444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The plant phenotyping market is a rapidly growing sector in the field of agriculture and plant sciences. It plays a crucial role in assessing and quantifying various plant traits, such as growth patterns, yield potential, disease resistance, and overall plant health. Plant phenotyping involves the use of advanced technologies and imaging techniques to gather data and analyze plant characteristics on a large scale. This market has gained significant traction in recent years due to the increasing demand for sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
Meaning
Plant phenotyping refers to the process of measuring and analyzing various physical and biochemical characteristics of plants. It involves the use of sophisticated equipment and techniques to capture and interpret data related to plant growth, development, and response to environmental stimuli. The aim of plant phenotyping is to understand and improve plant performance, optimize crop yield, enhance disease resistance, and develop new plant varieties with desirable traits. This field encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including biology, genetics, imaging technology, data analysis, and agronomy.
Executive Summary
The plant phenotyping market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years and is expected to continue expanding at a steady pace. Factors such as increasing global population, changing climatic conditions, and the need for sustainable food production have fueled the demand for advanced plant phenotyping technologies. These technologies enable researchers, breeders, and farmers to gain insights into plant characteristics and make informed decisions regarding crop management, breeding programs, and precision agriculture. The market is characterized by the presence of several key players offering innovative solutions and services to cater to the diverse needs of the industry.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
The plant phenotyping market is driven by several factors that are shaping the landscape of modern agriculture. These drivers include:
Market Restraints
While the plant phenotyping market shows promising growth prospects, there are certain challenges and constraints that need to be addressed. These include:
Market Opportunities
The plant phenotyping market offers several opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders. These opportunities include:
Market Dynamics
The plant phenotyping market is driven by dynamic factors that influence its growth and development. These dynamics include:
Regional Analysis
The plant phenotyping market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as agricultural practices, technological advancements, research capabilities, and economic conditions. The major regions analyzed in the market include:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Plant Phenotyping Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

Segmentation
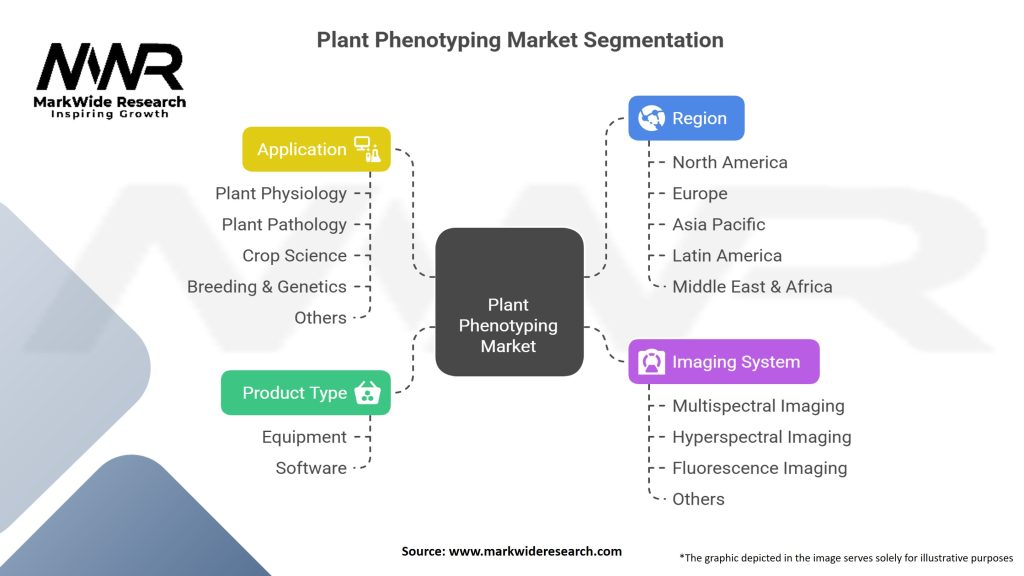
The plant phenotyping market can be segmented based on various parameters, including technology, application, end-user, and region. The key segmentation categories include:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The plant phenotyping market offers several key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, including:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides an overview of the plant phenotyping market by examining its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had both positive and negative impacts on the plant phenotyping market.
Positive Impacts:
Negative Impacts:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The plant phenotyping market is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years. Technological advancements, increasing awareness about sustainable agriculture, and the need for precision farming practices will drive market expansion. The integration of AI, robotics, and remote sensing technologies will enhance phenotyping capabilities and enable high-throughput, non-destructive, and real-time data collection. Collaboration between industry players, academia, and research organizations will foster innovation and technology transfer. Investments in data analytics, user-friendly interfaces, and standardization efforts will shape the future of plant phenotyping, facilitating informed decision-making, optimized resource utilization, and sustainable crop production.
Conclusion
The plant phenotyping market is poised for substantial growth, driven by the need for sustainable agriculture, advancements in imaging technologies, and collaborations between stakeholders. Plant phenotyping enables the assessment and quantification of various plant traits, supporting crop improvement, disease resistance, and resource optimization. While challenges such as high initial investment and data management persist, the market offers opportunities in emerging economies, precision agriculture, and crop breeding.
Integration of AI, robotics, and remote sensing will shape the future of plant phenotyping, enhancing data collection, analysis, and decision-making capabilities. Despite the Covid-19 pandemic’s disruptions, the market is expected to rebound and witness accelerated adoption of digital technologies in plant phenotyping. With continued research, innovation, and collaboration, the plant phenotyping market will contribute to sustainable and efficient agricultural practices worldwide.
What is plant phenotyping?
Plant phenotyping refers to the process of measuring and analyzing the observable characteristics of plants, such as growth patterns, morphology, and physiological traits. This data is crucial for understanding plant responses to environmental conditions and for improving crop breeding techniques.
What are the key companies in the plant phenotyping market?
Key companies in the plant phenotyping market include LemnaTec, PhenoVue, and KeyGene, which are known for their innovative technologies and solutions in plant analysis and breeding. These companies focus on providing advanced phenotyping platforms and services, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the plant phenotyping market?
The growth of the plant phenotyping market is driven by the increasing demand for food security, advancements in agricultural technology, and the need for sustainable farming practices. Additionally, the rise in research activities related to plant genetics and breeding is contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the plant phenotyping market face?
The plant phenotyping market faces challenges such as high costs associated with advanced phenotyping technologies and the complexity of data analysis. Furthermore, the integration of phenotyping data into existing agricultural practices can be difficult for some growers.
What opportunities exist in the plant phenotyping market?
Opportunities in the plant phenotyping market include the development of more affordable and user-friendly phenotyping tools, as well as the potential for collaboration between technology providers and agricultural researchers. The increasing focus on precision agriculture also presents significant growth potential.
What trends are shaping the plant phenotyping market?
Trends in the plant phenotyping market include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for data analysis, the use of high-throughput phenotyping systems, and the growing emphasis on phenomics in plant breeding programs. These innovations are enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of plant assessments.
Plant Phenotyping Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Equipment, Software |
| Imaging System | Multispectral Imaging, Hyperspectral Imaging, Fluorescence Imaging, Others |
| Application | Plant Physiology, Plant Pathology, Crop Science, Breeding & Genetics, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Plant Phenotyping Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at