444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Qatar analysis of key sectors and investment opportunities market represents a comprehensive examination of the nation’s diverse economic landscape and emerging investment potential. Qatar’s strategic positioning as a global energy hub, combined with its ambitious National Vision 2030, has created unprecedented opportunities across multiple sectors including energy, infrastructure, technology, and financial services. The country’s robust economic diversification efforts have resulted in sustained growth rates exceeding 3.5% annually, positioning Qatar as one of the most attractive investment destinations in the Middle East region.
Economic transformation initiatives have fundamentally reshaped Qatar’s investment landscape, with the government implementing comprehensive reforms to attract foreign direct investment and reduce dependency on hydrocarbon revenues. The nation’s commitment to infrastructure development, technological innovation, and human capital enhancement has created a dynamic ecosystem that supports both traditional and emerging sectors. Investment opportunities span across healthcare, education, tourism, manufacturing, and digital transformation sectors, each offering unique value propositions for international investors.
Strategic location advantages continue to position Qatar as a gateway to regional markets, with world-class transportation infrastructure and logistics capabilities supporting trade flows across the Gulf Cooperation Council region and beyond. The country’s political stability, favorable regulatory environment, and strong financial institutions provide a secure foundation for long-term investment strategies. Sector diversification efforts have achieved remarkable progress, with non-oil sectors contributing increasingly significant portions to the national GDP and employment generation.
The Qatar analysis of key sectors and investment opportunities market refers to the comprehensive evaluation and strategic assessment of Qatar’s economic sectors, investment climate, and business opportunities available to domestic and international investors. This analysis encompasses detailed examination of sector-specific growth drivers, regulatory frameworks, market dynamics, and investment potential across Qatar’s diversified economy. The market analysis provides critical insights into emerging trends, competitive landscapes, and strategic opportunities that define Qatar’s investment ecosystem.
Investment opportunity assessment involves systematic evaluation of market conditions, regulatory environments, infrastructure capabilities, and growth prospects across various economic sectors. This comprehensive approach enables investors, policymakers, and business leaders to make informed decisions regarding capital allocation, market entry strategies, and long-term investment planning. The analysis incorporates both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights to provide a holistic understanding of Qatar’s economic landscape.
Qatar’s investment landscape has undergone remarkable transformation, driven by strategic diversification initiatives and comprehensive economic reforms. The nation’s commitment to reducing hydrocarbon dependency has resulted in robust growth across non-oil sectors, with technology and innovation sectors experiencing growth rates of over 12% annually. Key investment opportunities span infrastructure development, healthcare expansion, educational excellence, tourism development, and digital transformation initiatives.
Strategic positioning advantages include world-class infrastructure, political stability, favorable business environment, and strong financial institutions that support sustainable economic growth. The government’s proactive approach to regulatory reform and investment facilitation has created an attractive ecosystem for foreign direct investment. Sector diversification success is evident in the expanding contributions of manufacturing, services, and technology sectors to overall economic output.
Investment climate improvements have been supported by comprehensive legal frameworks, streamlined business registration processes, and enhanced intellectual property protection mechanisms. The country’s focus on human capital development and technological innovation has created a skilled workforce capable of supporting advanced industries and knowledge-based economic activities.
Economic diversification progress has achieved significant milestones, with key insights revealing the transformation of Qatar’s investment landscape:
Economic diversification imperatives serve as primary drivers for Qatar’s investment market development, with government initiatives actively promoting non-oil sector growth and foreign investment attraction. The National Vision 2030 provides a comprehensive framework for sustainable development, emphasizing human development, social progress, economic diversification, and environmental sustainability. These strategic priorities have created substantial investment opportunities across multiple sectors.
Infrastructure development programs continue to drive investment demand, with major projects in transportation, utilities, healthcare, and education sectors requiring significant capital investment and technical expertise. The country’s commitment to hosting international events and developing world-class facilities has accelerated infrastructure investment and created opportunities for international contractors and service providers.
Technology adoption acceleration has emerged as a critical driver, with government and private sector initiatives promoting digital transformation, smart city development, and innovation ecosystem enhancement. The focus on artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and Internet of Things applications has created substantial opportunities for technology companies and investors. Regulatory support for innovation and entrepreneurship has further strengthened the technology sector’s growth prospects.
Population growth and urbanization trends continue to drive demand for housing, healthcare, education, and consumer services, creating investment opportunities in real estate development, retail, and service sectors. The country’s commitment to improving quality of life and social infrastructure has resulted in sustained investment in community facilities and public services.
Regulatory complexity in certain sectors can present challenges for investors, particularly in highly regulated industries such as banking, telecommunications, and energy. While Qatar has made significant progress in streamlining business processes, some sectors still require extensive compliance procedures and regulatory approvals that may extend project timelines and increase implementation costs.
Market size limitations due to Qatar’s relatively small domestic population can constrain certain investment opportunities, particularly in consumer-focused sectors that rely on large domestic markets for profitability. Investors must often consider regional expansion strategies to achieve optimal scale and returns on investment.
Competition for skilled labor remains a challenge, with demand for qualified professionals often exceeding local supply across technical and specialized sectors. This situation can result in increased labor costs and recruitment challenges for businesses operating in knowledge-intensive industries.
Economic volatility related to global energy markets can impact overall economic conditions, despite diversification efforts. While Qatar has made substantial progress in reducing hydrocarbon dependency, energy sector performance continues to influence broader economic conditions and investment sentiment.
Healthcare sector expansion presents exceptional investment opportunities, driven by population growth, aging demographics, and government commitment to healthcare excellence. The development of specialized medical facilities, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and healthcare technology solutions offers substantial potential for investors with relevant expertise and capabilities.
Education and training sector opportunities continue to expand, with demand for international educational institutions, vocational training programs, and professional development services. The government’s focus on human capital development and knowledge economy transition has created favorable conditions for educational investment and partnership opportunities.
Tourism and hospitality development represents a high-priority sector with significant growth potential, supported by major infrastructure investments and international event hosting capabilities. Investment opportunities span luxury hospitality, cultural tourism, business travel services, and entertainment facilities that cater to diverse visitor segments.
Technology and innovation sectors offer substantial opportunities in fintech, healthtech, edtech, and smart city solutions. The government’s commitment to digital transformation and innovation ecosystem development has created favorable conditions for technology companies and venture capital investment. Startup ecosystem development initiatives provide additional opportunities for early-stage investment and entrepreneurship support.
Investment flow patterns demonstrate increasing diversification across sectors, with traditional energy-focused investment gradually expanding to include technology, healthcare, education, and infrastructure sectors. The government’s proactive approach to investment promotion has resulted in foreign direct investment growth rates exceeding 8% annually across priority sectors, indicating strong investor confidence in Qatar’s economic prospects.
Competitive landscape evolution reflects the entry of international companies and investors seeking to capitalize on Qatar’s growth opportunities and strategic location advantages. Local companies are increasingly forming partnerships with international firms to access technology, expertise, and global market networks, creating collaborative investment opportunities.
Regulatory environment improvements continue to enhance market accessibility and investment attractiveness, with ongoing reforms addressing business licensing, foreign ownership restrictions, and intellectual property protection. These improvements have contributed to Qatar’s rising rankings in international business environment assessments and investment attractiveness indices.
Market maturation processes are evident in the development of sophisticated financial markets, professional services capabilities, and institutional frameworks that support complex investment transactions and business operations. The evolution of local capital markets and investment banking capabilities has enhanced access to financing for both domestic and international investors.
Comprehensive data collection methodologies incorporate primary research through stakeholder interviews, industry surveys, and expert consultations with government officials, business leaders, and investment professionals. Secondary research encompasses analysis of official government publications, industry reports, financial statements, and economic indicators to provide quantitative foundations for market assessment.
Sector-specific analysis employs detailed examination of individual industry segments, including market size estimation, growth trend analysis, competitive landscape assessment, and regulatory environment evaluation. This approach ensures comprehensive coverage of investment opportunities and market dynamics across Qatar’s diverse economic sectors.
Stakeholder engagement processes include consultations with government agencies, private sector organizations, international investors, and industry associations to gather diverse perspectives on market conditions and investment opportunities. These engagements provide valuable insights into practical challenges and opportunities facing investors in Qatar’s market.
Data validation procedures ensure accuracy and reliability through cross-referencing multiple sources, expert review processes, and continuous monitoring of market developments. Regular updates and revisions maintain the relevance and accuracy of market analysis and investment opportunity assessments.
Doha metropolitan area dominates Qatar’s economic activity and investment opportunities, accounting for approximately 75% of total economic output and hosting the majority of major businesses, government institutions, and infrastructure projects. The capital city’s comprehensive development plans include smart city initiatives, transportation upgrades, and commercial district expansion that create substantial investment opportunities.
Industrial zones development in areas such as Mesaieed and Ras Laffan has created specialized investment opportunities in manufacturing, petrochemicals, and logistics sectors. These zones offer world-class infrastructure, streamlined regulatory processes, and strategic access to international markets, making them attractive locations for industrial investment and development.
Northern regions present emerging opportunities in agriculture, renewable energy, and eco-tourism development, supported by government initiatives to promote balanced regional development and economic diversification. Investment in sustainable agriculture technologies and renewable energy projects aligns with Qatar’s environmental sustainability objectives.
Coastal areas development focuses on tourism, hospitality, and recreational facilities that capitalize on Qatar’s natural assets and strategic location. Major resort developments and waterfront projects offer investment opportunities in luxury hospitality, entertainment, and residential sectors that cater to both domestic and international markets.
Major investment players in Qatar’s market include both domestic and international entities across various sectors:
International partnerships play crucial roles in Qatar’s investment landscape, with major global companies establishing local presence and joint ventures to access market opportunities and contribute expertise to national development objectives.
By Sector Categories:
By Investment Type:
Energy sector transformation continues to evolve beyond traditional hydrocarbon focus, with increasing emphasis on renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable technologies. Solar energy projects have achieved significant progress, with installations demonstrating capacity growth rates exceeding 15% annually. The sector’s diversification creates opportunities for clean technology investors and energy service companies.
Healthcare sector expansion reflects Qatar’s commitment to becoming a regional medical hub, with major hospital developments, specialized treatment centers, and medical research facilities creating substantial investment opportunities. The integration of healthcare technology and telemedicine solutions has accelerated, particularly following global health challenges that highlighted the importance of healthcare system resilience.
Education sector development encompasses both K-12 and higher education segments, with international institutions establishing campuses and partnerships with local organizations. The focus on STEM education, vocational training, and lifelong learning has created opportunities for educational technology companies and training service providers.
Technology sector growth spans multiple subsectors including fintech, healthtech, edtech, and smart city solutions. Government initiatives supporting digital transformation and innovation have resulted in technology sector employment growth exceeding 10% annually, indicating robust sector development and investment potential.
Investors benefit from Qatar’s stable political environment, strong regulatory frameworks, and strategic location advantages that provide access to regional markets and international trade routes. The country’s commitment to economic diversification creates multiple investment opportunities across emerging and traditional sectors, supported by government incentives and facilitation programs.
Businesses gain access to world-class infrastructure, skilled workforce, and supportive business environment that enables efficient operations and growth. The availability of advanced telecommunications, transportation, and utilities infrastructure reduces operational costs and enhances competitiveness in regional and global markets.
Government entities achieve economic diversification objectives through private sector participation and foreign investment attraction. Public-private partnerships enable efficient delivery of public services and infrastructure development while leveraging private sector expertise and capital.
Local communities benefit from job creation, skills development, and improved quality of life resulting from investment in healthcare, education, and infrastructure sectors. The emphasis on human capital development ensures that economic growth translates into social progress and community development.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital transformation acceleration has become a dominant trend across all sectors, with government and private organizations investing heavily in technology infrastructure, digital services, and automation solutions. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digitalization efforts, creating substantial opportunities for technology companies and digital service providers. E-government initiatives have achieved significant progress, with digital service adoption rates exceeding 80% across major government services.
Sustainability and environmental focus has gained prominence, with increasing emphasis on renewable energy, green building standards, and environmental protection measures. The Qatar National Vision 2030 emphasizes environmental sustainability, creating opportunities for clean technology companies and sustainable development projects.
Innovation ecosystem development has accelerated through government initiatives supporting startups, entrepreneurship, and technology commercialization. The establishment of innovation hubs, incubators, and venture capital funds has created a supportive environment for technology companies and innovative business models.
Healthcare system modernization continues to drive investment in medical technology, telemedicine, and specialized healthcare services. The focus on becoming a regional medical hub has resulted in major hospital developments and medical research facility investments that create opportunities for healthcare investors and service providers.
Major infrastructure projects have achieved significant milestones, including the completion of transportation networks, utility upgrades, and telecommunications infrastructure that support economic development and investment attraction. The Hamad International Airport expansion and Doha Metro system have enhanced Qatar’s connectivity and logistics capabilities.
Regulatory reforms have streamlined business registration processes, enhanced foreign ownership provisions, and strengthened intellectual property protection mechanisms. According to MarkWide Research analysis, these reforms have contributed to improved business environment rankings and increased foreign investment flows.
Financial market development has progressed through capital market reforms, Islamic finance expansion, and fintech sector growth. The Qatar Stock Exchange has implemented technological upgrades and regulatory improvements that enhance market efficiency and investor access.
Education sector partnerships with international institutions have expanded, with major universities establishing campuses and research facilities in Qatar. These developments support human capital development objectives and create opportunities for educational service providers and technology companies.
Sector diversification strategies should focus on high-growth areas including technology, healthcare, education, and tourism that align with Qatar’s National Vision 2030 objectives. Investors should consider partnerships with local entities to navigate regulatory requirements and access market opportunities effectively.
Technology sector investment presents exceptional opportunities, particularly in fintech, healthtech, and smart city solutions that address local market needs while offering regional expansion potential. The government’s support for digital transformation creates favorable conditions for technology companies and venture capital investment.
Infrastructure investment should focus on sustainable and smart infrastructure solutions that support Qatar’s long-term development objectives. Public-private partnership opportunities in transportation, utilities, and social infrastructure offer attractive risk-adjusted returns for qualified investors.
Regional expansion strategies should leverage Qatar’s strategic location and business environment advantages to access broader Gulf Cooperation Council markets. Companies establishing operations in Qatar can benefit from preferential trade agreements and regional market access opportunities.
Economic diversification progress is expected to accelerate, with non-oil sectors projected to achieve growth rates exceeding 6% annually over the next five years. The continued implementation of National Vision 2030 initiatives will create substantial investment opportunities across priority sectors including healthcare, education, technology, and tourism.
Infrastructure development momentum will continue through major projects in transportation, utilities, and social infrastructure that support economic growth and quality of life improvements. The completion of World Cup infrastructure has created legacy assets that support tourism and business development objectives.
Technology sector expansion is anticipated to accelerate through government support for innovation, startup development, and digital transformation initiatives. MWR projections indicate that technology sector employment and investment will continue growing at double-digit rates, driven by increasing demand for digital solutions and smart city applications.
Regional hub development potential remains strong, with Qatar’s strategic location, infrastructure capabilities, and business environment advantages positioning the country as an attractive base for regional operations and international business activities. The focus on becoming a knowledge economy will create additional opportunities for high-value services and innovation-driven industries.
Qatar’s investment landscape presents exceptional opportunities across diverse sectors, supported by strategic government initiatives, world-class infrastructure, and favorable business environment conditions. The country’s commitment to economic diversification has created substantial potential in healthcare, education, technology, tourism, and infrastructure sectors that offer attractive returns for qualified investors.
Strategic advantages including political stability, financial strength, regulatory improvements, and regional connectivity position Qatar as an attractive investment destination for both domestic and international investors. The ongoing implementation of National Vision 2030 provides a clear framework for sustainable development and investment opportunity creation.
Future prospects remain highly positive, with continued economic diversification, infrastructure development, and innovation ecosystem enhancement creating multiple pathways for investment success. The combination of government support, private sector dynamism, and strategic location advantages ensures that Qatar will continue to offer compelling investment opportunities across its evolving economic landscape.
What is Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities?
Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities refers to the comprehensive evaluation of various sectors within Qatar’s economy, identifying potential areas for investment and growth. This analysis encompasses sectors such as energy, tourism, and finance, providing insights into market dynamics and opportunities.
What are the key companies in the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities Market?
Key companies involved in the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities include Qatar Petroleum, Qatar National Bank, and Ooredoo, among others. These companies play significant roles in their respective sectors, influencing investment trends and economic development.
What are the main drivers of the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities Market?
The main drivers of the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities include the country’s strategic location, substantial natural gas reserves, and government initiatives aimed at economic diversification. These factors contribute to attracting foreign investment and fostering sectoral growth.
What challenges does the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities Market face?
Challenges in the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities include fluctuating oil prices, regulatory hurdles, and competition from neighboring countries. These factors can impact investment decisions and sector performance.
What future opportunities exist in the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities Market?
Future opportunities in the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities include advancements in renewable energy, growth in the tourism sector, and the development of smart city initiatives. These areas present significant potential for investors looking to capitalize on emerging trends.
What trends are shaping the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities Market?
Trends shaping the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities include increased digital transformation across industries, a focus on sustainability, and the rise of e-commerce. These trends are influencing how businesses operate and invest in the region.
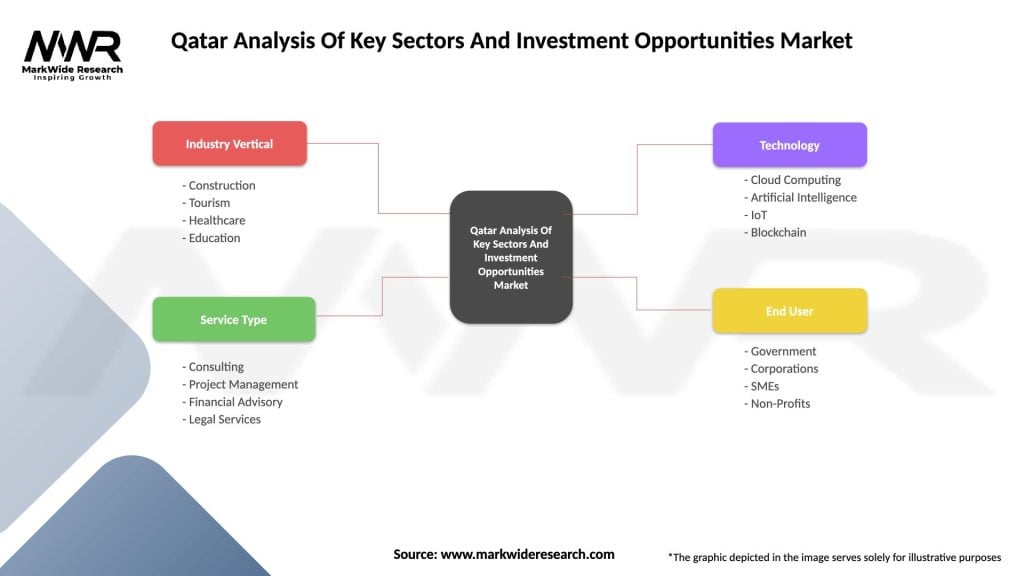
Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Industry Vertical | Construction, Tourism, Healthcare, Education |
| Service Type | Consulting, Project Management, Financial Advisory, Legal Services |
| Technology | Cloud Computing, Artificial Intelligence, IoT, Blockchain |
| End User | Government, Corporations, SMEs, Non-Profits |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Qatar Analysis Of Key Sectors And Investment Opportunities Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at