444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The placental stem cell collection and storage market represents a crucial segment within the field of regenerative medicine. Placental stem cells, sourced from the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth, hold immense therapeutic potential for treating a plethora of diseases and medical conditions. The market revolves around the collection, processing, preservation, and storage of these valuable stem cells, offering hope for regenerative therapies and personalized medicine.
Meaning
Placental stem cell collection and storage entail the extraction of stem cells from the umbilical cord and placenta following childbirth, with subsequent cryopreservation for future therapeutic use. These stem cells, rich in regenerative properties, hold promise for treating various diseases and medical conditions, underscoring their significance in the realm of regenerative medicine.
Executive Summary
The placental stem cell collection and storage market have witnessed exponential growth, driven by escalating research and development endeavors, increasing awareness regarding regenerative therapies, and growing investments in healthcare infrastructure. While presenting vast opportunities for market players, the landscape is not devoid of challenges, necessitating a nuanced understanding of market dynamics, drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The placental stem cell collection and storage market operate within a dynamic landscape shaped by evolving healthcare trends, technological innovations, regulatory frameworks, and consumer preferences. A nuanced understanding of market dynamics is imperative for stakeholders to capitalize on emerging opportunities, navigate regulatory challenges, and sustain competitiveness.
Regional Analysis
Regional disparities in the placental stem cell collection and storage market are influenced by variations in healthcare infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, reimbursement policies, and cultural attitudes towards stem cell research. An in-depth analysis of regional nuances facilitates strategic decision-making and market expansion endeavors.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
Segmentation of the placental stem cell collection and storage market facilitates a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics, consumer preferences, and emerging trends, enabling stakeholders to tailor their strategies and offerings to specific market segments.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The placental stem cell collection and storage market offer several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides insights into the placental stem cell collection and storage market’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats, guiding strategic decision-making and market positioning efforts.
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has exerted both direct and indirect impacts on the placental stem cell collection and storage market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The placental stem cell collection and storage market are poised for sustained growth and innovation in the coming years, driven by escalating demand for regenerative therapies, technological advancements, and expanding applications in personalized medicine. However, regulatory challenges, ethical considerations, and technological constraints necessitate strategic foresight and proactive adaptation to emerging market dynamics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the placental stem cell collection and storage market represent a pivotal segment within the broader landscape of regenerative medicine, offering transformative therapeutic solutions for diverse medical conditions and unmet patient needs. While presenting vast opportunities for industry stakeholders, the market is not without its challenges, including regulatory complexities, ethical considerations, and technological constraints. By prioritizing innovation, regulatory compliance, and consumer education, industry stakeholders can navigate market challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities, fostering continued growth and advancement in the field of stem cell therapy and regenerative medicine.
What is Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage?
Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage refers to the process of obtaining stem cells from the placenta after childbirth and preserving them for potential future medical use. These stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, making them valuable for regenerative medicine and treatment of various diseases.
What are the key players in the Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market?
Key players in the Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market include companies like Cryo-Cell International, LifeCell International, and StemCyte, among others. These companies are involved in the collection, processing, and storage of placental stem cells for therapeutic applications.
What are the growth factors driving the Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market?
The growth of the Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market is driven by increasing awareness of regenerative medicine, advancements in stem cell research, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases. Additionally, the potential for personalized medicine is encouraging more parents to consider stem cell banking.
What challenges does the Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market face?
The Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, ethical concerns regarding stem cell use, and the high costs associated with collection and storage. These factors can limit accessibility and consumer adoption.
What opportunities exist in the Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market?
Opportunities in the Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market include expanding applications in treating various medical conditions, increasing partnerships between hospitals and stem cell banks, and growing public interest in stem cell therapies. Innovations in storage technology also present new avenues for growth.
What trends are shaping the Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market?
Trends in the Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market include the rise of public awareness campaigns about the benefits of stem cell banking, advancements in cryopreservation techniques, and the development of new therapies utilizing placental stem cells. These trends are influencing consumer choices and market dynamics.
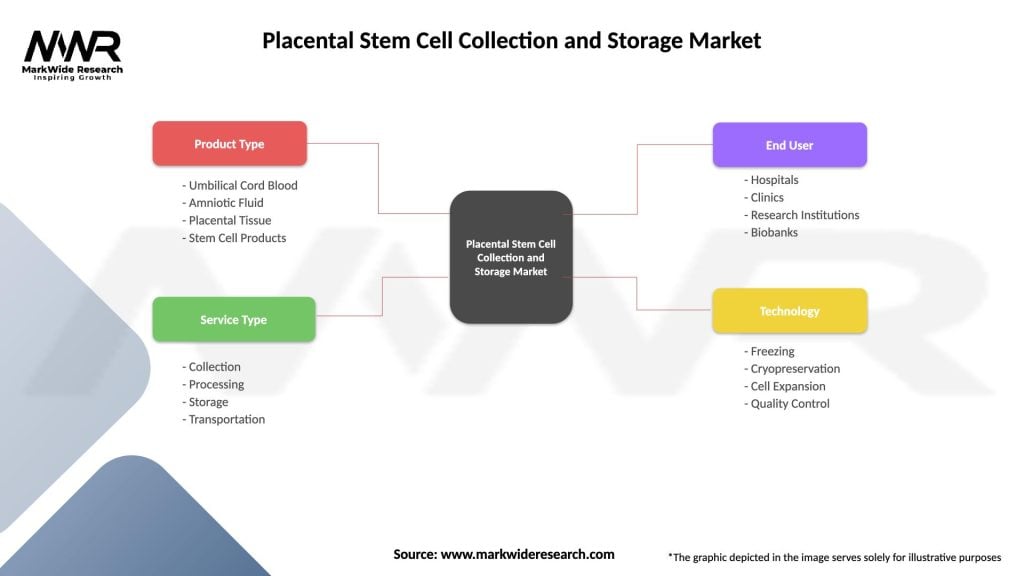
Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Umbilical Cord Blood, Amniotic Fluid, Placental Tissue, Stem Cell Products |
| Service Type | Collection, Processing, Storage, Transportation |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Research Institutions, Biobanks |
| Technology | Freezing, Cryopreservation, Cell Expansion, Quality Control |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Placental Stem Cell Collection and Storage Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at