444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector market refers to the industry involved in the planning, development, construction, and maintenance of physical infrastructure assets in the country. These assets include transportation networks, utilities, energy facilities, public buildings, and telecommunications systems. The Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector plays a vital role in supporting economic growth, attracting investments, improving connectivity, and enhancing the quality of life for its citizens. The market offers significant opportunities for local and international companies across various segments of infrastructure development.
Meaning
Infrastructure refers to the essential physical and organizational structures, facilities, and systems that support economic activity and social well-being. In the context of the Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector market, it encompasses a wide range of assets, including roads, bridges, airports, ports, railways, power plants, water supply systems, hospitals, schools, and telecommunication networks. The development and maintenance of these assets are critical for driving economic growth, ensuring sustainable development, and improving the overall quality of life in the country.
Executive Summary
The Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector market is experiencing rapid growth due to the country’s ambitious development plans, large-scale infrastructure projects, and efforts to diversify the economy. The government’s commitment to investing in infrastructure, coupled with favorable policies and regulations, has attracted significant investments from both public and private sectors. The market offers lucrative opportunities for infrastructure developers, construction companies, engineering firms, and service providers across various segments. However, challenges such as project financing, regulatory complexities, and skilled labor shortages need to be addressed to sustain the market’s growth momentum.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector market is characterized by a dynamic and evolving landscape. It is influenced by government policies, economic factors, technological advancements, and social and environmental considerations. The market dynamics include a mix of public and private sector involvement, partnerships, and collaborations. Infrastructure development projects require the coordination and cooperation of various stakeholders, including government agencies, investors, contractors, engineers, and service providers.
Regional Analysis
The infrastructure sector market in Saudi Arabia is spread across various regions, with key development hubs in major cities such as Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dammam. These regions experience significant infrastructure investment and serve as economic centers, driving the demand for infrastructure development and upgrades.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
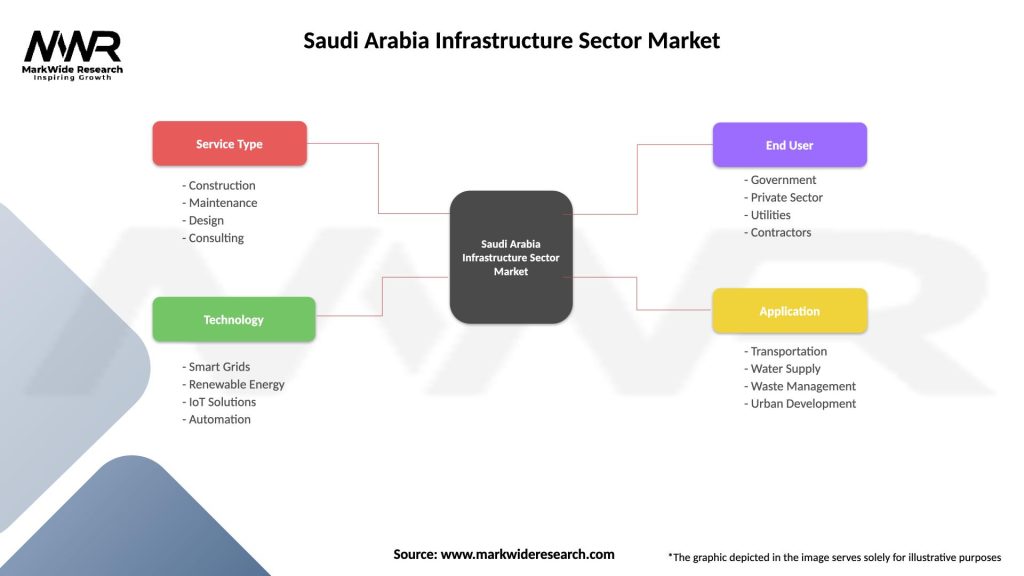
Segmentation
The Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector market. The pandemic resulted in project delays, disruptions to supply chains, and financial challenges. However, the government’s stimulus packages, infrastructure investment commitments, and economic recovery plans are expected to drive the market’s recovery and future growth.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector market is promising. The government’s commitment to infrastructure development, economic diversification, and sustainability provides a strong foundation for future growth. The market is expected to witness increased investment, the completion of mega projects, and the adoption of advanced technologies. Ongoing efforts to improve regulatory frameworks, project financing mechanisms, and skill development are likely to support the market’s sustained growth.
Conclusion
The Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector market presents significant opportunities for infrastructure developers, construction companies, engineering firms, and service providers. The government’s focus on economic diversification, sustainability, and social development drives the demand for infrastructure projects across various sectors. The market’s growth potential, favorable investment environment, and strategic geographic location make it an attractive destination for domestic and international players. However, addressing challenges such as project financing, regulatory complexities, and skilled labor shortages is crucial to ensure the market’s sustainable growth. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and sustainability, the Saudi Arabia infrastructure sector is poised for a promising future.
What is Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector?
The Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector encompasses the development and maintenance of essential facilities and systems, including transportation networks, utilities, and public services that support economic growth and improve quality of life.
What are the key players in the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market?
Key players in the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market include Saudi Aramco, Saudi Binladin Group, and Al Habtoor Group, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector include government investment in Vision 2030 initiatives, urbanization, and the need for improved transportation and utility services.
What challenges does the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market face?
Challenges in the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market include regulatory hurdles, project financing issues, and the need for skilled labor to execute large-scale projects.
What opportunities exist in the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market?
Opportunities in the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market include the expansion of renewable energy projects, smart city developments, and enhancements in public transportation systems.
What trends are shaping the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market?
Trends shaping the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market include increased adoption of digital technologies, sustainable construction practices, and a focus on public-private partnerships to drive infrastructure development.
Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Construction, Maintenance, Design, Consulting |
| Technology | Smart Grids, Renewable Energy, IoT Solutions, Automation |
| End User | Government, Private Sector, Utilities, Contractors |
| Application | Transportation, Water Supply, Waste Management, Urban Development |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at