444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market is witnessing exponential growth driven by increasing demand for non-invasive temperature monitoring solutions, technological advancements in sensor technology, and rising healthcare awareness. Smart thermometers offer real-time temperature monitoring, data analytics, and connectivity features, revolutionizing patient care and public health surveillance.
Meaning
Smart and non-contact thermometers are medical devices used for measuring body temperature without direct skin contact. These thermometers utilize infrared technology to detect thermal radiation emitted by the body, providing accurate temperature readings quickly and non-invasively.
Executive Summary
The Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market is experiencing rapid expansion fueled by advancements in sensor technology, growing healthcare awareness, and the need for non-invasive temperature monitoring solutions amidst the COVID-19 pandemic. Stakeholders must capitalize on key market trends, innovate, and adapt to evolving consumer needs to drive market growth and differentiation.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, regulatory requirements, and market dynamics. Stakeholders must navigate these dynamics to capitalize on opportunities and address challenges effectively.
Regional Analysis
The Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market exhibits regional variations driven by factors such as healthcare infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, technological adoption, and market demand. Key regions include North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
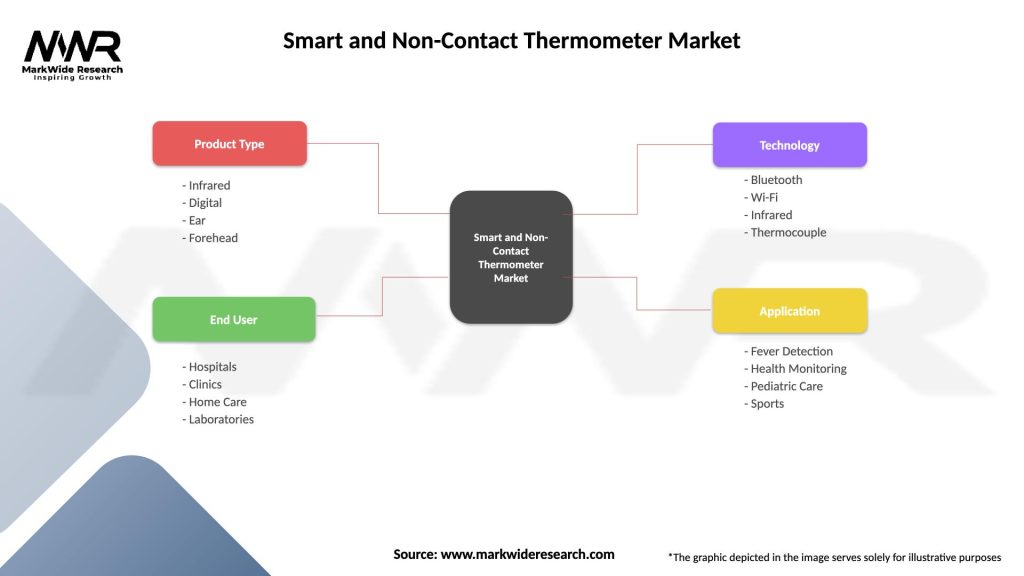
Segmentation
The Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market can be segmented based on product type, technology, application, end user, and geography, providing insights into market dynamics, trends, and growth opportunities across diverse segments.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has catalyzed the adoption of smart and non-contact thermometers for fever screening, public health surveillance, and pandemic preparedness efforts. Industry stakeholders have responded by ramping up production, enhancing product features, and ensuring supply chain resilience to meet surging demand for temperature monitoring solutions.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market is poised for significant growth driven by increasing demand for non-invasive temperature monitoring solutions, technological advancements in sensor technology, and pandemic preparedness efforts. Industry stakeholders must leverage key market trends, innovate, and adapt to evolving consumer needs to drive market growth and differentiation.
Conclusion
The Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market represents a critical segment within the healthcare industry, offering non-invasive temperature monitoring solutions for various clinical and non-clinical applications. With increasing demand for infection control, telehealth integration, and pandemic preparedness, smart thermometers have emerged as essential tools for healthcare professionals, caregivers, and individuals. By investing in research and development, telehealth integration, regulatory compliance, and education initiatives, stakeholders can capitalize on market opportunities, drive innovation, and contribute to advancements in healthcare and public health surveillance.
What is Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer?
Smart and Non-Contact Thermometers are devices that measure body temperature without direct contact, often using infrared technology. They are widely used in healthcare settings, homes, and public places for quick and hygienic temperature assessments.
What are the key players in the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market?
Key players in the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market include companies like Braun, Omron, and Philips, which are known for their innovative temperature measurement solutions. These companies focus on enhancing accuracy and user experience, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market?
The growth of the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market is driven by increasing health awareness, the rise in infectious diseases, and the demand for quick and non-invasive temperature measurement solutions. Additionally, technological advancements in thermometer design contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market face?
Challenges in the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market include the potential for inaccurate readings due to environmental factors and the need for regular calibration. Furthermore, competition from traditional thermometers may hinder market growth.
What opportunities exist in the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market?
Opportunities in the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market include the integration of smart technology for data tracking and remote monitoring. The growing trend of telehealth services also presents avenues for expanding the use of these thermometers in various healthcare settings.
What trends are shaping the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market?
Trends in the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market include the increasing adoption of smart home healthcare devices and the development of multifunctional thermometers that can measure other vital signs. Additionally, the focus on user-friendly designs and mobile app integration is gaining traction.
Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Infrared, Digital, Ear, Forehead |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Home Care, Laboratories |
| Technology | Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Infrared, Thermocouple |
| Application | Fever Detection, Health Monitoring, Pediatric Care, Sports |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Smart and Non-Contact Thermometer Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at