444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Saudi Arabia waste management market represents a rapidly evolving sector driven by the Kingdom’s ambitious Vision 2030 sustainability goals and increasing environmental consciousness. Saudi Arabia is experiencing unprecedented growth in waste generation due to rapid urbanization, industrial expansion, and population growth, creating substantial opportunities for innovative waste management solutions. The market encompasses comprehensive services including collection, transportation, treatment, recycling, and disposal of municipal solid waste, industrial waste, and hazardous materials.
Market dynamics indicate robust expansion with the sector experiencing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% as the Kingdom prioritizes circular economy principles and sustainable waste management practices. The government’s commitment to achieving 95% waste diversion from landfills by 2035 has catalyzed significant investments in advanced waste-to-energy facilities, recycling infrastructure, and smart waste management technologies.
Regional development varies significantly across the Kingdom, with major metropolitan areas like Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dammam leading adoption of modern waste management systems. The market benefits from substantial government support through the National Waste Management Strategy, which allocates significant resources toward developing integrated waste management infrastructure and promoting private sector participation through public-private partnerships.
The Saudi Arabia waste management market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of services, technologies, and infrastructure dedicated to the collection, processing, treatment, and disposal of various waste streams generated across the Kingdom. This market encompasses municipal solid waste management, industrial waste handling, hazardous waste treatment, recycling operations, and emerging waste-to-energy solutions designed to address the growing environmental challenges while supporting economic diversification objectives.
Waste management in Saudi Arabia involves multiple stakeholders including government entities, private companies, technology providers, and international partners working collaboratively to develop sustainable solutions. The market includes traditional services such as waste collection and landfill operations, as well as advanced technologies including automated sorting systems, anaerobic digestion facilities, plasma gasification, and smart bin monitoring systems that optimize collection routes and reduce operational costs.
Strategic importance of this market extends beyond environmental protection to encompass economic opportunities through job creation, resource recovery, and energy generation. The sector plays a crucial role in supporting Saudi Arabia’s transition toward a circular economy model while addressing the challenges of rapid urban growth and industrial development.
Saudi Arabia’s waste management sector stands at a transformational juncture, driven by government initiatives, regulatory reforms, and increasing private sector investment. The market demonstrates strong growth potential with waste generation increasing at approximately 3.5% annually due to population growth and economic development. Key market drivers include the National Transformation Program, NEOM megaproject requirements, and the Kingdom’s commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2060.
Technology adoption is accelerating across the sector, with smart waste management solutions gaining 40% market penetration in major urban centers. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, artificial intelligence, and data analytics is revolutionizing waste collection efficiency and operational optimization. Waste-to-energy projects represent a particularly dynamic segment, with several large-scale facilities under development to convert municipal solid waste into renewable energy.
Market challenges include the need for significant infrastructure investment, workforce development, and public awareness campaigns to improve waste segregation practices. However, government support through favorable policies, financial incentives, and regulatory frameworks creates a conducive environment for market expansion. The sector benefits from international partnerships and technology transfer agreements that bring global expertise to local operations.
Strategic insights reveal several critical factors shaping the Saudi Arabia waste management market landscape:
Primary market drivers propelling the Saudi Arabia waste management sector include comprehensive government initiatives and evolving environmental consciousness. The Vision 2030 program serves as the fundamental catalyst, establishing ambitious targets for waste diversion and recycling that require substantial infrastructure investment and technological advancement.
Rapid urbanization across the Kingdom generates increasing volumes of municipal solid waste, with urban areas experiencing 4.2% annual growth in waste generation. This demographic shift creates immediate demand for expanded collection services, treatment facilities, and disposal infrastructure. Industrial development associated with economic diversification efforts further amplifies waste management requirements across manufacturing, petrochemical, and construction sectors.
Environmental regulations implemented by the Saudi Environmental Authority establish mandatory waste management standards and penalties for non-compliance, driving market demand for professional services. The introduction of extended producer responsibility programs requires manufacturers to manage product lifecycle waste, creating new market segments and business opportunities.
Energy security considerations promote waste-to-energy solutions as viable alternatives to traditional disposal methods. The government’s commitment to generating 50% of electricity from renewable sources by 2030 includes significant waste-to-energy components, driving investment in advanced conversion technologies and integrated energy recovery systems.
Significant market restraints challenge the rapid expansion of Saudi Arabia’s waste management sector, primarily centered on infrastructure limitations and behavioral factors. Capital investment requirements for modern waste management facilities represent substantial financial barriers, particularly for smaller municipalities and private operators seeking to upgrade aging infrastructure or implement advanced technologies.
Technical expertise shortage constrains market growth as the sector requires specialized knowledge in areas such as waste-to-energy operations, hazardous waste treatment, and environmental compliance. The limited availability of qualified personnel with experience in advanced waste management technologies creates operational challenges and increases dependency on international expertise and training programs.
Public awareness limitations regarding waste segregation and recycling practices reduce the effectiveness of waste management programs. Current source separation rates remain below 25% in most urban areas, complicating downstream processing and reducing the economic viability of recycling operations. Cultural resistance to behavioral changes related to waste disposal practices requires sustained education and incentive programs.
Geographic challenges associated with the Kingdom’s vast territory and dispersed population centers increase collection and transportation costs. Remote areas face particular difficulties in accessing comprehensive waste management services, creating disparities in service quality and environmental protection across different regions.
Substantial market opportunities emerge from Saudi Arabia’s commitment to sustainable development and circular economy principles. The NEOM megaproject presents unprecedented opportunities for implementing cutting-edge waste management technologies and establishing the region as a global showcase for sustainable urban development. This initiative requires comprehensive waste management solutions that integrate seamlessly with smart city infrastructure and renewable energy systems.
Waste-to-energy sector offers particularly attractive opportunities as the Kingdom seeks to diversify its energy portfolio while addressing waste disposal challenges. Technology partnerships with international leaders in plasma gasification, anaerobic digestion, and advanced thermal treatment create pathways for knowledge transfer and joint venture development.
Recycling industry expansion represents significant potential as the government implements extended producer responsibility programs and circular economy initiatives. The development of material recovery facilities and specialized recycling plants for plastics, metals, and organic waste creates new business opportunities and supports local manufacturing industries with recovered materials.
Digital transformation opportunities include the implementation of smart waste management systems, predictive analytics, and automated collection technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in waste sorting and route optimization presents competitive advantages for early adopters and technology providers.
Market dynamics in Saudi Arabia’s waste management sector reflect the complex interplay between government policy, technological advancement, and economic development priorities. The sector experiences accelerating momentum driven by regulatory mandates, environmental awareness, and investment in sustainable infrastructure that creates a positive feedback loop encouraging further market expansion.
Competitive landscape evolution shows increasing participation from international waste management companies partnering with local entities to leverage global expertise while meeting Saudi content requirements. This collaboration model facilitates technology transfer and capacity building while ensuring compliance with local regulations and cultural considerations.
Supply chain integration becomes increasingly important as waste management operations connect with recycling industries, energy production, and manufacturing sectors. The development of integrated waste management hubs that combine collection, processing, and energy recovery functions optimizes operational efficiency and economic returns.
Innovation cycles accelerate as the market matures, with emerging technologies such as blockchain for waste tracking, drone-based monitoring, and advanced materials recovery gaining traction. Research and development investments by both government and private sector entities drive continuous improvement in waste management efficiency and environmental performance.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for analyzing the Saudi Arabia waste management market incorporates multiple data sources and analytical approaches to ensure accuracy and reliability. Primary research includes structured interviews with industry executives, government officials, technology providers, and end-users across different regions of the Kingdom to gather firsthand insights into market conditions and trends.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government publications, industry reports, regulatory documents, and academic studies related to waste management practices and environmental policies in Saudi Arabia. MarkWide Research analysts utilize proprietary databases and market intelligence platforms to validate findings and identify emerging trends that may impact future market development.
Data triangulation methods ensure research validity by cross-referencing information from multiple sources and applying statistical analysis to identify patterns and correlations. Quantitative analysis includes examination of waste generation statistics, infrastructure capacity data, and investment flows to establish market sizing and growth projections.
Qualitative assessment focuses on understanding market dynamics, competitive positioning, and strategic factors influencing industry development. Expert interviews and stakeholder consultations provide insights into challenges, opportunities, and future outlook that complement quantitative findings and enhance overall research quality.
Regional market analysis reveals significant variations in waste management infrastructure and service quality across Saudi Arabia’s diverse geographic and demographic landscape. The Central Region, anchored by Riyadh, commands approximately 35% market share due to high population density, government presence, and advanced infrastructure development that supports comprehensive waste management services.
Western Region including Jeddah and Makkah represents 28% of market activity, driven by religious tourism, commercial activities, and port operations that generate diverse waste streams requiring specialized management approaches. The region benefits from established logistics networks and proximity to international markets that facilitate technology import and expertise exchange.
Eastern Province accounts for 22% market share, with industrial waste management dominating due to extensive petrochemical operations and manufacturing activities. The region demonstrates strong demand for hazardous waste treatment services and industrial recycling solutions that support the circular economy objectives of major industrial complexes.
Northern and Southern regions collectively represent 15% of market activity, characterized by emerging opportunities associated with mega-projects such as NEOM and Red Sea Development. These areas require comprehensive waste management infrastructure development to support planned urban and industrial developments while maintaining environmental sustainability standards.
Competitive landscape in the Saudi Arabia waste management market features a diverse mix of international corporations, regional players, and emerging local companies competing across different service segments and geographic markets. Market leadership varies by segment, with established international firms dominating complex waste-to-energy projects while local companies maintain strong positions in traditional collection and disposal services.
Strategic partnerships characterize competitive dynamics as international companies collaborate with local entities to meet Saudi content requirements while leveraging global expertise and technology platforms.
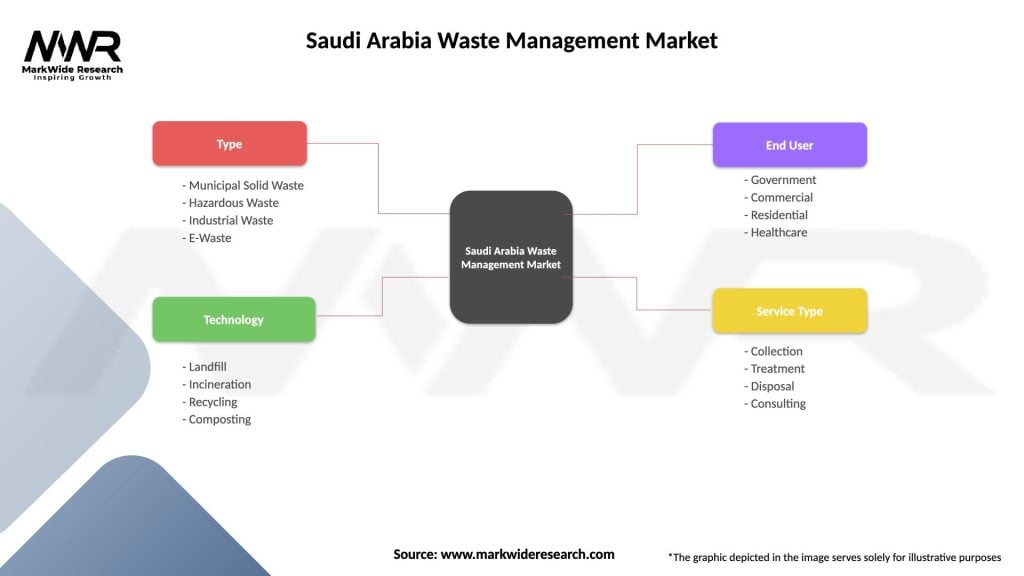
Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct categories based on waste type, service offerings, and end-user requirements that shape competitive dynamics and investment priorities within the Saudi Arabia waste management sector.
By Waste Type:
By Service Type:
Municipal solid waste management represents the largest market category, driven by rapid urbanization and population growth across Saudi cities. This segment experiences steady growth of 3.8% annually as municipalities expand service coverage and improve collection efficiency through technology adoption and infrastructure investment.
Industrial waste management demonstrates strong growth potential linked to economic diversification initiatives and manufacturing sector expansion. The category benefits from stringent environmental regulations requiring proper waste handling and disposal, creating consistent demand for specialized services and treatment facilities.
Hazardous waste treatment emerges as a high-value segment due to regulatory requirements and safety considerations that demand specialized expertise and certified facilities. This category experiences premium pricing and long-term contract structures that provide stable revenue streams for qualified service providers.
Waste-to-energy conversion represents the fastest-growing category, supported by government initiatives and renewable energy targets. The segment attracts significant investment and international partnerships as Saudi Arabia seeks to reduce landfill dependency while generating clean energy from waste resources.
Recycling and material recovery gains momentum through circular economy initiatives and extended producer responsibility programs. This category creates new business models focused on resource recovery and secondary material production that support local manufacturing industries.
Industry participants in the Saudi Arabia waste management market benefit from substantial government support, growing demand, and favorable regulatory environment that creates multiple value creation opportunities. Service providers gain access to long-term contracts with stable revenue streams while contributing to national sustainability objectives and environmental protection goals.
Technology companies benefit from increasing demand for advanced waste management solutions including smart collection systems, automated sorting equipment, and waste-to-energy technologies. The market provides opportunities for innovation and technology demonstration that can be scaled to other regional markets.
Investors find attractive returns through infrastructure development projects, public-private partnerships, and emerging technology ventures supported by government incentives and guaranteed off-take agreements. The sector offers diversification benefits and alignment with global sustainability investment trends.
Local communities benefit from improved environmental quality, job creation, and economic development associated with waste management infrastructure. Skills development programs and technology transfer initiatives create capacity building opportunities that support long-term economic growth and environmental stewardship.
Government entities achieve policy objectives related to environmental protection, economic diversification, and sustainable development while reducing long-term environmental liabilities and public health risks associated with inadequate waste management.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital transformation emerges as the dominant trend reshaping Saudi Arabia’s waste management landscape, with IoT integration achieving 45% adoption rate among major service providers. Smart bin sensors, GPS tracking systems, and predictive analytics optimize collection routes while reducing operational costs and environmental impact through improved efficiency.
Circular economy implementation gains significant traction as the Kingdom prioritizes resource recovery and waste-to-resource conversion. Extended producer responsibility programs drive innovation in packaging design and product lifecycle management while creating new market opportunities for recycling and material recovery operations.
Public-private partnerships become the preferred model for large-scale infrastructure development, combining government policy support with private sector efficiency and innovation. These collaborations facilitate technology transfer and capacity building while ensuring alignment with national sustainability objectives and local content requirements.
Waste-to-energy expansion accelerates as the Kingdom seeks to diversify energy sources and reduce landfill dependency. Advanced thermal treatment technologies and anaerobic digestion facilities convert municipal solid waste into renewable energy while addressing disposal challenges in urban areas.
Regional integration trends show increasing collaboration between Saudi waste management companies and regional partners to share expertise, technologies, and best practices across the Gulf Cooperation Council countries and broader Middle East region.
Major industry developments demonstrate accelerating momentum in Saudi Arabia’s waste management sector transformation. The National Waste Management Strategy launch establishes comprehensive framework for achieving 81% waste diversion from landfills by 2035 through integrated infrastructure development and technology adoption programs.
NEOM waste management contract awards represent landmark achievements in sustainable urban development, incorporating cutting-edge technologies such as pneumatic waste collection systems, AI-powered sorting facilities, and integrated waste-to-energy plants that set new standards for environmental performance and operational efficiency.
Saudi Investment Recycling Company establishment as the national recycling champion demonstrates government commitment to developing domestic capabilities in waste processing and material recovery. The company’s mandate includes developing large-scale recycling infrastructure and promoting circular economy principles across industrial sectors.
International partnership agreements with leading global waste management companies facilitate technology transfer and expertise development. MWR analysis indicates these collaborations accelerate market maturation and improve service quality standards across the Kingdom.
Regulatory framework updates including new environmental standards and waste management licensing requirements create market structure and encourage professional service delivery while ensuring environmental protection and public health safety.
Strategic recommendations for market participants emphasize the importance of early positioning in high-growth segments while building local capabilities and partnerships. Technology investment should focus on scalable solutions that can adapt to evolving regulatory requirements and market conditions while delivering measurable environmental and economic benefits.
Partnership strategies should prioritize collaboration with local entities to meet Saudi content requirements while leveraging international expertise and proven technologies. Joint ventures and technology licensing arrangements provide pathways for market entry and expansion while sharing risks and investment requirements.
Capacity building initiatives represent critical success factors as the market requires substantial workforce development and technical expertise. Companies should invest in training programs and knowledge transfer initiatives that build local capabilities while ensuring operational excellence and safety standards.
Innovation focus should target emerging opportunities in waste-to-energy, smart waste management, and circular economy applications that align with government priorities and market demand. Research and development investments in locally relevant solutions can create competitive advantages and market differentiation.
Geographic expansion strategies should consider regional variations in infrastructure development and market maturity while building scalable operations that can adapt to different market conditions and customer requirements across the Kingdom.
Future market outlook for Saudi Arabia’s waste management sector remains highly positive, driven by sustained government commitment, increasing environmental awareness, and continued economic diversification efforts. MarkWide Research projects the market will experience robust growth with compound annual growth rate of 8.5% through 2030 as infrastructure development accelerates and technology adoption expands.
Technology evolution will continue transforming traditional waste management operations through artificial intelligence, automation, and digital integration that improve efficiency while reducing costs. Smart city initiatives across major urban centers will drive demand for integrated waste management solutions that connect seamlessly with broader urban infrastructure systems.
Circular economy maturation will create new business models and revenue streams as resource recovery becomes economically viable and environmentally necessary. The development of industrial symbiosis networks will optimize material flows between different industries while minimizing waste generation and disposal requirements.
Regional leadership potential positions Saudi Arabia as a hub for waste management innovation and expertise that can be exported to other emerging markets. The Kingdom’s investment in advanced technologies and sustainable practices creates opportunities for technology export and consulting services across the broader region.
Long-term sustainability objectives will drive continued investment in renewable energy integration, carbon footprint reduction, and environmental protection measures that position the waste management sector as a key contributor to national climate goals and international sustainability commitments.
Saudi Arabia’s waste management market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector positioned for substantial growth and transformation over the coming decade. The convergence of government policy support, environmental necessity, and economic opportunity creates a compelling investment landscape that attracts both domestic and international participation across multiple market segments.
Strategic advantages including strong government backing, growing demand, and favorable regulatory environment provide solid foundations for market development while emerging technologies and circular economy principles drive innovation and efficiency improvements. The sector’s alignment with Vision 2030 objectives ensures continued policy support and resource allocation that sustain long-term growth momentum.
Market participants who establish early positions in high-growth segments while building local capabilities and strategic partnerships are well-positioned to capitalize on expanding opportunities. The emphasis on technology adoption, sustainability, and operational excellence creates competitive advantages for companies that invest in innovation and capacity building initiatives that serve evolving market needs and regulatory requirements.
What is Waste Management?
Waste management refers to the collection, transportation, processing, recycling, and disposal of waste materials. It encompasses various methods and technologies aimed at reducing waste’s environmental impact and promoting sustainability.
What are the key players in the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market?
Key players in the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market include companies like Saudi Investment Recycling Company, Veolia, and Suez, which provide a range of waste management services and solutions, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market?
The growth of the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market is driven by increasing urbanization, government initiatives for sustainable waste management, and rising awareness about environmental protection. These factors are leading to enhanced waste collection and recycling efforts.
What challenges does the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market face?
The Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market faces challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, lack of public awareness regarding waste segregation, and regulatory compliance issues. These challenges hinder effective waste management practices.
What opportunities exist in the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market?
Opportunities in the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market include the development of advanced recycling technologies, public-private partnerships for waste management projects, and increasing investments in sustainable waste solutions. These factors can enhance operational efficiency and environmental benefits.
What trends are shaping the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market?
Trends in the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market include the adoption of smart waste management technologies, increased focus on circular economy practices, and the integration of waste-to-energy solutions. These trends aim to improve waste processing and reduce landfill dependency.
Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Municipal Solid Waste, Hazardous Waste, Industrial Waste, E-Waste |
| Technology | Landfill, Incineration, Recycling, Composting |
| End User | Government, Commercial, Residential, Healthcare |
| Service Type | Collection, Treatment, Disposal, Consulting |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Saudi Arabia Waste Management Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at