutions while others emphasize cost-effective alternatives for price-sensitive applications. Strategic acquisitions and joint ventures are common approaches for market expansion.
By Technology:
By Application:
By End-User:
Industrial applications represent the largest and most dynamic market segment, driven by diverse manufacturing sectors requiring specialized water treatment solutions. Mining operations, particularly in Chile, Peru, and Brazil, generate substantial demand for membrane systems capable of handling challenging water chemistry and achieving high recovery rates.
Municipal treatment category shows steady growth as cities modernize aging infrastructure and expand service coverage. Large metropolitan areas are implementing membrane bioreactors and advanced filtration systems to meet growing population demands and environmental standards.
Desalination applications are emerging as important growth drivers, particularly in coastal regions experiencing water stress. Countries with extensive coastlines are exploring membrane-based desalination as a reliable freshwater source for municipal and industrial use.
Water recycling systems are gaining importance as industries and municipalities seek to reduce water consumption and environmental impact. Membrane technology enables high-quality water recovery suitable for various reuse applications.
Technology categories show distinct performance characteristics and application suitability. Reverse osmosis maintains market leadership due to versatility and proven performance, while ultrafiltration and microfiltration serve specialized pretreatment and clarification requirements.
Service categories including system design, installation, maintenance, and membrane replacement are becoming increasingly important as markets mature. Comprehensive service offerings differentiate suppliers and improve customer relationships.
Technology providers benefit from expanding market opportunities driven by infrastructure modernization and environmental regulations. South America’s diverse industrial base and growing urban populations create sustained demand for advanced membrane solutions.
End-users gain significant operational advantages including improved water quality, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced regulatory compliance. Membrane systems offer reliable performance and automated operation reducing labor requirements and operational complexity.
System integrators capitalize on growing demand for turnkey solutions combining membrane technology with complementary treatment processes. Local expertise in project management and regulatory compliance provides competitive advantages.
Government agencies achieve environmental protection and public health objectives through advanced water treatment infrastructure. Membrane technology supports sustainable development goals and improves quality of life for citizens.
Financial institutions find attractive investment opportunities in water infrastructure projects with stable returns and positive environmental impact. Public-private partnerships provide risk mitigation and long-term revenue streams.
Environmental consultants benefit from increasing demand for technical expertise in system selection, regulatory compliance, and environmental impact assessment. Specialized knowledge of membrane technology applications creates valuable consulting opportunities.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Smart technology integration is transforming membrane system operations through IoT sensors, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities. These innovations improve system reliability while reducing operational costs and downtime.
Energy efficiency improvements continue advancing through better membrane materials, system design optimization, and energy recovery technologies. New developments are achieving 20-30% energy savings compared to conventional membrane systems.
Modular system design is gaining popularity for its flexibility and scalability advantages. Containerized and skid-mounted systems enable rapid deployment and easy capacity expansion as requirements change.
Membrane material innovation focuses on improving fouling resistance, chemical compatibility, and operational lifespan. Advanced materials are extending membrane life while maintaining high performance standards.
Automation advancement reduces manual intervention requirements and improves process consistency. Automated cleaning systems, chemical dosing, and performance optimization are becoming standard features.
Sustainability focus drives development of environmentally friendly membrane materials and energy-efficient system designs. Circular economy principles are influencing membrane recycling and waste reduction initiatives.
Technology partnerships between international membrane manufacturers and regional system integrators are expanding market reach and improving customer support capabilities. These collaborations combine global expertise with local market knowledge.
Manufacturing localization initiatives are establishing regional production facilities to reduce costs and delivery times. Several major suppliers are investing in South American manufacturing capabilities to better serve local markets.
Research collaborations between universities, government agencies, and industry participants are advancing membrane technology development. These partnerships focus on addressing regional water treatment challenges and developing cost-effective solutions.
Regulatory harmonization efforts across South American countries are creating more consistent market conditions and facilitating cross-border business development. Standardized testing protocols and performance criteria benefit both suppliers and users.
Digital transformation initiatives are integrating advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning into membrane system operations. These technologies enable predictive maintenance and performance optimization.
Sustainability programs are promoting responsible membrane disposal and recycling practices. Industry initiatives focus on reducing environmental impact throughout the membrane lifecycle from production to disposal.
Market entry strategies should prioritize local partnerships and comprehensive service capabilities to succeed in South American markets. Understanding regional regulatory requirements and customer preferences is essential for effective market penetration.
Technology positioning must balance performance capabilities with cost considerations to address diverse market segments. Flexible product portfolios accommodating various application requirements and budget constraints will maximize market opportunities.
Service excellence becomes increasingly important as markets mature and competition intensifies. Comprehensive technical support, training programs, and maintenance services differentiate suppliers and build customer loyalty.
Investment priorities should focus on emerging applications including desalination, industrial water recycling, and decentralized treatment systems. These segments offer higher growth potential compared to traditional municipal applications.
Risk management strategies must address economic volatility, currency fluctuations, and political uncertainties common in South American markets. Diversified geographic presence and flexible business models help mitigate these risks.
Innovation focus should emphasize energy efficiency, automation, and smart technology integration to meet evolving customer requirements. MWR analysis suggests that these features are becoming essential for competitive positioning.
Growth projections for the South America membrane water and wastewater treatment market indicate sustained expansion driven by continued infrastructure investment, industrial development, and environmental regulations. The market is expected to maintain robust growth rates exceeding 8% annually over the next decade.
Technology evolution will continue improving membrane performance while reducing costs and energy consumption. Next-generation materials and system designs promise enhanced efficiency and longer operational life, making membrane technology more accessible to diverse applications.
Market maturation across different segments will create opportunities for specialized solutions and value-added services. Industrial applications are expected to maintain leadership while municipal and commercial segments show accelerating growth.
Regional development patterns suggest that Brazil and Argentina will continue dominating market activity while smaller countries present emerging opportunities. Coastal nations are likely to increase desalination investments as water scarcity concerns intensify.
Investment trends indicate growing interest from international development banks and private investors in water infrastructure projects. Public-private partnerships will facilitate large-scale membrane system deployments across the region.
Competitive dynamics will intensify as more suppliers enter the market and technology commoditization continues. Success will depend on innovation capabilities, service excellence, and deep understanding of local market requirements.
The South America membrane water and wastewater treatment market represents a dynamic and rapidly expanding sector with substantial growth potential driven by environmental regulations, infrastructure modernization, and industrial development. Regional diversity creates multiple opportunities across various applications and geographic markets, while technology advancement continues improving system performance and cost-effectiveness.
Market fundamentals remain strong with increasing water scarcity concerns, stricter environmental standards, and growing industrial water consumption supporting sustained demand for advanced membrane solutions. The region’s extensive industrial base, urbanization trends, and government infrastructure investments provide solid foundations for continued market expansion.
Success factors for market participants include comprehensive service capabilities, local partnerships, technology innovation, and deep understanding of regional requirements. Companies that can effectively combine global expertise with local market knowledge will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities while managing inherent risks.
Future prospects indicate that the South America membrane water and wastewater treatment market will continue evolving toward more sophisticated, efficient, and sustainable solutions. As technology costs decline and performance improves, membrane systems will become increasingly accessible to diverse applications, supporting the region’s sustainable development objectives and environmental protection goals.
What is Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment?
Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment refers to processes that use semi-permeable membranes to separate contaminants from water and wastewater. This technology is widely used in various applications, including municipal water treatment, industrial wastewater management, and desalination.
What are the key players in the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market?
Key players in the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market include Veolia Environnement, SUEZ, and Xylem Inc. These companies are known for their innovative solutions and extensive experience in water treatment technologies, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market?
The growth of the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market is driven by increasing water scarcity, stringent environmental regulations, and the rising demand for clean water. Additionally, advancements in membrane technology are enhancing treatment efficiency and reducing operational costs.
What challenges does the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market face?
Challenges in the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market include high initial investment costs and the need for skilled personnel to operate advanced systems. Furthermore, membrane fouling and maintenance can pose significant operational hurdles.
What opportunities exist in the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market?
Opportunities in the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market include the growing focus on sustainable water management practices and the increasing adoption of advanced treatment technologies. There is also potential for expansion in rural areas where access to clean water is limited.
What trends are shaping the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market?
Trends in the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market include the integration of smart technologies for monitoring and control, the development of more efficient membrane materials, and a shift towards decentralized treatment solutions. These trends are aimed at improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
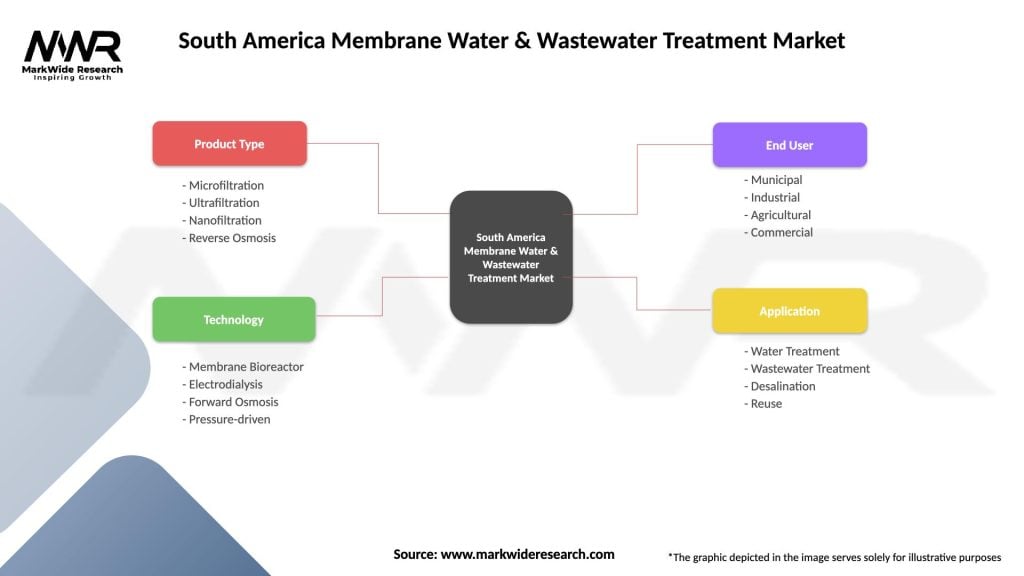
South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Microfiltration, Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration, Reverse Osmosis |
| Technology | Membrane Bioreactor, Electrodialysis, Forward Osmosis, Pressure-driven |
| End User | Municipal, Industrial, Agricultural, Commercial |
| Application | Water Treatment, Wastewater Treatment, Desalination, Reuse |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the South America Membrane Water & Wastewater Treatment Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at