444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The shadow banking market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, revolutionizing the traditional financial landscape. It has emerged as an alternative financial system that operates alongside the mainstream banking sector. The term “shadow banking” refers to a range of non-bank financial intermediaries and activities that provide credit and liquidity to the economy.
Meaning
Shadow banking encompasses various entities such as hedge funds, money market funds, investment banks, and other non-bank financial institutions. These entities engage in activities similar to traditional banks, such as lending, borrowing, and investing, but operate with less regulatory oversight. The term “shadow” implies that these activities are not directly visible to regulators or subject to the same stringent regulations as traditional banks.
Executive Summary
The shadow banking market has experienced exponential growth in recent years, driven by factors such as technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and increasing demand for credit. This market analysis aims to provide comprehensive insights into the key trends, opportunities, and challenges shaping the industry landscape.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The shadow banking market operates in a dynamic environment influenced by various factors. Key dynamics shaping the market include:
Regional Analysis
The shadow banking market exhibits regional variations, influenced by factors such as regulatory frameworks, market maturity, and economic conditions. Key regional insights include:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Shadow Banking Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

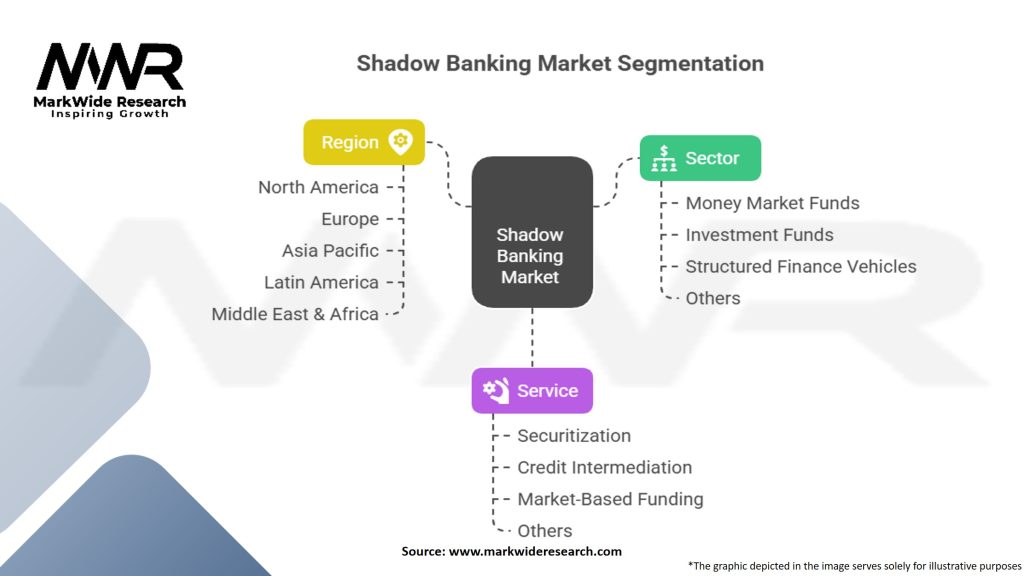
Segmentation
The shadow banking market can be segmented based on the following factors:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the shadow banking market. Key effects include:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The shadow banking market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, evolving regulatory frameworks, and changing consumer preferences. Key trends and developments that will shape the future of the market include:
In conclusion, the analysis of the shadow banking market highlights its significance and potential impact on the global financial landscape. Shadow banking, comprising non-bank financial institutions and activities, plays a vital role in providing credit and liquidity to the economy. This market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by factors such as regulatory arbitrage, technological advancements, and increased demand for alternative financing options. However, it also poses risks, including potential systemic vulnerabilities and lack of transparency. To mitigate these risks, policymakers and regulators need to strike a balance between promoting innovation and ensuring financial stability. Continued monitoring, enhanced oversight, and robust regulatory frameworks are necessary to manage the evolving dynamics of the shadow banking sector and safeguard the overall financial system.
What is Shadow Banking?
Shadow banking refers to the system of financial intermediaries that operate outside traditional banking regulations. This includes entities like hedge funds, private equity firms, and money market funds that provide services similar to banks, such as lending and investment, but without the same oversight.
What are the key players in the Shadow Banking Market?
Key players in the Shadow Banking Market include companies like BlackRock, Citadel, and Apollo Global Management, which engage in various financial activities such as asset management and investment services, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Shadow Banking Market?
The growth of the Shadow Banking Market is driven by factors such as the demand for alternative financing solutions, the increasing complexity of financial products, and the search for higher yields by investors. Additionally, regulatory constraints on traditional banks have pushed borrowers towards shadow banking entities.
What challenges does the Shadow Banking Market face?
The Shadow Banking Market faces challenges including regulatory scrutiny, potential liquidity risks, and the lack of transparency in financial transactions. These factors can lead to systemic risks that may affect the broader financial system.
What opportunities exist in the Shadow Banking Market?
Opportunities in the Shadow Banking Market include the potential for innovation in financial products and services, the expansion of fintech solutions, and the ability to cater to underserved markets. As traditional banks tighten lending standards, shadow banking can fill the gap for borrowers.
What trends are shaping the Shadow Banking Market?
Trends shaping the Shadow Banking Market include the rise of digital platforms for lending, increased collaboration between traditional banks and shadow banking entities, and a growing focus on sustainable finance. These trends are influencing how financial services are delivered and consumed.
Shadow Banking Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Sector | Money Market Funds, Investment Funds, Structured Finance Vehicles, Others |
| Service | Securitization, Credit Intermediation, Market-Based Funding, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Shadow Banking Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at