444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Smart Manufacturing Devices encompass a wide range of advanced tools, equipment, and systems that leverage interconnected technologies to optimize manufacturing operations. These devices are designed to enhance productivity, quality, and operational efficiency while reducing costs and human intervention. From intelligent sensors and robotic systems to predictive maintenance solutions and automated production lines, these devices are transforming traditional factories into smart, connected ecosystems.
Meaning
At its core, Smart Manufacturing aims to create a seamless synergy between physical manufacturing processes and digital technologies. This integration allows manufacturers to monitor, analyze, and optimize their operations in real-time, leading to better decision-making, resource allocation, and ultimately, improved business outcomes. By gathering and analyzing data from various points within the manufacturing process, companies can uncover insights that drive continuous improvement and innovation.
Executive Summary
The Smart Manufacturing Devices market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, growing demand for automated and intelligent manufacturing solutions, and the need for streamlined and agile production processes. This market offers a plethora of opportunities for businesses to enhance their competitiveness and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
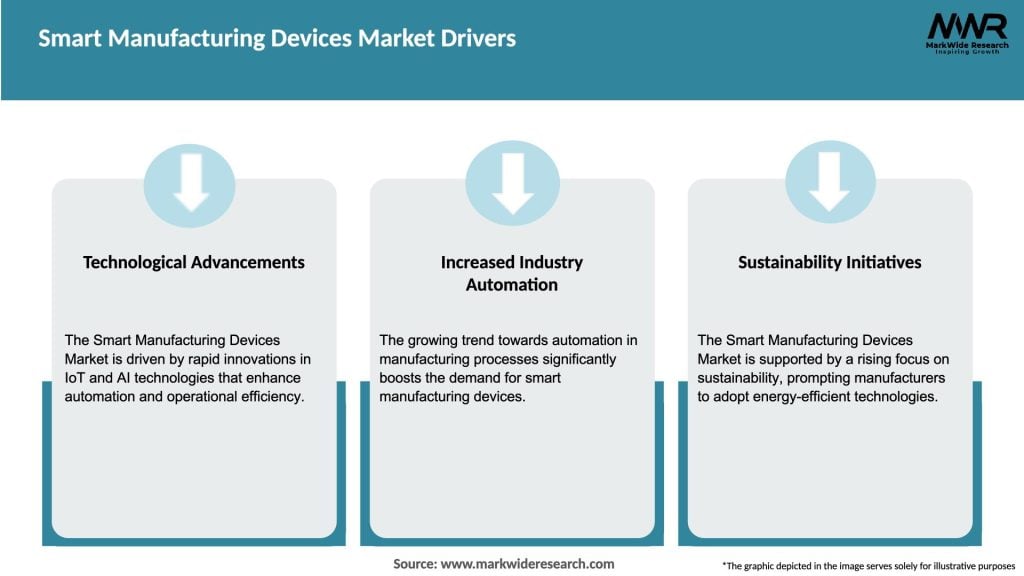
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Smart Manufacturing Devices market is characterized by its dynamic nature, as it constantly evolves in response to technological advancements and changing industry demands. Manufacturers are actively adopting these devices to enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and remain competitive in the market.
Regional Analysis
The adoption of Smart Manufacturing Devices is a global phenomenon, with varying degrees of penetration across different regions. Developed economies such as North America and Europe are leading the charge due to their robust technological infrastructure and established manufacturing sectors. Meanwhile, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are rapidly embracing these devices to drive industrial growth.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
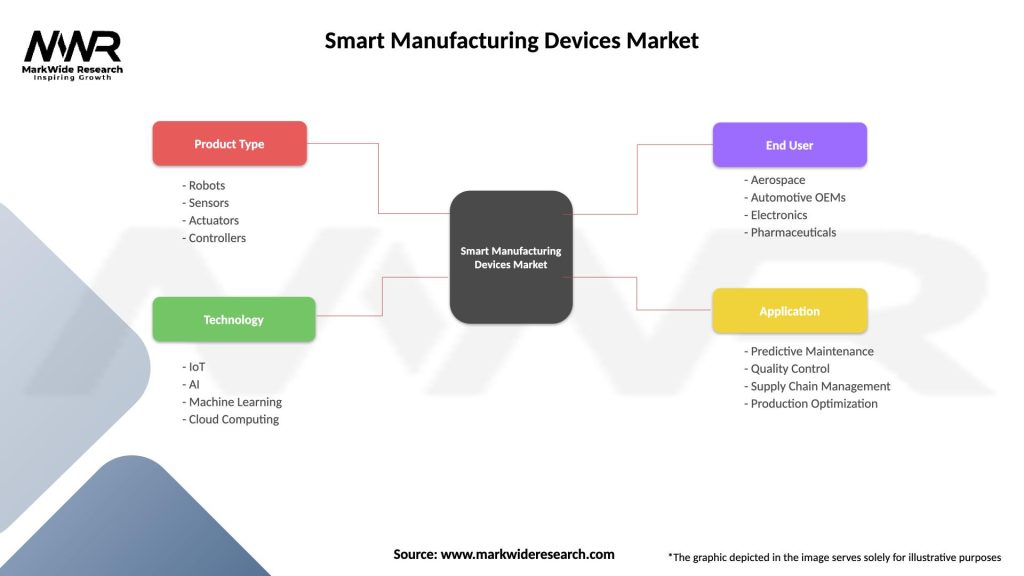
Segmentation
The market can be segmented based on device type, industry vertical, and geographic region. Device types include intelligent sensors, industrial robots, 3D printers, automation systems, and more. Industry verticals range from automotive and aerospace to electronics and pharmaceuticals.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, prompting manufacturers to rethink their strategies. Smart Manufacturing Devices helped companies adapt to disruptions by enabling remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and agile production shifts.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Smart Manufacturing Devices market is poised for substantial growth as technological advancements continue to drive innovation. Industry players that embrace digital transformation and smart technologies are likely to thrive in the evolving manufacturing landscape.
Conclusion
The Smart Manufacturing Devices market represents a seismic shift in the world of manufacturing, ushering in an era of unprecedented efficiency, quality, and agility. As companies strive to remain competitive in an increasingly digitalized world, the adoption of these devices is no longer a luxury but a necessity. By embracing the power of smart technologies, manufacturers are not only revolutionizing their processes but also shaping the future of industry on a global scale.
What is Smart Manufacturing Devices?
Smart Manufacturing Devices refer to advanced tools and equipment that utilize technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to enhance manufacturing processes. These devices improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enable real-time monitoring and control of production systems.
What are the key players in the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market?
Key players in the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market include Siemens, Rockwell Automation, Honeywell, and ABB, among others. These companies are known for their innovative solutions that integrate smart technologies into manufacturing processes.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market include the increasing demand for automation, the need for operational efficiency, and the rising adoption of Industry Four Point Zero technologies. These factors are pushing manufacturers to invest in smart devices to stay competitive.
What challenges does the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market face?
The Smart Manufacturing Devices Market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs, cybersecurity risks, and the need for skilled workforce to operate advanced technologies. These factors can hinder the adoption of smart manufacturing solutions.
What opportunities exist in the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market?
Opportunities in the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market include the expansion of smart factories, advancements in AI and machine learning, and the growing emphasis on sustainability in manufacturing processes. These trends are likely to create new avenues for innovation and growth.
What trends are shaping the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market?
Trends shaping the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market include the integration of AI and machine learning for predictive maintenance, the rise of collaborative robots, and the increasing use of data analytics for decision-making. These innovations are transforming traditional manufacturing practices.
Smart Manufacturing Devices Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Robots, Sensors, Actuators, Controllers |
| Technology | IoT, AI, Machine Learning, Cloud Computing |
| End User | Aerospace, Automotive OEMs, Electronics, Pharmaceuticals |
| Application | Predictive Maintenance, Quality Control, Supply Chain Management, Production Optimization |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Smart Manufacturing Devices Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at