444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The radar simulators market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by advancements in radar technology and the increasing need for realistic training scenarios. Radar simulators are essential tools used in the training of radar operators, engineers, and technicians. These simulators accurately replicate the behavior of radar systems and provide a virtual environment for training and testing purposes.
Meaning
Radar simulators are software or hardware-based systems designed to imitate the operation of radar systems. They recreate the radar’s functionality, including signal generation, target detection, and tracking. These simulators are used to train radar operators, test radar equipment, and develop radar algorithms and techniques. By simulating various scenarios, radar simulators enable users to understand radar operation, practice radar skills, and evaluate radar system performance.
Executive Summary
The radar simulators market is experiencing steady growth due to the increasing demand for efficient radar training solutions. These simulators offer a cost-effective and safe alternative to real-world radar training exercises. They allow users to train in a controlled environment, reducing risks and expenses associated with live training sessions. Furthermore, radar simulators provide a customizable training experience that can be tailored to different skill levels and operational requirements.
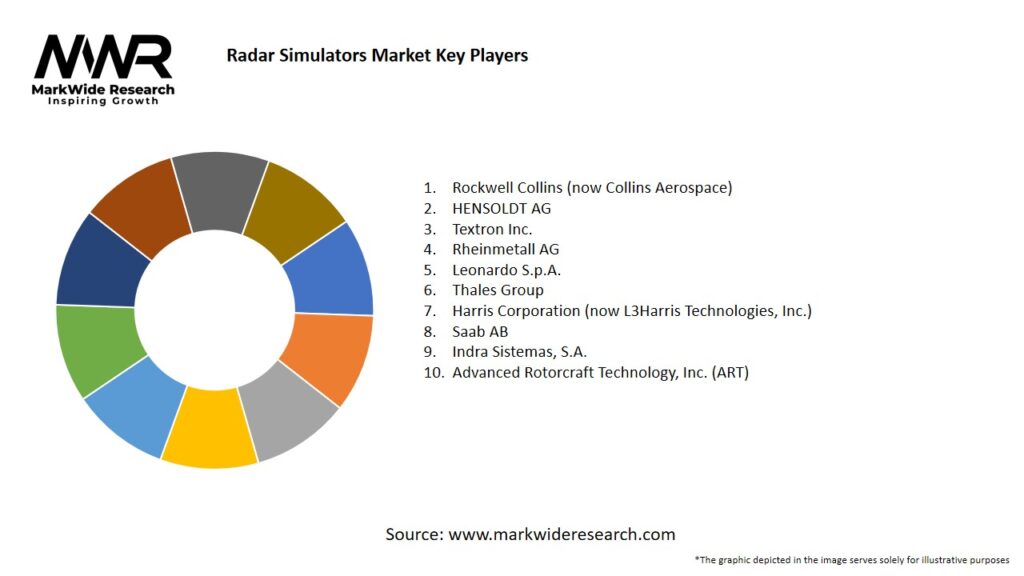
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
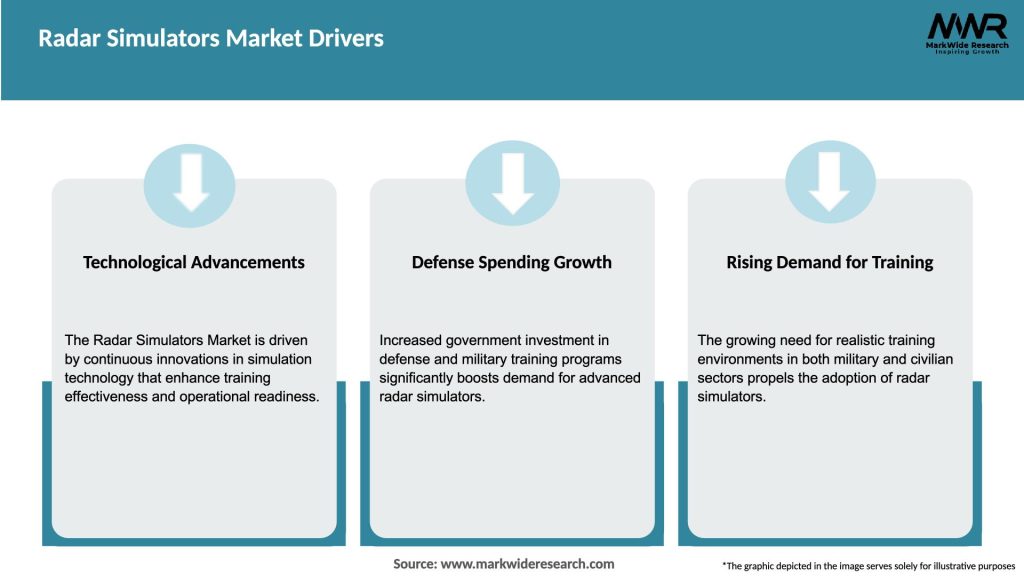
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The radar simulators market is characterized by intense competition and continuous technological advancements. Key players in the market are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and acquisitions to strengthen their market position. The market is witnessing the emergence of cloud-based radar simulators, which offer scalability, flexibility, and cost advantages.
The increasing demand for realistic training solutions, the integration of AI and ML technologies, and the emphasis on improving operational efficiency are driving market growth. However, challenges such as high initial investments, limited awareness, and cybersecurity risks need to be addressed to unlock the full potential of the radar simulators market.
Regional Analysis
The radar simulators market is geographically segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa. North America dominates the market due to the presence of major defense and aviation players in the region. The Asia Pacific region is expected to witness substantial growth, driven by increasing defense expenditure and the growing aviation industry.
Europe holds a significant market share due to the strong presence of defense equipment manufacturers and the emphasis on military training programs. Latin America and the Middle East and Africa are also witnessing growth opportunities, driven by rising defense budgets and the need to enhance security and surveillance capabilities.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Radar Simulators Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
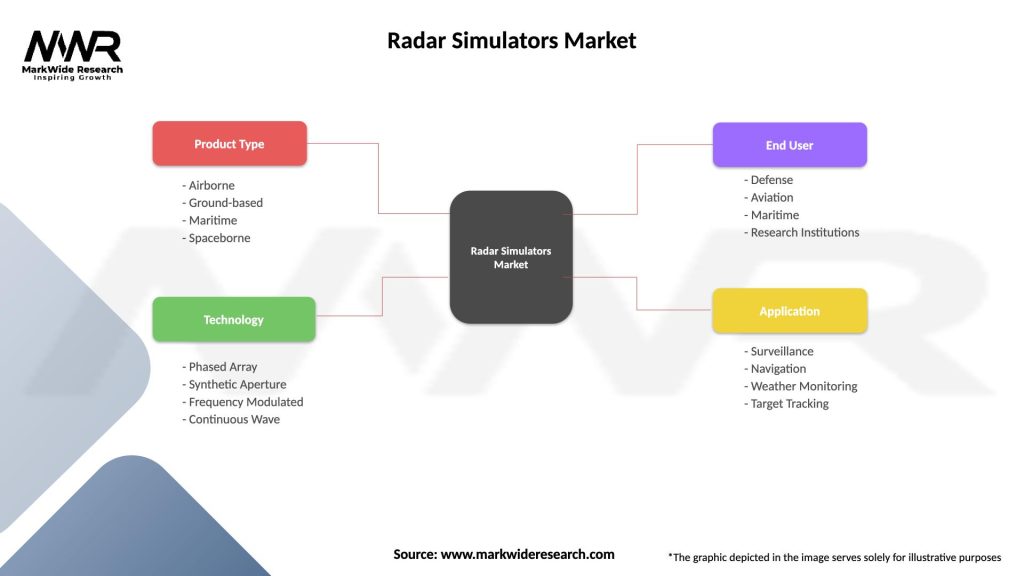
Segmentation
The radar simulators market can be segmented based on the following criteria:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had both positive and negative impacts on the radar simulators market. On one hand, the pandemic has disrupted live training exercises and restricted in-person training sessions, leading to an increased reliance on virtual training solutions such as radar simulators. Organizations have shifted their focus to remote training to ensure the continuity of radar operator training programs.
On the other hand, the pandemic has caused delays in procurement processes and reduced defense budgets in some regions, affecting the demand for radar simulators. However, the long-term impact is expected to be positive, as the need for efficient and cost-effective training solutions remains strong, and the market is projected to recover and grow post-pandemic.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The radar simulators market is expected to witness steady growth in the coming years. The increasing demand for trained radar operators and the need for realistic training scenarios will drive market expansion. Technological advancements, such as the integration of AI, ML, AR, and VR, will further enhance the realism and effectiveness of radar simulators.
The market will experience growth opportunities in emerging sectors, including autonomous vehicles and emerging economies investing in defense modernization. However, challenges such as high initial investments, limited awareness, and cybersecurity risks need to be addressed to unlock the full potential of the radar simulators market.
Conclusion
The radar simulators market is witnessing steady growth, driven by the increasing need for realistic and cost-effective radar training solutions. These simulators offer a safe and controlled training environment, allowing radar operators and technicians to practice their skills, test radar systems, and develop radar algorithms.
The market is driven by factors such as rising defense expenditure, technological advancements, and increased focus on realistic training. However, challenges such as high initial investments, limited awareness, and cybersecurity risks need to be overcome for market expansion. Key players in the market are continuously innovating and collaborating to develop advanced radar simulators with enhanced features and functionalities. The market is expected to grow, driven by emerging applications in autonomous vehicles, integration of AR and VR technologies, and expansion in emerging markets.
What is Radar Simulators?
Radar simulators are advanced systems designed to replicate the functionality of radar systems for training, testing, and research purposes. They are used in various applications, including military training, aerospace testing, and automotive safety systems.
What are the key players in the Radar Simulators Market?
Key players in the Radar Simulators Market include companies such as CAE Inc., Northrop Grumman Corporation, and Thales Group, which provide innovative radar simulation solutions for defense and commercial applications, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Radar Simulators Market?
The Radar Simulators Market is driven by the increasing demand for advanced training solutions in military applications, the rise in aerospace and defense spending, and the growing need for safety and testing in automotive industries.
What challenges does the Radar Simulators Market face?
Challenges in the Radar Simulators Market include the high costs associated with developing sophisticated simulation technologies and the rapid pace of technological advancements that require continuous updates and improvements.
What opportunities exist in the Radar Simulators Market?
Opportunities in the Radar Simulators Market include the expansion of simulation technologies into emerging sectors such as autonomous vehicles and the increasing integration of artificial intelligence to enhance simulation accuracy and realism.
What trends are shaping the Radar Simulators Market?
Trends in the Radar Simulators Market include the growing adoption of virtual and augmented reality for immersive training experiences, advancements in software simulation capabilities, and the increasing focus on cybersecurity measures in radar systems.
Radar Simulators Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Airborne, Ground-based, Maritime, Spaceborne |
| Technology | Phased Array, Synthetic Aperture, Frequency Modulated, Continuous Wave |
| End User | Defense, Aviation, Maritime, Research Institutions |
| Application | Surveillance, Navigation, Weather Monitoring, Target Tracking |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Radar Simulators Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at