444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Shale Market is a dynamic sector within the energy industry, characterized by the extraction and production of oil and natural gas from shale rock formations. Shale formations contain significant reserves of hydrocarbons trapped within tight rock formations, requiring advanced drilling and extraction techniques such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking) to access and recover these resources. The shale market has experienced rapid growth in recent years, driven by technological advancements, increasing global energy demand, and the abundance of shale reserves in regions such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
Meaning
The Shale Market refers to the exploration, development, and production of oil and natural gas from shale formations using unconventional extraction techniques. Shale rock is a type of sedimentary rock that contains organic-rich materials, such as kerogen, which can be converted into hydrocarbons under high pressure and temperature conditions. Shale extraction involves drilling horizontal wells into shale formations and injecting a mixture of water, sand, and chemicals at high pressure to fracture the rock and release trapped hydrocarbons. The extracted oil and gas are then collected and processed for commercial use, providing a significant source of energy for various industries and applications.
Executive Summary
The Shale Market continues to play a crucial role in the global energy landscape, providing a reliable and abundant source of oil and natural gas to meet growing energy demand. Technological innovations such as horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing have unlocked vast reserves of shale resources, transforming countries like the United States into major energy producers and exporters. Despite environmental and regulatory challenges, the shale market remains resilient, driven by continued investments in exploration and production, as well as the emergence of new shale regions around the world.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of the Shale Market:
Market Restraints
Despite its growth potential, the Shale Market faces several challenges:
Market Opportunities
The Shale Market presents several opportunities for growth and innovation:
Market Dynamics
The Shale Market is influenced by various dynamic factors:
Regional Analysis
North America, particularly the United States, dominates the global Shale Market, accounting for a significant portion of shale oil and gas production. Key shale basins in North America include the Permian Basin, Eagle Ford Shale, Bakken Formation, Marcellus Shale, and Utica Shale. Other regions with emerging shale plays include Latin America (e.g., Vaca Muerta in Argentina), Europe (e.g., Permian Basin in the United Kingdom), and Asia-Pacific (e.g., Cooper Basin in Australia). Each region presents unique geological, regulatory, and market conditions that influence shale development opportunities and challenges.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Shale Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
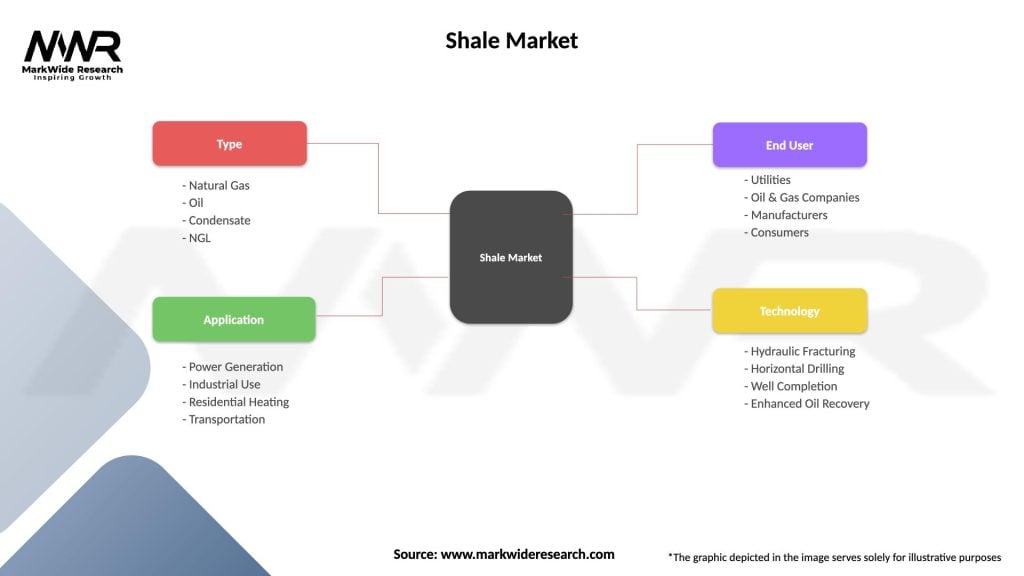
Segmentation
The Shale Market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the Shale Market, disrupting supply chains, reducing energy demand, and causing oil and gas price volatility. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and economic slowdowns led to reduced energy consumption and investment in shale projects, resulting in production cuts, bankruptcies, and job losses across the industry. However, as economies recover and energy demand rebounds, the shale market is expected to regain momentum, supported by government stimulus measures, infrastructure investments, and technology innovation.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Shale Market is poised for continued growth and transformation, driven by technological innovation, energy transition, and evolving market dynamics. While challenges such as environmental concerns, regulatory uncertainty, and market volatility persist, the shale industry remains resilient and adaptable, leveraging its strengths in technology, resource abundance, and operational expertise to navigate uncertainties and capitalize on emerging opportunities. With a focus on sustainability, collaboration, and innovation, the shale sector is well-positioned to play a pivotal role in meeting global energy needs and shaping the future of the energy landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Shale Market continues to be a vital component of the global energy mix, providing a reliable and abundant source of oil and natural gas to meet growing energy demand. Despite challenges and uncertainties, the shale industry remains resilient, driven by technological innovation, economic benefits, and energy security considerations. By embracing sustainability, innovation, and stakeholder engagement, shale companies can navigate market dynamics, address environmental concerns, and unlock new opportunities for growth and value creation in the evolving energy landscape.
What is Shale?
Shale is a fine-grained sedimentary rock that is rich in organic material and can be a significant source of hydrocarbons, particularly oil and natural gas. It is characterized by its ability to be split into thin layers and is often found in formations that are targeted for extraction in the energy sector.
What are the key players in the Shale Market?
Key players in the Shale Market include companies such as EOG Resources, Pioneer Natural Resources, and Devon Energy, which are involved in the exploration and production of shale oil and gas. These companies utilize advanced extraction techniques to maximize yield and efficiency, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Shale Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Shale Market include advancements in hydraulic fracturing technology, increasing energy demand, and the rising need for domestic energy sources. Additionally, the ability to extract oil and gas from previously inaccessible reserves has significantly boosted production levels.
What challenges does the Shale Market face?
The Shale Market faces several challenges, including environmental concerns related to water usage and pollution, regulatory hurdles, and fluctuating oil prices. These factors can impact the profitability and sustainability of shale extraction operations.
What opportunities exist in the Shale Market for the future?
Opportunities in the Shale Market include the potential for technological innovations that improve extraction efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Additionally, the growing global demand for cleaner energy sources may drive investment in shale gas as a transitional fuel.
What trends are currently shaping the Shale Market?
Current trends in the Shale Market include a shift towards more sustainable extraction practices, increased investment in renewable energy integration, and the adoption of digital technologies for monitoring and optimizing production. These trends reflect a broader industry move towards efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Shale Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Natural Gas, Oil, Condensate, NGL |
| Application | Power Generation, Industrial Use, Residential Heating, Transportation |
| End User | Utilities, Oil & Gas Companies, Manufacturers, Consumers |
| Technology | Hydraulic Fracturing, Horizontal Drilling, Well Completion, Enhanced Oil Recovery |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Shale Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at