444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The powder metallurgy market represents a critical segment within advanced manufacturing technologies, characterized by innovative material processing techniques and expanding industrial applications. This specialized sector encompasses the production of metal powders, their consolidation into useful shapes, and the development of components serving diverse industries including automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics. Powder metallurgy enables manufacturing of complex geometries, unique material combinations, and high-performance components that traditional metalworking methods cannot economically produce or achieve. The market demonstrates robust growth momentum driven by increasing demand for lightweight materials, precision manufacturing requirements, sustainability considerations favoring material efficiency, and technological advancements expanding application possibilities.
Manufacturing capabilities span conventional press-and-sinter processes, metal injection molding, additive manufacturing techniques, and advanced consolidation methods including hot isostatic pressing and spark plasma sintering. Regional dynamics reveal concentrated development in established industrial economies while emerging markets invest substantially in building local powder metallurgy infrastructure supporting domestic manufacturing capabilities. According to MarkWide Research analysis, the sector is experiencing substantial expansion with projected growth at a CAGR of 7.2% through the forecast period. Industry participants range from integrated metal powder producers and component manufacturers to specialized equipment suppliers and material technology developers, creating a comprehensive ecosystem supporting powder metallurgy advancement and commercial deployment across multiple industrial sectors globally.
The powder metallurgy market refers to the global industry encompassing production, processing, and application of metal powders to manufacture components and materials through processes including compaction, sintering, and advanced consolidation techniques. This includes metal powder production through atomization and other methods, component manufacturing via press-and-sinter operations, metal injection molding, additive manufacturing applications, and development of specialized alloys and composite materials achievable uniquely through powder metallurgy processing routes.
Market transformation in powder metallurgy reflects fundamental shifts in manufacturing paradigms toward greater material efficiency, design flexibility, and performance optimization. The sector has evolved from niche applications serving specific technical requirements to mainstream manufacturing technology competing directly with traditional metalworking across numerous applications. Key growth drivers include automotive lightweighting imperatives, aerospace performance requirements, sustainability mandates favoring near-net-shape manufacturing, and additive manufacturing proliferation expanding powder metallurgy’s technological scope. The market landscape features diverse stakeholders including metal powder producers, component manufacturers, equipment suppliers, and material science organizations advancing powder metallurgy capabilities. Manufacturing advantages over conventional methods include exceptional material utilization exceeding 95% efficiency compared to subtractive processes, ability to produce complex geometries without extensive machining, and unique material combinations impossible through melting metallurgy.
Technological developments continue expanding performance boundaries with advanced powders, innovative consolidation processes, and digital manufacturing integration enhancing consistency and capability. Automotive applications dominate current demand with powder metallurgy components serving critical functions in transmissions, engines, and structural applications where precision and reliability remain paramount. The manufacturing ecosystem demonstrates increasing sophistication with dedicated production facilities, specialized testing capabilities, and comprehensive quality management systems ensuring components meet stringent performance requirements across safety-critical applications.
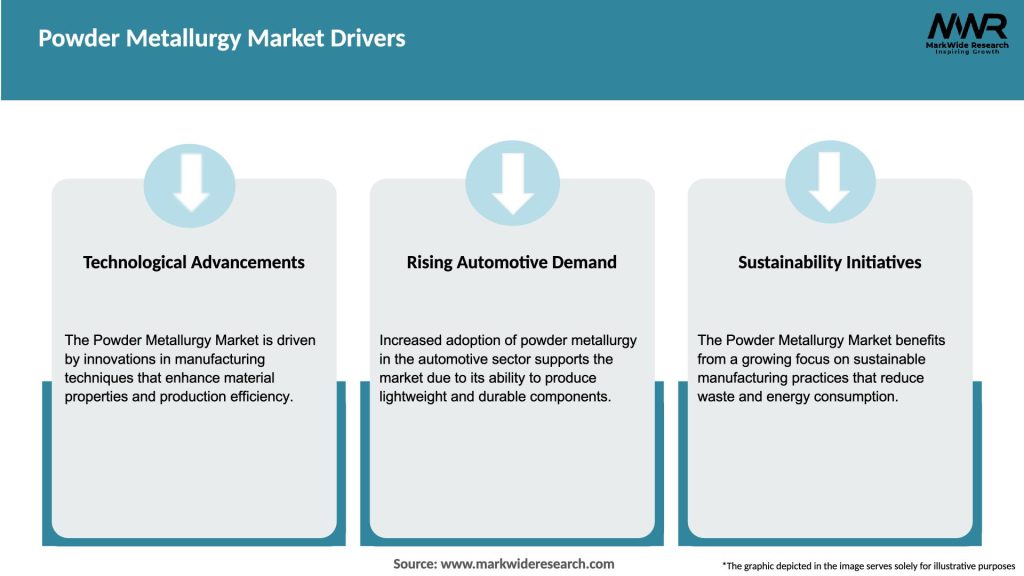
Critical market dynamics shaping the powder metallurgy landscape include:
Multiple catalysts propel growth in the powder metallurgy market. Automotive lightweighting imperatives driven by fuel efficiency regulations and electric vehicle range optimization create demand for powder metallurgy components offering strength-to-weight advantages over conventional materials. Manufacturing cost efficiency through near-net-shape production, minimal material waste, and reduced secondary operations makes powder metallurgy increasingly competitive against traditional metalworking for high-volume applications. Design optimization opportunities enable engineers to create complex geometries, integrated features, and functionally graded materials impossible through casting or machining alone. Material performance requirements in demanding applications including aerospace turbine components, medical implants, and industrial tooling drive adoption of advanced powder metallurgy alloys and processes. Sustainability considerations favor powder metallurgy’s exceptional material utilization and energy efficiency relative to subtractive manufacturing methods generating significant waste.
Precision manufacturing demands across industries require tight tolerances and consistent quality that modern powder metallurgy processes reliably deliver through process control and automation. Additive manufacturing proliferation expands metal powder consumption substantially with 3D printing technologies utilizing powder metallurgy feedstocks for aerospace, medical, and tooling applications. Emerging market industrialization creates fundamental demand growth as countries develop domestic manufacturing capabilities requiring powder metallurgy components for machinery, vehicles, and infrastructure equipment. Magnetic material applications including electric motors, transformers, and electronic devices increasingly utilize powder metallurgy’s unique ability to produce soft magnetic components with optimized properties. Industrial machinery evolution toward higher efficiency and performance drives specification of powder metallurgy components in pumps, compressors, and power transmission systems. Metal injection molding advancement enables powder metallurgy to address smaller, more complex component applications previously dominated by conventional metalworking or plastic alternatives, with the technology achieving annual growth rates exceeding 10% in specific application segments.
Significant challenges constrain market growth despite favorable overall dynamics. Capital intensity requirements for powder metallurgy facilities including specialized presses, sintering furnaces, and powder handling systems create substantial entry barriers and limit capacity expansion responsiveness. Size limitations inherent in conventional press-and-sinter processes restrict component dimensions, preventing powder metallurgy from addressing large structural applications dominated by casting and forging. Material costs for metal powders typically exceed conventional bulk metal pricing due to additional processing required for powder production, though superior material utilization often offsets this disadvantage. Design constraints including draft angles, uniform wall thickness requirements, and ejection considerations limit geometric freedom despite powder metallurgy’s advantages over some traditional processes. Property limitations in conventional powder metallurgy components including lower ductility and impact resistance compared to wrought materials restrict applications in certain demanding service conditions.
Process economics favor high-volume production with substantial tooling investments making powder metallurgy less competitive for low-volume applications where flexible manufacturing methods prove more cost-effective. Technical expertise requirements for powder handling, process optimization, and quality control remain specialized, creating workforce challenges and knowledge barriers for new market entrants. Automotive market cyclicality creates demand volatility given automotive industry’s dominant market share, with economic downturns significantly impacting powder metallurgy component consumption. Electric vehicle transition eliminates certain traditional powder metallurgy applications including transmission components while new opportunities in electric drivetrains develop more gradually. Alternative technology competition from advanced casting processes, precision forging, and additive manufacturing challenges powder metallurgy in specific applications where multiple technologies prove viable. Environmental regulations around metal powder handling, sintering emissions, and workplace safety impose compliance costs and operational constraints, with implementation requirements varying substantially across global manufacturing regions.
Substantial opportunities exist for market participants across the value chain. Electric vehicle components including electric motor soft magnetic parts, battery system structural elements, and thermal management components create significant growth opportunities offsetting traditional transmission application losses. Additive manufacturing expansion drives metal powder demand with aerospace, medical, and tooling applications requiring specialized powder characteristics and expanding total addressable market substantially. Advanced material development including high-entropy alloys, metal matrix composites, and functionally graded materials enable performance levels unattainable through conventional metallurgy, commanding premium pricing and expanding application possibilities. Medical device applications leverage powder metallurgy’s ability to produce porous structures for bone ingrowth, patient-specific geometries through additive manufacturing, and biocompatible materials for implants. Aerospace component opportunities expand as aircraft manufacturers pursue weight reduction and performance optimization, with powder metallurgy offering unique capabilities for turbine components and structural applications.
Industrial automation growth increases demand for precision components in robotics, actuators, and motion control systems where powder metallurgy’s dimensional accuracy provides competitive advantages. Renewable energy applications including wind turbine gearboxes, solar tracking systems, and hydroelectric machinery utilize powder metallurgy components for reliability and performance. Emerging market penetration offers substantial growth potential as industrializing nations develop local powder metallurgy capabilities serving domestic automotive, machinery, and consumer goods manufacturing. Metal injection molding expansion into new applications including consumer electronics, firearms, and industrial tools leverages the technology’s ability to produce small, complex components economically. Sustainable manufacturing positioning enables powder metallurgy to capitalize on corporate and regulatory sustainability mandates given superior material efficiency and potential for recycled powder utilization. Digital manufacturing integration through process monitoring, artificial intelligence optimization, and predictive maintenance creates opportunities for technology suppliers and enhances component manufacturer competitiveness.
Complex interactions between technological, industrial, and economic forces shape market evolution. Automotive industry transformation through electrification, autonomous driving, and mobility services fundamentally alters powder metallurgy demand patterns with traditional applications declining while new opportunities emerge. Technology competition intensifies as casting, forging, and additive manufacturing advance, requiring powder metallurgy to continuously improve cost-effectiveness and performance capabilities. Raw material price volatility for base metals including iron, copper, and specialty alloying elements impacts powder metallurgy economics, though material efficiency provides partial insulation from price fluctuations. Globalization dynamics including trade policies, regional manufacturing strategies, and supply chain considerations influence facility location decisions and competitive positioning. Consolidation trends among powder metallurgy component manufacturers create larger entities with enhanced research capabilities and global reach, though the industry maintains numerous specialized players. Vertical integration strategies see some powder producers forward-integrating into component manufacturing while component manufacturers backward-integrate into powder production to secure supply and capture value.
Quality expectations continuously escalate particularly for safety-critical automotive and aerospace applications, driving investment in advanced testing equipment and process control systems. Standardization efforts through industry organizations establish common specifications, testing protocols, and design guidelines facilitating technology adoption and reducing customer risk perceptions. Intellectual property considerations around powder formulations, process parameters, and component designs create competitive differentiation while occasionally generating licensing opportunities. Economic cycles impact capital investment decisions and end-market demand, with powder metallurgy demonstrating moderate cyclicality tied primarily to automotive and industrial machinery production volumes. Regulatory landscapes evolve with potential new requirements around emissions, workplace safety, and material traceability influencing operational practices, with compliance costs representing approximately 5-8% of manufacturing expenses in highly regulated markets.
Comprehensive research underpinning this analysis employed multiple methodologies ensuring accuracy and market insight. Primary research included structured interviews with powder metallurgy manufacturers, equipment suppliers, automotive engineers, and material scientists providing firsthand perspectives on technological capabilities, market dynamics, and competitive positioning. Secondary research synthesized information from industry association publications, technical journals, patent databases, and company financial reports to understand technology trends and market development patterns. Market sizing utilized automotive production statistics, industrial machinery output data, and powder metallurgy content-per-application estimates to build comprehensive demand models across end-use segments. Value chain analysis mapped relationships from raw material suppliers through powder producers and component manufacturers to end-use applications, understanding value distribution and competitive dynamics at each stage. Technology assessment evaluated emerging processes including additive manufacturing variants, advanced consolidation techniques, and novel powder production methods to project future capabilities and application expansion. Competitive benchmarking examined major market participants analyzing their technology portfolios, manufacturing footprints, customer relationships, and strategic priorities.
Regional analysis investigated market characteristics across major manufacturing regions considering industrial structure, automotive production concentrations, and regulatory environments. Application analysis assessed powder metallurgy penetration rates across various end-use segments identifying growth opportunities and competitive dynamics. Material science review examined academic research and development programs to understand emerging alloy systems and processing innovations potentially impacting commercial markets. Expert validation involved consulting with powder metallurgy specialists, automotive engineers, and manufacturing strategists to verify findings, challenge assumptions, and incorporate nuanced insights reflecting practical market realities and technical constraints affecting powder metallurgy adoption and growth trajectories.
Asia-Pacific dominates global powder metallurgy production with approximately 45% market share, driven by massive automotive manufacturing concentrations in China, Japan, and South Korea combined with growing industrial machinery sectors. China represents the largest single market reflecting its position as the world’s leading automotive producer and increasingly sophisticated manufacturing capabilities in powder metallurgy technologies. Japanese companies maintain technological leadership in advanced powder metallurgy processes and materials, with major manufacturers serving global automotive and electronics industries. India demonstrates rapid growth as automotive production expands and local powder metallurgy infrastructure develops supporting both domestic consumption and export opportunities. North America maintains significant market presence with approximately 28% global share, characterized by mature powder metallurgy industry serving automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
United States hosts numerous powder metallurgy component manufacturers and leads in additive manufacturing adoption driving specialized powder demand. Mexico emerges as an important manufacturing location with automotive industry investments driving powder metallurgy component production for both domestic assembly and export. Europe represents a sophisticated market with strong automotive applications and leading aerospace and industrial machinery sectors utilizing advanced powder metallurgy components. Germany maintains powder metallurgy excellence with automotive suppliers and machinery manufacturers driving technological advancement and quality standards. Eastern European countries attract powder metallurgy investments serving cost-competitive manufacturing while accessing European automotive supply chains. Latin America shows moderate development with Brazil representing the primary market, though economic volatility and limited automotive production growth constrain powder metallurgy sector expansion. Middle East demonstrates emerging interest particularly in aerospace and industrial applications, though limited manufacturing infrastructure restricts current market development. Africa remains largely undeveloped for powder metallurgy with South Africa hosting modest capabilities, though long-term potential exists as industrialization progresses across the continent.
The competitive environment features diverse participants with varying strategies and capabilities:
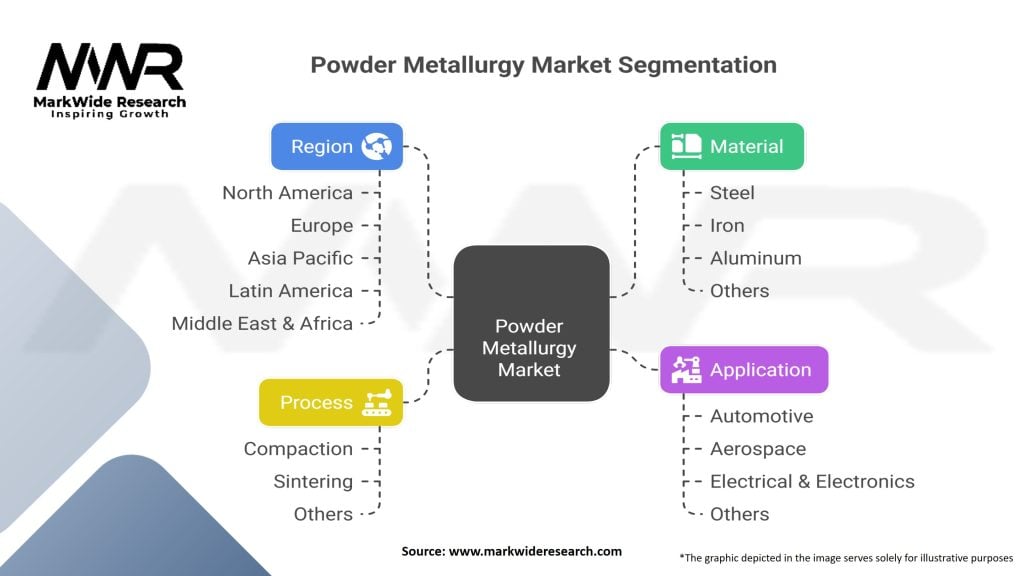
By Material Type: The market segments into ferrous powders including iron and steel compositions dominating volume applications, non-ferrous powders encompassing copper, aluminum, titanium, and nickel-based materials, and specialized powders including precious metals and advanced alloys. Ferrous materials represent approximately 80% of powder consumption driven by automotive applications, while non-ferrous and specialty powders serve aerospace, medical, and high-performance industrial applications.
By Technology: Classification includes press-and-sinter processes representing traditional high-volume manufacturing, metal injection molding enabling complex small components, additive manufacturing utilizing powder feedstocks for 3D printing applications, and advanced techniques including hot isostatic pressing and spark plasma sintering. Press-and-sinter methods dominate current production volumes while additive manufacturing demonstrates the fastest growth trajectory.
By Application: Market applications span automotive components including transmission parts, engine components, and structural elements; aerospace components for turbines and structural applications; industrial machinery parts for pumps, compressors, and power transmission; consumer goods including tools and appliances; medical devices and implants; and electronics applications. Automotive applications represent the largest segment with diversified growth across other end uses reducing concentration risk.
By End-Use Industry: Segments include automotive manufacturing representing the dominant demand driver, aerospace and defense requiring high-performance materials and precision components, industrial machinery and equipment, consumer products manufacturing, medical device production, and electronics manufacturing. Industry diversification continues as powder metallurgy penetrates new applications beyond traditional automotive focus.
By Production Process: Categories encompass conventional sintering utilizing traditional furnace technologies, warm compaction processes improving green strength and dimensional control, high-temperature sintering for advanced materials and properties, and hybrid processes combining powder metallurgy with conventional metalworking to optimize performance and economics.
Automotive Transmission Components represent the largest powder metallurgy application category with synchronizer rings, gear components, and structural parts utilizing the technology’s precision and cost-effectiveness. Design optimization for electric vehicle transmissions creates opportunities despite overall transmission complexity reduction in EVs. Performance requirements including fatigue resistance, wear characteristics, and dimensional stability demand careful material selection and process control ensuring reliable operation throughout vehicle lifecycles.
Metal Injection Molding constitutes a rapidly growing subsegment enabling production of small, geometrically complex components economically. Process advantages include exceptional design freedom, tight tolerances, and excellent surface finish rivaling machined components. Application expansion into consumer electronics, medical devices, and firearms demonstrates technology versatility and market opportunity beyond traditional industrial applications. Material development continues expanding available alloy systems making metal injection molding viable for increasingly demanding applications.
Additive Manufacturing Powders represent a transformative category with specialized requirements regarding particle size distribution, flowability, and purity. Aerospace applications drive premium powder demand with turbine components and structural parts requiring stringent quality control and material certification. Medical applications utilize additive manufacturing to produce patient-specific implants and porous structures facilitating bone ingrowth. Powder recycling becomes increasingly important for economic and sustainable operations, though process development continues addressing quality maintenance challenges.
Soft Magnetic Components serve electric motors, transformers, and electromagnetic devices where powder metallurgy enables optimized magnetic properties and complex geometries. Electric vehicle motors increasingly specify powder metallurgy soft magnetic materials achieving superior efficiency compared to traditional laminated steel cores. Material innovations including insulated powder particles and advanced iron-silicon alloys enhance performance while expanding application possibilities. Manufacturing processes must carefully control compaction pressure and sintering conditions preserving magnetic properties while achieving required mechanical strength.
Aerospace Engine Components utilize powder metallurgy’s unique capabilities to produce high-performance alloys and complex geometries impossible through conventional processing. Turbine disks manufactured through powder metallurgy achieve exceptional property uniformity and material utilization compared to forged alternatives. Additive manufacturing enables rapid prototyping and production of complex cooling passages optimizing engine efficiency and performance. Qualification requirements remain stringent with extensive testing and certification processes ensuring component reliability in demanding service conditions.
Component Manufacturers gain competitive advantages through powder metallurgy’s design flexibility, material efficiency, and precision capabilities enabling differentiation in cost-sensitive markets. Near-net-shape production reduces manufacturing costs while consistent quality and automation potential enhance operational efficiency and profitability.
Automotive OEMs benefit from powder metallurgy components offering reliable performance, cost-effective manufacturing for high-volume applications, and lightweighting opportunities supporting fuel efficiency and electric vehicle range objectives. Supply chain maturity provides confidence in component quality and delivery reliability for safety-critical applications.
Powder Producers participate in a growing market with diverse applications creating multiple revenue streams while technical expertise and quality consistency generate competitive moats. Long-term customer relationships and application development partnerships provide business stability and growth visibility.
Equipment Suppliers find attractive markets for presses, furnaces, powder handling systems, and process control technologies as powder metallurgy adoption expands globally. Service and upgrade opportunities generate recurring revenues supplementing capital equipment sales.
Research Organizations advance materials science and manufacturing technology through powder metallurgy research creating intellectual property, publication opportunities, and industry collaboration supporting funding and institutional recognition.
End Users ultimately benefit from powder metallurgy enabling component performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness that alternative manufacturing methods cannot match, contributing to product quality and competitive positioning across diverse industries.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Additive Manufacturing Integration transforms powder metallurgy from purely conventional consolidation processes to encompass advanced 3D printing technologies. Aerospace adoption leads commercial implementation with turbine components, structural parts, and complex brackets demonstrating technology viability. Powder specifications for additive manufacturing demand tighter particle size control, higher purity, and specialized flowability characteristics compared to conventional press-and-sinter applications. Hybrid manufacturing combining additive and subtractive processes optimizes cost and performance, utilizing 3D printing for complex features while employing conventional machining for critical surfaces.
Sustainable Manufacturing Focus elevates powder metallurgy’s inherent material efficiency advantages while driving additional sustainability initiatives. Recycled powder utilization in additive manufacturing and conventional processes reduces environmental impact while potentially lowering costs. Energy-efficient sintering technologies including rapid sintering and alternative heating methods reduce manufacturing carbon footprints. Lifecycle analysis demonstrates powder metallurgy environmental advantages across component lifecycles when accounting for material waste reduction and secondary operation elimination.
Digital Manufacturing Transformation enhances powder metallurgy through process monitoring, data analytics, and artificial intelligence applications. In-process monitoring systems track critical parameters during compaction and sintering enabling real-time adjustments maintaining quality consistency. Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze equipment performance data preventing unexpected failures and optimizing production schedules. Simulation tools enable virtual process optimization reducing physical trial iterations and accelerating new product development.
Advanced Material Development expands powder metallurgy capabilities beyond traditional alloy systems toward exotic materials and unique property combinations. High-entropy alloys produced through powder metallurgy demonstrate exceptional properties for extreme environment applications. Metal matrix composites combining metallic matrices with ceramic reinforcements achieve property combinations impossible through conventional metallurgy. Functionally graded materials with spatially varying compositions optimize component performance for complex service conditions.
Miniaturization Trends particularly through metal injection molding enable powder metallurgy to address increasingly small, complex components in consumer electronics, medical devices, and precision instruments. Micro-forming capabilities produce components with features measured in micrometers serving specialized applications. High-volume automation makes metal injection molding cost-competitive for small parts previously dominated by machining or other processes, with component weight reductions exceeding 75% achieved in some miniaturization applications.
Recent years have witnessed numerous significant developments influencing market trajectories. Major automotive manufacturers announced substantial electric vehicle investments fundamentally altering powder metallurgy demand patterns and application priorities across the industry. Additive manufacturing equipment costs declined significantly while capabilities improved, accelerating commercial adoption across aerospace, medical, and industrial applications driving specialized powder demand. Consolidation activity among powder metallurgy component manufacturers created larger entities with enhanced research capabilities and global manufacturing footprints serving international customers. Material innovations including new alloy compositions and advanced processing techniques expanded powder metallurgy performance boundaries enabling new application opportunities.
Industry standards evolved through collaborative efforts establishing consistent specifications for additive manufacturing powders facilitating technology adoption and reducing quality uncertainties. Sustainability initiatives by major automotive and aerospace companies established clear expectations for material efficiency and recyclability influencing powder metallurgy process development. Patent activity increased substantially with companies protecting innovations in powder production methods, novel alloy systems, and advanced consolidation processes. Strategic partnerships between powder producers and equipment manufacturers optimized integrated solutions for specific applications. Facility investments particularly in Asia and North America expanded regional manufacturing capacity addressing growing demand while improving supply chain resilience. Quality certifications for aerospace and medical applications drove process improvements and documentation rigor elevating overall industry quality standards.
Strategic planning for powder metallurgy participants should emphasize application diversification reducing automotive industry dependence while capitalizing on growth in aerospace, medical, and additive manufacturing segments. Technology investment in advanced processes including metal injection molding, additive manufacturing, and hot isostatic pressing enables premium application access and margin improvement. Material development programs focusing on novel alloys and composite systems create differentiation opportunities and intellectual property assets.
Electric vehicle transition requires proactive strategy development identifying new component opportunities in electric motors, battery systems, and thermal management while managing traditional transmission application declines. Customer collaboration during vehicle design phases ensures optimal powder metallurgy integration and protects market positions as automotive architectures evolve. Manufacturing flexibility enabling efficient small-batch production alongside high-volume operations addresses diversified market requirements across automotive and non-automotive applications.
Sustainability leadership positioning emphasizes powder metallurgy’s inherent environmental advantages while developing concrete initiatives around recycled materials, energy efficiency, and lifecycle impact reduction. Transparent reporting of environmental metrics differentiates sustainability leaders and potentially commands premium positioning with environmentally conscious customers. Circular economy integration through powder recycling programs and end-of-life component recovery aligns with automotive industry sustainability commitments.
Digital transformation investments in process monitoring, data analytics, and artificial intelligence optimization enhance operational efficiency while improving quality consistency. Workforce development programs addressing powder metallurgy expertise ensure talent availability supporting business growth and technology advancement. Academic partnerships access cutting-edge research while creating talent pipelines for specialized technical positions.
Geographic expansion into emerging markets balances growth opportunities against investment risks and competitive dynamics. Local manufacturing presence in high-growth regions demonstrates commitment while potentially accessing preferential sourcing consideration from regional customers. Supply chain resilience through diversified powder sourcing and strategic inventory management mitigates disruption risks while maintaining quality consistency.
Long-term prospects for the powder metallurgy market remain fundamentally positive despite near-term challenges from automotive industry transformation. MarkWide Research projects sustained robust growth with the sector achieving continued expansion as additive manufacturing proliferates, electric vehicle component opportunities develop, and emerging markets industrialize. Application diversification reduces historical automotive concentration creating more balanced demand patterns and improved resilience against individual industry cyclicality.
Technology evolution continues with additive manufacturing, advanced consolidation processes, and novel material systems expanding powder metallurgy capabilities and addressable markets. Metal 3D printing transitions from prototyping toward production applications across aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors driving substantial powder demand growth. Conventional process enhancement through automation, digitalization, and quality system advancement maintains competitiveness against alternative manufacturing technologies while improving cost-effectiveness.
Automotive transformation creates mixed impacts with traditional transmission and engine component applications declining while electric motor, battery system, and lightweight structural opportunities emerge. Net automotive impact likely remains positive long-term as vehicle production volumes grow globally and powder metallurgy content evolves toward new application areas. Component complexity increases as automakers pursue performance optimization and cost reduction through integrated designs leveraging powder metallurgy’s geometric freedom.
Material innovation unlocks new performance levels with advanced alloys, composites, and functionally graded materials enabling applications previously impossible through powder metallurgy processing. Lightweight materials including aluminum and titanium powder metallurgy gain traction as industries pursue weight reduction for efficiency and performance benefits. High-temperature materials for aerospace and energy applications demonstrate powder metallurgy’s unique capabilities producing components withstanding extreme service conditions.
Sustainability imperative positions powder metallurgy favorably given superior material utilization and energy efficiency relative to many alternative manufacturing processes. Circular economy integration advances with powder recycling, component remanufacturing, and end-of-life material recovery becoming standard industry practices. Carbon footprint reduction through renewable energy adoption, efficient processing, and transportation optimization aligns powder metallurgy manufacturing with global climate objectives.
Regional dynamics evolve with Asia-Pacific maintaining manufacturing leadership while North America and Europe focus on high-value applications and advanced technologies. Emerging market development in India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America creates growth opportunities as local automotive and industrial sectors expand. Supply chain reconfiguration toward regional resilience influences facility location decisions and manufacturing network strategies.
Competitive landscape may experience selective consolidation as larger entities seek scale advantages and comprehensive capabilities, though the market maintains room for specialized players focusing on specific technologies or applications. Vertical integration trends see some participants expanding across value chain stages from powder production through component manufacturing and finishing operations. Strategic partnerships between material suppliers, equipment manufacturers, and component producers create integrated solutions optimizing performance and cost for specific applications.
Investment patterns favor advanced technologies including additive manufacturing, metal injection molding, and specialized processes serving high-value applications. Capacity additions concentrate in high-growth regions and technology segments while mature conventional operations focus on efficiency improvement and automation. Research and development intensity increases as companies pursue differentiation through proprietary materials, processes, and application expertise. Quality infrastructure investments including advanced testing equipment, process monitoring systems, and data analytics capabilities support demanding aerospace, medical, and automotive applications requiring rigorous validation and documentation.
The powder metallurgy market represents a dynamic and evolving sector within advanced manufacturing, characterized by fundamental technological advantages, expanding application diversity, and continuous innovation addressing emerging industry requirements. Material efficiency leadership positions powder metallurgy favorably in an increasingly sustainability-conscious manufacturing environment where waste reduction and resource optimization carry growing importance. Despite facing challenges including automotive industry dependence, capital intensity requirements, and competition from alternative technologies, the sector demonstrates remarkable adaptability and resilience through application diversification and technological advancement. Diverse stakeholders including metal powder producers, component manufacturers, equipment suppliers, and research organizations collectively advance powder metallurgy capabilities while expanding commercial applications across industries.
Regional dynamics reveal strong manufacturing concentrations in Asia-Pacific while North America and Europe maintain sophisticated capabilities in advanced applications and premium segments. Technology convergence between conventional powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing creates synergies expanding total addressable markets while leveraging complementary strengths of established and emerging processing methods. Automotive industry transformation through electrification presents both challenges and opportunities, requiring strategic adaptation while opening new component applications in electric drivetrains and battery systems. Application expansion into aerospace, medical devices, industrial machinery, and consumer products reduces historical automotive concentration creating more balanced and resilient demand patterns. Material innovation continues unlocking new performance levels through advanced alloys, composites, and processing techniques enabling applications previously beyond powder metallurgy capabilities.
The powder metallurgy market exemplifies manufacturing technology evolution through continuous improvement, strategic adaptation, and innovation responding to changing industry requirements and emerging opportunities. As global manufacturing prioritizes sustainability, precision, and design optimization, powder metallurgy’s inherent advantages position the technology for sustained growth serving diverse industries worldwide. The sector’s outlook remains fundamentally positive supported by technological advancement, application diversification, and alignment with key manufacturing trends including lightweighting, material efficiency, and complex geometry production. Industry participants demonstrating technological leadership, application expertise, and strategic adaptability appear well-positioned to capitalize on evolving opportunities while navigating challenges inherent in a dynamic, globally competitive manufacturing landscape.
What is powder metallurgy?
Powder metallurgy is a manufacturing process that involves the production of metal parts from powdered materials. This technique is widely used for creating complex shapes and components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Who are the key players in the powder metallurgy market?
Key players in the powder metallurgy market include companies like GKN Powder Metallurgy, Hoeganaes Corporation, and PMG Group, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the powder metallurgy market?
The growth of the powder metallurgy market is driven by the increasing demand for lightweight materials in automotive applications, advancements in manufacturing technologies, and the rising need for efficient production processes.
What challenges does the powder metallurgy market face?
Challenges in the powder metallurgy market include the high initial costs of equipment, limitations in the size of parts that can be produced, and competition from alternative manufacturing methods such as casting and machining.
What opportunities exist in the powder metallurgy market?
Opportunities in the powder metallurgy market include the growing adoption of additive manufacturing techniques, the development of new alloys and materials, and the expansion of applications in renewable energy technologies.
What trends are shaping the powder metallurgy market?
Trends in the powder metallurgy market include the increasing use of automation in production processes, the rise of sustainable manufacturing practices, and the integration of smart technologies for improved quality control.
Powder Metallurgy Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | Steel, Iron, Aluminum, Others |
| Application | Automotive, Aerospace, Electrical & Electronics, Others |
| Process | Compaction, Sintering, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Powder Metallurgy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at