444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The population screening market is witnessing significant growth and is expected to expand at a steady pace in the coming years. Population screening refers to the systematic examination of a large group of individuals to identify any potential health conditions or diseases. It plays a crucial role in preventive healthcare, enabling early detection and intervention, which can lead to improved health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Meaning
Population screening involves the application of various screening tests or procedures to identify individuals at risk or affected by a particular condition within a specific population. These screenings can target a wide range of health issues, including genetic disorders, infectious diseases, chronic conditions, and cancer. The objective is to identify individuals who may benefit from further diagnostic testing, treatment, or preventive measures.
Executive Summary
The population screening market is witnessing steady growth due to increasing awareness about early disease detection and the importance of preventive healthcare. The market offers a range of screening tests and technologies, including genetic screening, imaging-based screening, laboratory tests, and point-of-care diagnostics. These screening methods are implemented in various settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and community-based screening programs.
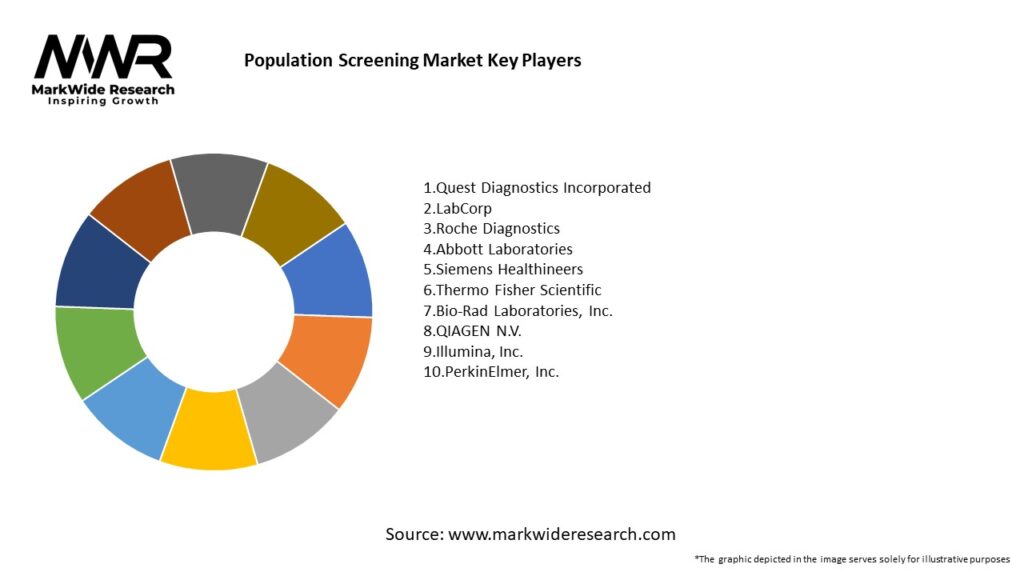
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
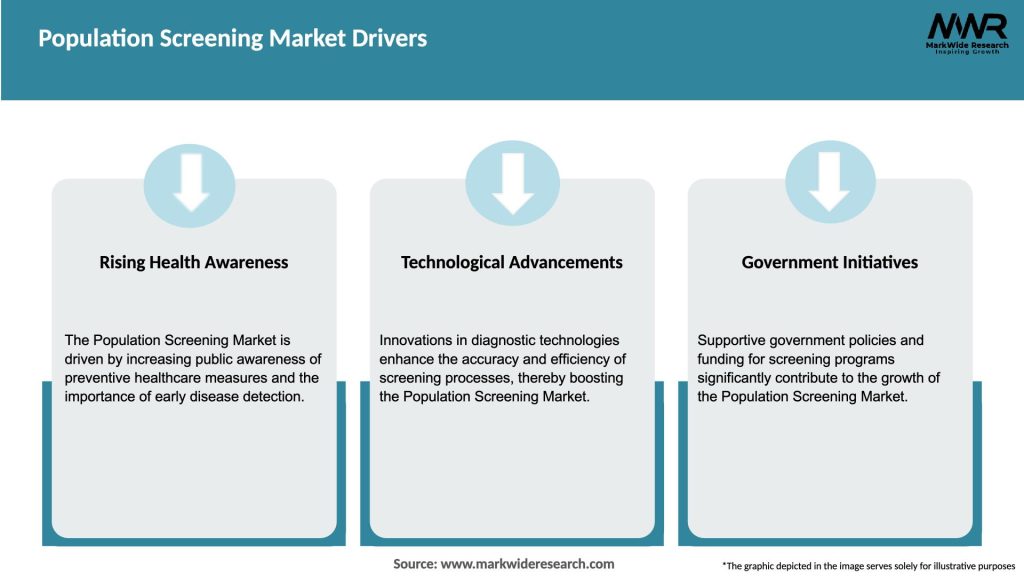
Market Dynamics
The population screening market is driven by a combination of factors, including disease burden, technological advancements, government initiatives, and growing awareness among individuals. These dynamics shape the landscape of population screening and influence market growth and adoption rates. The market is characterized by collaborations between healthcare providers, research institutions, and technology companies to develop innovative screening solutions and expand the reach of screening programs.
Regional Analysis
The population screening market exhibits regional variations based on factors such as disease prevalence, healthcare infrastructure, government policies, and cultural attitudes towards screening. North America and Europe have well-established population screening programs, supported by advanced healthcare systems and government initiatives. Asia Pacific and Latin America present significant growth opportunities due to the rising disease burden, increasing healthcare investments, and evolving healthcare policies.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Population Screening Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
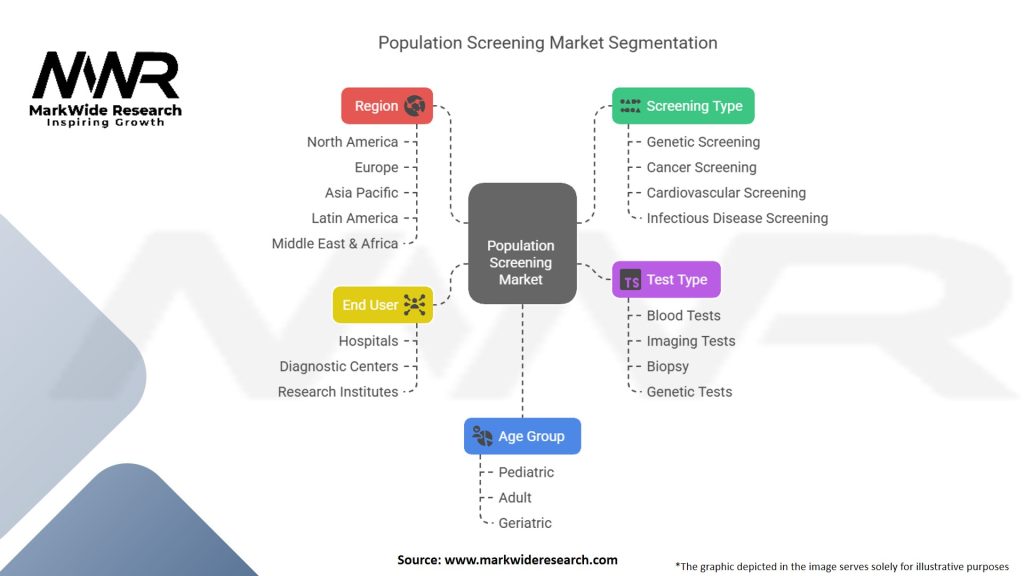
Segmentation
The population screening market can be segmented based on various factors, including screening type, target population, and geographical regions. The segmentation allows for a more detailed analysis of specific screening programs and their impact on different population groups.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted population screening programs worldwide. Many routine screenings were temporarily halted or postponed to prioritize resources for pandemic response. However, the pandemic has also highlighted the importance of population screening in identifying and managing infectious diseases. The integration of COVID-19 testing into population screening programs has become a priority, facilitating early detection and containment of the virus.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the population screening market looks promising, driven by advancements in screening technologies, growing awareness of preventive healthcare, and supportive government initiatives. The integration of AI, data analytics, and digital health solutions will further enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of screening programs. Personalized medicine will continue to shape the landscape of population screening, with a focus on targeted interventions and improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Population screening plays a vital role in preventive healthcare, enabling early disease detection, personalized treatment plans, and improved health outcomes. The market is driven by factors such as increasing disease burden, technological advancements, and government support. Ethical considerations, cost constraints, and limited accessibility present challenges to the widespread implementation of screening programs. However, emerging markets, technological innovations, and the integration of digital health solutions offer significant growth opportunities. The future of the population screening market looks promising, with a continued focus on early detection, personalized medicine, and the adoption of AI and data analytics. Collaborations, public awareness, and investments in infrastructure and resources will be crucial for the successful implementation and expansion of population screening initiatives. By prioritizing preventive healthcare through population screening, we can improve public health, reduce disease burden, and enhance the well-being of individuals and communities.
What is population screening?
Population screening refers to the systematic examination of a group of individuals to identify those at risk of a specific health condition, allowing for early intervention and management. This process is crucial in public health for conditions such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
What are the key companies in the Population Screening Market?
Key companies in the Population Screening Market include Quest Diagnostics, LabCorp, and Roche, which provide various screening tests and services. These companies are known for their innovations in diagnostic technologies and extensive testing networks, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Population Screening Market?
The Population Screening Market is driven by increasing awareness of preventive healthcare, advancements in diagnostic technologies, and rising incidences of chronic diseases. Additionally, government initiatives promoting regular health screenings contribute to market growth.
What challenges does the Population Screening Market face?
Challenges in the Population Screening Market include issues related to patient compliance, the high cost of screening programs, and disparities in access to healthcare services. These factors can hinder the effectiveness of screening initiatives.
What opportunities exist in the Population Screening Market?
Opportunities in the Population Screening Market include the development of personalized screening programs, integration of artificial intelligence in diagnostics, and expansion into emerging markets. These trends can enhance the effectiveness and reach of screening efforts.
What are the current trends in the Population Screening Market?
Current trends in the Population Screening Market include the increasing use of genetic screening, the rise of telehealth services for remote screenings, and a focus on holistic health assessments. These trends reflect a shift towards more comprehensive and accessible healthcare solutions.
Population Screening Market
| Segmentation Details | Information |
|---|---|
| Screening Type | Genetic Screening, Cancer Screening, Cardiovascular Screening, Infectious Disease Screening, Others |
| Test Type | Blood Tests, Imaging Tests, Biopsy, Genetic Tests, Others |
| End User | Hospitals, Diagnostic Centers, Research Institutes, Others |
| Age Group | Pediatric, Adult, Geriatric |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Population Screening Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at