444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
Qatar’s private K-12 education market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by a combination of favorable government policies, increasing demand for quality education, and a growing expatriate population. The market offers a wide range of educational options, catering to the diverse needs of students and parents. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the Qatar private K-12 education market, highlighting key insights, market drivers, restraints, opportunities, dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, category-wise insights, key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, SWOT analysis, market key trends, COVID-19 impact, key industry developments, analyst suggestions, future outlook, and a conclusive summary.
Meaning
Private K-12 education refers to educational institutions that are privately owned and operated, providing education from kindergarten to 12th grade. These institutions offer comprehensive educational programs, including a mix of national and international curricula, with an emphasis on academic excellence, character development, and holistic learning. Qatar’s private K-12 education market encompasses a wide range of schools, including international schools, bilingual schools, and schools offering specialized programs, such as STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education.
Executive Summary
The private K-12 education market in Qatar has experienced robust growth in recent years, driven by factors such as increasing demand for quality education, government support, and a rising expatriate population. The market offers a diverse range of educational options, catering to the needs of both Qatari nationals and expatriate families. International schools, in particular, have gained popularity due to their ability to offer globally recognized curricula and a multicultural learning environment. The COVID-19 pandemic has posed challenges to the market, but it has also accelerated the adoption of technology in education, opening up new avenues for growth and innovation.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The private K-12 education market in Qatar is characterized by dynamic forces that shape its growth and development. These dynamics include changing demographic patterns, evolving parent preferences, advancements in technology, policy reforms, and economic factors. Understanding and adapting to these dynamics is crucial for educational institutions operating in the market to remain competitive and meet the evolving needs of students and parents.
Regional Analysis
The private K-12 education market in Qatar is concentrated in urban centers such as Doha, Al Rayyan, and Al Wakrah. These regions have a high concentration of schools, offering a variety of curricula and educational programs. Doha, as the capital city and economic hub, accounts for a significant share of the market, attracting both Qatari and expatriate families seeking quality education. The market in other regions of Qatar is also witnessing growth, driven by infrastructure development and the expansion of educational facilities.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Qatar Private K12 Education Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
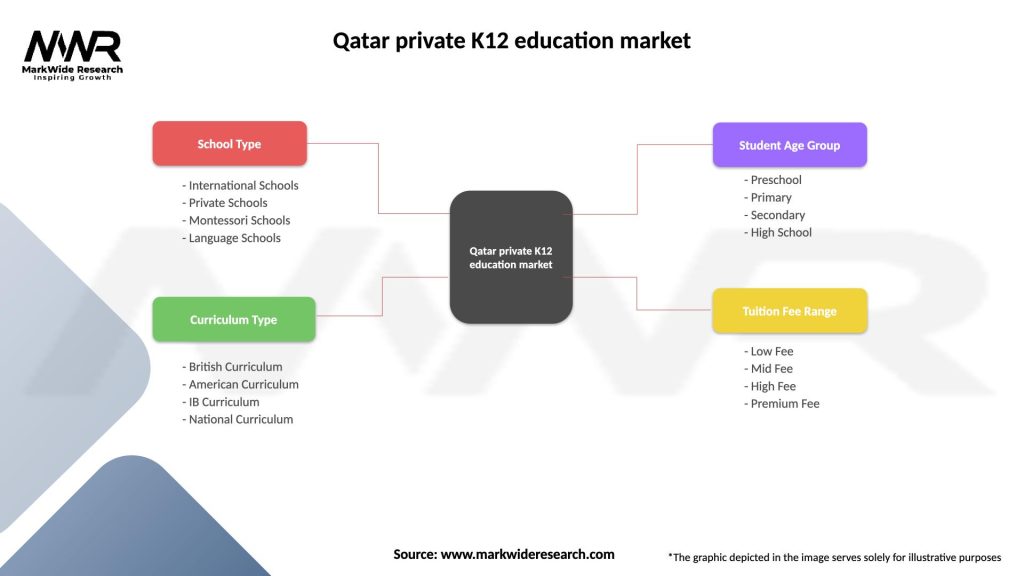
Segmentation
The private K-12 education market in Qatar can be segmented based on various factors, including curriculum, language of instruction, school type, and grade levels offered. The following are key segments within the market:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The private K-12 education market in Qatar offers several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, including:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis provides a comprehensive assessment of the private K-12 education market in Qatar:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
COVID-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the private K-12 education market in Qatar. School closures and the shift to remote learning have posed challenges for educational institutions, students, and parents. However, the pandemic has also accelerated the adoption of technology in education, highlighting the importance of digital infrastructure and online learning platforms. It has forced schools to innovate and adapt to new modes of teaching, leading to the development of blended learning models that combine in-person and online instruction. The pandemic has also highlighted the need for resilience and flexibility in the education sector, driving changes in teaching methodologies, assessment practices, and school operations.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the private K-12 education market in Qatar is promising. The market is expected to continue growing, driven by factors such as government support, increasing demand for quality education, and the country’s ambition to develop a knowledge-based economy. Technology will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of education, with blended learning models, personalized learning approaches, and online platforms becoming integral parts of the education system. Schools that can adapt to changing dynamics, leverage technology effectively, and offer innovative educational programs will be well-positioned to thrive in the evolving landscape.
Conclusion
The private K-12 education market in Qatar is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing demand, government support, and a growing expatriate population. The market offers a diverse range of educational options, including international schools, bilingual schools, and specialized programs. While the market presents opportunities, it is also characterized by challenges such as regulatory compliance, high competition, and affordability concerns. Educational institutions need to embrace technology, foster innovation, and prioritize student well-being to remain competitive. With supportive government policies, investments in infrastructure, and a focus on quality education, the future outlook for the market is promising.
What is private K12 education?
Private K12 education refers to educational institutions that provide primary and secondary education funded through tuition fees rather than government funding. These schools often offer specialized curricula, smaller class sizes, and various extracurricular activities.
What are the key players in the Qatar private K12 education market?
Key players in the Qatar private K12 education market include Doha British School, International School of London Qatar, and Qatar Academy, among others. These institutions are known for their diverse educational offerings and international curricula.
What are the growth factors driving the Qatar private K12 education market?
The growth of the Qatar private K12 education market is driven by factors such as increasing expatriate populations, rising demand for quality education, and government initiatives to enhance educational standards. Additionally, the emphasis on bilingual education is contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the Qatar private K12 education market face?
Challenges in the Qatar private K12 education market include high operational costs, competition among schools, and regulatory compliance issues. These factors can impact the sustainability and growth of private educational institutions.
What opportunities exist in the Qatar private K12 education market?
Opportunities in the Qatar private K12 education market include the potential for innovative educational technologies, the introduction of new curricula, and partnerships with international educational organizations. These can enhance the quality and appeal of private education.
What trends are shaping the Qatar private K12 education market?
Trends in the Qatar private K12 education market include a growing focus on STEM education, increased use of digital learning tools, and a shift towards personalized learning experiences. These trends reflect the evolving needs of students and parents in the region.
Qatar private K12 education market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| School Type | International Schools, Private Schools, Montessori Schools, Language Schools |
| Curriculum Type | British Curriculum, American Curriculum, IB Curriculum, National Curriculum |
| Student Age Group | Preschool, Primary, Secondary, High School |
| Tuition Fee Range | Low Fee, Mid Fee, High Fee, Premium Fee |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Qatar Private K12 Education Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at