444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Sink Float Tank Market caters to the growing demand for efficient waste separation solutions in recycling facilities, manufacturing plants, and waste management operations. Sink float tanks, also known as density separators or gravity separators, are essential equipment used to separate materials based on their density, facilitating the recycling of plastics, metals, glass, and other materials. As sustainability initiatives and environmental regulations drive the need for effective waste sorting and resource recovery, the sink float tank market experiences steady growth and innovation to meet evolving industry demands.
Meaning
Sink float tanks are specialized equipment designed to separate materials of different densities by exploiting the principle of buoyancy. The process involves introducing materials into a water-filled tank, where denser materials sink to the bottom while lighter materials float on the surface. By adjusting water flow rates and tank configurations, sink float tanks efficiently separate materials such as plastics, metals, paper, and glass, enabling recyclers to recover valuable resources and reduce waste sent to landfills or incineration.
Executive Summary
The Sink Float Tank Market witnesses sustained growth driven by increasing waste generation, rising recycling rates, and the need for efficient materials recovery solutions. Sink float tanks play a crucial role in the recycling industry by enabling the separation of mixed materials, improving material purity, and enhancing recycling yields. With advancements in technology, automation, and process optimization, the market offers opportunities for manufacturers, recyclers, and waste management companies to enhance their operational efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Sink Float Tank Market operates within a dynamic ecosystem shaped by factors such as waste generation trends, regulatory policies, technological innovations, market competition, and customer preferences. Market dynamics influence equipment design, performance standards, pricing models, and customer engagement strategies, driving continuous innovation, differentiation, and value creation across the recycling value chain.
Regional Analysis
Regional variations in waste composition, recycling infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and market maturity impact the adoption and deployment of sink float tanks within different geographic markets. Key regions driving market growth include North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa, each presenting unique opportunities and challenges for equipment manufacturers, recyclers, and waste management stakeholders.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Sink Float Tank Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
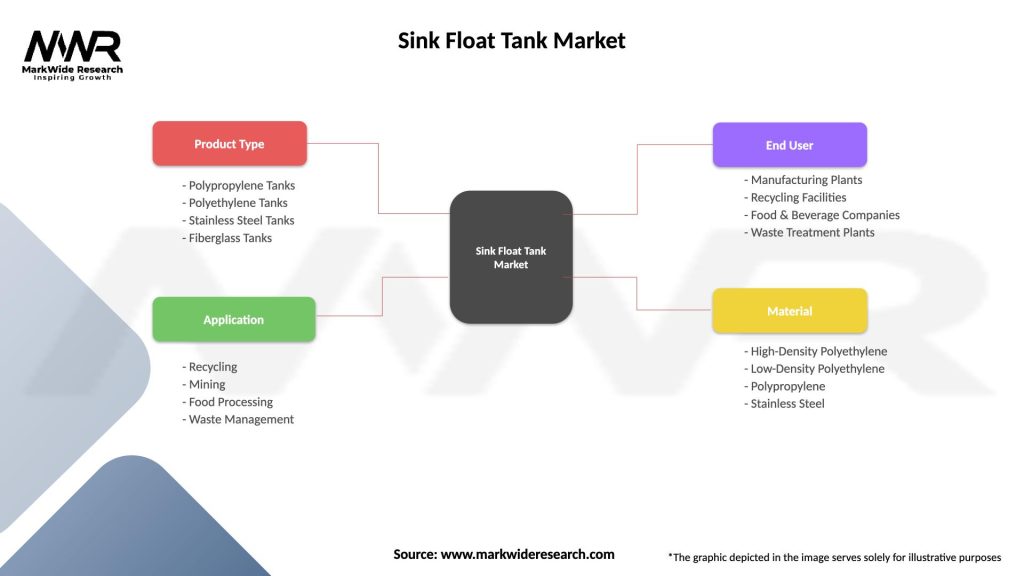
Segmentation
The Sink Float Tank Market can be segmented based on various criteria, including:
Segmentation enables equipment suppliers to tailor their product offerings, marketing strategies, and customer support services to specific market segments, addressing unique customer needs and maximizing market penetration.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected the Sink Float Tank Market by disrupting supply chains, delaying equipment installations, and impacting waste generation rates and recycling activities. However, the pandemic has also underscored the importance of resilient and sustainable waste management systems, driving investment in recycling infrastructure, including sink float tanks, to support circular economy objectives and enhance supply chain resilience.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Sink Float Tank Market is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by increasing waste volumes, regulatory mandates, technological advancements, and sustainability imperatives. Opportunities abound for equipment manufacturers, recyclers, and waste management stakeholders to leverage emerging trends, market dynamics, and industry developments to advance recycling infrastructure, enhance resource recovery, and promote environmental stewardship on a global scale.
Conclusion
The Sink Float Tank Market plays a pivotal role in the global recycling ecosystem, enabling efficient materials separation, resource recovery, and waste reduction across diverse industries and applications. By leveraging technology innovation, sustainability initiatives, and collaborative partnerships, stakeholders can unlock new opportunities, address market challenges, and contribute to a more circular and sustainable future for waste management and resource recovery worldwide.
What is Sink Float Tank?
A Sink Float Tank is a specialized vessel used in various industries to separate materials based on their density. It is commonly utilized in recycling processes, mineral processing, and waste management to efficiently sort and classify different materials.
What are the key players in the Sink Float Tank Market?
Key players in the Sink Float Tank Market include companies like Eriez Manufacturing, GEA Group, and Metso Outotec, which provide innovative solutions for material separation and processing, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Sink Float Tank Market?
The growth of the Sink Float Tank Market is driven by increasing demand for efficient recycling processes, the need for effective waste management solutions, and advancements in material separation technologies.
What challenges does the Sink Float Tank Market face?
Challenges in the Sink Float Tank Market include the high initial investment costs for advanced systems, the need for skilled operators, and competition from alternative separation technologies.
What opportunities exist in the Sink Float Tank Market?
Opportunities in the Sink Float Tank Market include the expansion of recycling initiatives globally, the development of eco-friendly materials, and the integration of automation and smart technologies in separation processes.
What trends are shaping the Sink Float Tank Market?
Trends in the Sink Float Tank Market include the increasing adoption of sustainable practices, the rise of circular economy initiatives, and innovations in tank design that enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Sink Float Tank Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Polypropylene Tanks, Polyethylene Tanks, Stainless Steel Tanks, Fiberglass Tanks |
| Application | Recycling, Mining, Food Processing, Waste Management |
| End User | Manufacturing Plants, Recycling Facilities, Food & Beverage Companies, Waste Treatment Plants |
| Material | High-Density Polyethylene, Low-Density Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Stainless Steel |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at