444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The self-propelled transplanter market revolves around advanced agricultural machinery designed to automate and streamline the process of transplanting seedlings in large-scale farming operations. These machines offer efficiency, precision, and labor-saving benefits, catering primarily to the commercial agriculture sector. With increasing mechanization in farming practices and the demand for enhanced productivity, the self-propelled transplanter market is witnessing significant growth globally.
Meaning
Self-propelled transplanters are specialized agricultural equipment used for planting seedlings into the soil with precision and efficiency. They are equipped with features such as adjustable planting distances, GPS navigation systems, and automated seedling handling mechanisms. These machines play a crucial role in modern agricultural practices by reducing labor costs, minimizing transplanting time, and optimizing crop establishment.
Executive Summary
The self-propelled transplanter market is experiencing robust growth driven by technological advancements, increasing adoption of precision farming techniques, and the need for operational efficiency in large-scale agriculture. Key market players are focusing on innovation, product development, and strategic partnerships to capitalize on the growing demand for mechanized transplanting solutions.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of the self-propelled transplanter market:
Market Restraints
Despite growth prospects, the self-propelled transplanter market faces challenges such as:
Market Opportunities
The self-propelled transplanter market offers opportunities for:
Market Dynamics
The dynamics of the self-propelled transplanter market are influenced by:
Regional Analysis
Regional trends in the self-propelled transplanter market include:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Self-propelled Transplanter Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
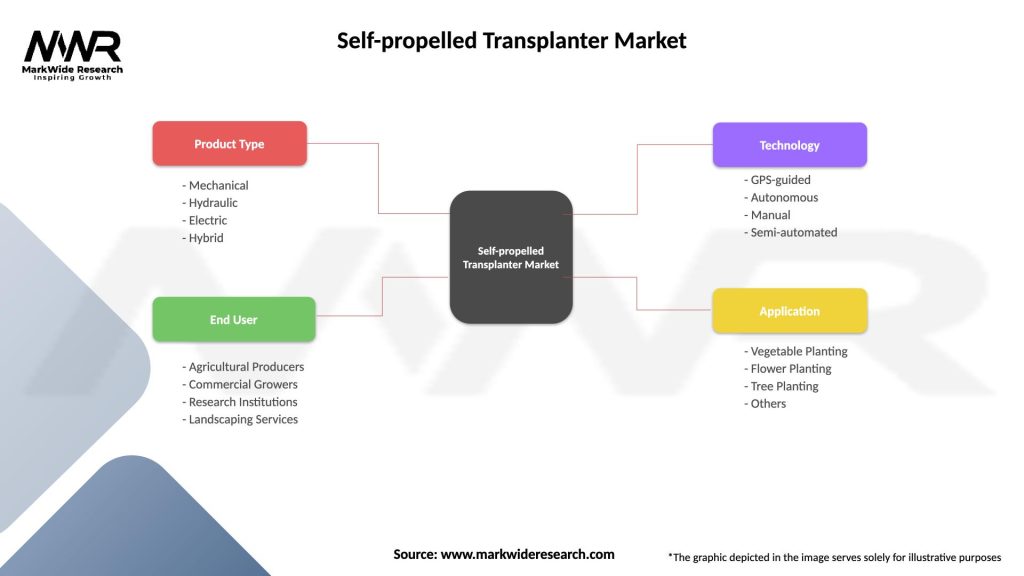
Segmentation
The self-propelled transplanter market can be segmented based on:
Category-wise Insights
Different categories of self-propelled transplanters cater to specific crop planting needs:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The self-propelled transplanter market offers benefits such as:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Key trends in the self-propelled transplanter market include:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic influenced the self-propelled transplanter market by:
Key Industry Developments
Recent developments in the self-propelled transplanter market include:
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market insights, analysts suggest strategies for industry participants:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the self-propelled transplanter market is promising, driven by:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the self-propelled transplanter market is poised for growth with rising demand for mechanized farming solutions, technological advancements, and the need for sustainable agricultural practices. Despite challenges such as high costs and technical requirements, strategic initiatives in innovation, market expansion, and sustainability will drive market success and capitalize on emerging opportunities in the global agriculture sector.
What is Self-propelled Transplanter?
A self-propelled transplanter is a specialized agricultural machine designed to automate the planting of seedlings in fields. It enhances efficiency by reducing labor costs and ensuring precise planting depth and spacing.
What are the key companies in the Self-propelled Transplanter Market?
Key companies in the self-propelled transplanter market include Kubota Corporation, John Deere, and Yanmar Co., Ltd., among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Self-propelled Transplanter Market?
The self-propelled transplanter market is driven by the increasing demand for mechanization in agriculture, the need for efficient planting methods, and the rising labor costs in farming.
What challenges does the Self-propelled Transplanter Market face?
Challenges in the self-propelled transplanter market include high initial investment costs, the need for skilled operators, and potential technical issues with machinery.
What opportunities exist in the Self-propelled Transplanter Market?
Opportunities in the self-propelled transplanter market include advancements in technology, such as automation and precision agriculture, and the growing trend of sustainable farming practices.
What trends are shaping the Self-propelled Transplanter Market?
Trends in the self-propelled transplanter market include the integration of GPS technology for improved accuracy, the development of eco-friendly models, and the increasing adoption of smart farming solutions.
Self-propelled Transplanter Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Mechanical, Hydraulic, Electric, Hybrid |
| End User | Agricultural Producers, Commercial Growers, Research Institutions, Landscaping Services |
| Technology | GPS-guided, Autonomous, Manual, Semi-automated |
| Application | Vegetable Planting, Flower Planting, Tree Planting, Others |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Self-propelled Transplanter Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at