444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Oman agriculture market represents a vital sector within the Sultanate’s economic diversification strategy, contributing significantly to food security and sustainable development initiatives. Agricultural activities in Oman encompass traditional farming practices alongside modern technological innovations, creating a dynamic landscape that supports both subsistence and commercial farming operations. The market demonstrates remarkable resilience despite challenging climatic conditions, with agricultural productivity showing consistent improvement through advanced irrigation systems and drought-resistant crop varieties.
Market dynamics indicate substantial growth potential, with the sector experiencing a 6.2% annual growth rate in agricultural output over recent years. The government’s commitment to achieving food security objectives has resulted in increased investment in agricultural infrastructure, research facilities, and farmer support programs. Diversification efforts have expanded beyond traditional date palm cultivation to include vegetables, fruits, cereals, and livestock production, creating new opportunities for market participants.
Technological integration has become increasingly prominent, with precision agriculture techniques and smart farming solutions gaining traction among progressive farmers. The adoption of hydroponics systems and greenhouse cultivation has enabled year-round production of high-value crops, contributing to improved market stability and reduced import dependency. Water management innovations continue to play a crucial role in sustaining agricultural activities, with desalination and treated wastewater utilization showing 35% efficiency improvements in water usage.
The Oman agriculture market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of agricultural production, processing, distribution, and trade activities within the Sultanate of Oman, encompassing both traditional and modern farming practices that contribute to national food security and economic development.
Agricultural significance extends beyond mere food production to include cultural preservation, environmental sustainability, and rural development initiatives. The market encompasses various subsectors including crop production, livestock farming, aquaculture, and agro-processing industries that collectively support the nation’s agricultural value chain. Traditional farming methods such as the ancient falaj irrigation system coexist with modern technologies, creating a unique agricultural landscape that reflects Oman’s rich heritage while embracing innovation.
Market participants range from smallholder farmers maintaining family traditions to large-scale commercial enterprises employing advanced agricultural technologies. The sector includes government initiatives, private sector investments, cooperative societies, and international partnerships that collectively drive agricultural development and modernization efforts throughout the country.
Strategic positioning of Oman’s agriculture market reflects the government’s commitment to achieving sustainable food security while reducing dependence on food imports. The sector demonstrates robust growth potential through diversification initiatives, technological adoption, and enhanced productivity measures that align with the Oman Vision 2040 objectives. Investment priorities focus on water-efficient farming techniques, climate-resilient crop varieties, and value-added processing capabilities that strengthen the agricultural value chain.
Market performance indicators reveal significant improvements in agricultural productivity, with crop yields increasing by 28% over the past five years through improved farming practices and technology adoption. The livestock sector has shown particular strength, contributing substantially to domestic protein production and reducing reliance on imported meat products. Export opportunities for high-quality dates, organic produce, and specialty crops continue to expand, creating new revenue streams for agricultural enterprises.
Sustainability initiatives have gained prominence, with organic farming practices and environmentally friendly production methods becoming increasingly important market differentiators. The integration of renewable energy solutions in agricultural operations has demonstrated cost savings while supporting environmental conservation goals. Digital transformation in agriculture continues to accelerate, with smart farming technologies and data-driven decision-making tools enhancing operational efficiency and crop management practices.
Agricultural diversification has emerged as a cornerstone strategy for enhancing market resilience and reducing vulnerability to external shocks. The following key insights highlight critical market developments:
Market intelligence suggests that the convergence of traditional knowledge with modern technology creates unique competitive advantages for Omani agricultural products. Quality standards have improved substantially, with many producers achieving international certifications that facilitate access to premium export markets.
Government initiatives serve as primary catalysts for agricultural market growth, with comprehensive policy frameworks supporting farmer development, infrastructure improvement, and technology adoption. The National Food Security Strategy emphasizes reducing import dependency while enhancing domestic production capabilities through targeted investments and support programs. Subsidies and incentives for modern farming equipment, irrigation systems, and greenhouse construction have accelerated the adoption of advanced agricultural practices.
Water scarcity challenges have paradoxically driven innovation in agricultural efficiency, leading to the development of sophisticated water management systems and drought-resistant crop varieties. Desalination technology integration with agricultural operations has created new possibilities for expanding cultivated areas and improving crop reliability. Climate adaptation strategies continue to drive investment in protected agriculture and controlled environment farming systems.
Consumer demand for fresh, locally produced food has strengthened market fundamentals, with increasing awareness of food quality and safety driving preference for domestic agricultural products. Tourism industry growth has created substantial demand for high-quality local produce, supporting premium pricing and encouraging quality improvements. Export opportunities in regional and international markets provide additional revenue streams and incentivize production scaling and quality enhancement initiatives.
Water availability remains the most significant constraint affecting agricultural expansion and productivity in Oman’s arid climate. Despite technological advances, water costs continue to impact farming profitability, particularly for water-intensive crops and traditional irrigation methods. Salinity issues in groundwater sources pose ongoing challenges for crop production and soil health management, requiring continuous investment in soil improvement and water treatment technologies.
Climate variability and extreme weather events create production uncertainties that affect market stability and farmer income security. High temperatures and irregular rainfall patterns limit crop selection and growing seasons, necessitating protected cultivation methods that increase production costs. Pest and disease management challenges in hot, humid conditions require ongoing investment in crop protection measures and integrated pest management systems.
Limited arable land availability constrains agricultural expansion opportunities, making intensive farming and vertical integration essential for meeting growing food demand. Skilled labor shortages in modern agricultural techniques and technology operation create bottlenecks in productivity improvement efforts. Market access challenges for smallholder farmers limit their ability to benefit from premium pricing opportunities and value-added processing initiatives.
Organic agriculture presents substantial growth opportunities as consumer awareness of health and environmental benefits continues to expand both domestically and internationally. Premium pricing for certified organic products creates attractive profit margins that justify the investment in organic certification and sustainable farming practices. Export potential for organic dates, vegetables, and specialty crops offers significant revenue enhancement opportunities for progressive farmers and agribusiness enterprises.
Agro-processing development represents a major opportunity for value addition and market expansion, with potential for establishing food processing facilities that serve both domestic and export markets. Technology partnerships with international agricultural companies can accelerate the adoption of advanced farming techniques and access to global markets. Vertical farming and controlled environment agriculture offer solutions for year-round production and water-efficient cultivation of high-value crops.
Tourism integration through agritourism initiatives can create additional revenue streams while promoting local agricultural products and traditional farming practices. Research collaboration with international institutions can accelerate the development of climate-adapted crop varieties and innovative farming techniques. Financial technology applications in agriculture, including digital payment systems and crop insurance products, can improve market access and risk management for farmers.
Supply chain evolution continues to reshape market dynamics, with improved logistics infrastructure and cold storage facilities enhancing product quality and market reach. Digital platforms are transforming agricultural marketing, enabling direct farmer-to-consumer sales and reducing intermediary costs. Price volatility management through forward contracting and cooperative marketing initiatives provides greater income stability for agricultural producers.
Seasonal production patterns influence market dynamics significantly, with greenhouse cultivation and protected agriculture helping to stabilize supply throughout the year. Import substitution efforts continue to drive domestic production expansion, with local production meeting 42% of vegetable demand through improved farming techniques. Quality differentiation has become increasingly important, with premium products commanding higher prices in both domestic and export markets.
Competitive dynamics are shifting toward sustainability and innovation, with farmers adopting new technologies to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Collaboration networks among farmers, researchers, and technology providers are accelerating knowledge transfer and best practice adoption. Market consolidation trends are emerging as larger agricultural enterprises acquire smaller operations to achieve economies of scale and improve market competitiveness.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into Oman’s agricultural sector. Primary research includes extensive interviews with farmers, agricultural cooperatives, government officials, and industry stakeholders to gather firsthand insights into market conditions and trends. Field surveys across different agricultural regions provide detailed information about farming practices, productivity levels, and technology adoption rates.
Secondary research incorporates analysis of government statistics, agricultural reports, and industry publications to establish baseline market data and historical trends. Quantitative analysis of production data, trade statistics, and economic indicators provides measurable insights into market performance and growth patterns. Qualitative assessment of policy impacts, technological developments, and market dynamics offers deeper understanding of factors influencing agricultural development.
Data validation processes ensure accuracy and reliability through cross-referencing multiple sources and expert review of findings. Market modeling techniques project future trends based on current market dynamics and anticipated policy changes. Stakeholder feedback sessions validate research findings and provide additional insights into market opportunities and challenges facing the agricultural sector.
Northern regions of Oman, including Al Batinah, demonstrate the highest agricultural productivity due to favorable coastal climate conditions and established irrigation infrastructure. Date palm cultivation dominates this region, with 65% of national date production concentrated in Al Batinah governorates. Vegetable production has expanded significantly through greenhouse cultivation and modern farming techniques, serving both local markets and export opportunities.
Interior regions focus primarily on traditional agriculture and livestock farming, with goat and sheep production representing major economic activities. Oasis agriculture continues to play an important role in these areas, with ancient falaj systems supporting sustainable farming practices. Organic farming initiatives are gaining traction in interior regions due to minimal chemical input usage and traditional farming methods.
Southern regions including Dhofar benefit from unique monsoon climate conditions that support different crop varieties and agricultural practices. Coconut cultivation and tropical fruit production distinguish this region from other parts of Oman. Livestock grazing during the monsoon season provides additional agricultural income for rural communities. Frankincense production remains an important traditional agricultural activity with significant cultural and economic value.
Market leadership in Oman’s agriculture sector is distributed among various types of enterprises, from traditional family farms to modern commercial operations. Key players include:
Competitive strategies focus on technology adoption, quality improvement, and market diversification to maintain competitive advantages. Innovation initiatives include precision agriculture, automated irrigation systems, and integrated pest management programs. Strategic partnerships with international agricultural companies provide access to advanced technologies and global market opportunities.
By Crop Type:
By Farming Method:
By End Use:
Date palm cultivation remains the cornerstone of Omani agriculture, with over 8 million date palms producing various premium varieties that command high prices in international markets. Traditional varieties such as Khalas, Fard, and Naghal maintain strong cultural significance while newer varieties offer improved yield and disease resistance. Value-added processing of dates into paste, syrup, and other products creates additional revenue opportunities for producers.
Vegetable production has experienced remarkable growth through greenhouse cultivation and modern farming techniques, with tomato production increasing by 45% over recent years. Cucumber cultivation in controlled environments has achieved year-round production capabilities, reducing import dependency significantly. Leafy greens production using hydroponic systems demonstrates exceptional water efficiency while meeting growing consumer demand for fresh, locally produced vegetables.
Livestock farming contributes substantially to agricultural income, with goat and sheep production well-adapted to local climate conditions and traditional farming practices. Dairy farming has modernized significantly, with improved breeds and feeding practices enhancing milk production and quality. Poultry production meets a significant portion of domestic egg and meat demand through modern production facilities and integrated supply chains.
Farmers benefit from government support programs, subsidized inputs, and technical assistance that improve productivity and profitability. Access to modern technology through leasing programs and grants enables smallholder farmers to adopt advanced farming techniques without significant capital investment. Cooperative membership provides collective bargaining power, shared resources, and access to larger markets that individual farmers cannot reach independently.
Consumers enjoy increased availability of fresh, locally produced food that reduces dependence on imports and ensures food security. Quality improvements in local agricultural products provide better nutrition and food safety compared to imported alternatives. Price stability through domestic production helps control food inflation and reduces vulnerability to international market fluctuations.
Government achieves strategic objectives including food security, economic diversification, and rural development through agricultural sector growth. Employment creation in rural areas helps reduce urban migration and maintains traditional communities. Export earnings from high-quality agricultural products contribute to foreign exchange reserves and economic stability. Environmental benefits from sustainable farming practices support conservation goals and climate change mitigation efforts.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital agriculture is transforming traditional farming practices through IoT sensors, satellite monitoring, and data analytics that optimize resource usage and improve crop management. Smart irrigation systems automatically adjust water application based on soil moisture and weather conditions, achieving significant water savings. Drone technology for crop monitoring and precision application of fertilizers and pesticides is gaining adoption among progressive farmers.
Sustainable farming practices are becoming mainstream as environmental awareness increases and consumers demand eco-friendly products. Integrated pest management reduces chemical pesticide usage while maintaining crop protection effectiveness. Soil health improvement through organic matter addition and cover cropping enhances long-term productivity and environmental sustainability.
Vertical integration trends see agricultural producers expanding into processing, packaging, and direct marketing to capture greater value from their products. Contract farming arrangements provide guaranteed markets and stable prices for farmers while ensuring consistent supply for processors and retailers. Cooperative strengthening enables smallholder farmers to access modern technology, bulk purchasing benefits, and collective marketing opportunities.
Government initiatives have established new agricultural research centers focused on developing climate-adapted crop varieties and sustainable farming techniques. Public-private partnerships are accelerating technology transfer and infrastructure development in rural agricultural areas. Investment incentives for agricultural projects have attracted both domestic and international investors to the sector.
Infrastructure improvements include expanded cold storage facilities, improved rural road networks, and enhanced market facilities that strengthen the agricultural value chain. Water infrastructure projects including new desalination plants and treated wastewater systems provide additional water resources for agricultural use. Research collaborations with international institutions are developing innovative solutions for desert agriculture and water-efficient farming.
Technology partnerships with leading agricultural companies have introduced advanced greenhouse systems, precision agriculture tools, and automated farming equipment. Financial services tailored for agriculture, including crop insurance and equipment financing, provide better risk management and investment opportunities for farmers. Market development initiatives are expanding export opportunities and establishing new trade relationships for Omani agricultural products.
MarkWide Research analysis indicates that continued investment in water-efficient technologies and climate-adapted crop varieties will be essential for sustaining agricultural growth in Oman’s challenging environment. Strategic recommendations emphasize the importance of strengthening farmer education programs and technical support services to accelerate technology adoption and improve productivity.
Market development efforts should focus on building stronger linkages between producers and export markets, particularly for high-value crops such as organic dates and specialty vegetables. Value chain integration through processing and packaging capabilities can significantly enhance profitability and market competitiveness. Sustainability certification programs should be prioritized to access premium markets and meet growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Investment priorities should include renewable energy integration in agricultural operations, advanced greenhouse technologies, and digital farming solutions that improve efficiency and reduce operational costs. Policy support for agricultural research and development will be crucial for maintaining innovation momentum and addressing emerging challenges. Regional cooperation in agricultural trade and technology sharing can create mutual benefits and strengthen food security across the Gulf region.
Long-term prospects for Oman’s agriculture market remain positive, driven by continued government support, technological advancement, and growing demand for locally produced food. Production capacity is expected to expand through improved farming techniques and increased cultivation area under protected agriculture systems. Export potential for premium agricultural products will continue to grow as quality standards improve and international market access expands.
Technology integration will accelerate, with artificial intelligence and machine learning applications optimizing farming operations and resource management. Sustainability initiatives will become increasingly important, with carbon-neutral farming practices and renewable energy adoption becoming standard industry practices. Market diversification will reduce dependency on traditional crops and create new revenue opportunities through specialty and niche products.
MWR projections suggest that the agricultural sector will achieve 8.5% annual growth over the next five years through continued modernization and market expansion efforts. Water management innovations will enable sustainable expansion of agricultural activities while maintaining environmental conservation goals. Regional leadership in sustainable desert agriculture will position Oman as a knowledge hub and technology exporter for similar climatic regions worldwide.
Oman’s agriculture market demonstrates remarkable resilience and growth potential despite challenging environmental conditions, supported by strong government commitment, technological innovation, and strategic market development initiatives. The sector’s evolution from traditional farming practices to modern, technology-enhanced agriculture reflects successful adaptation to changing market demands and environmental constraints. Sustainable development principles guide market growth, ensuring long-term viability while meeting immediate food security objectives.
Strategic positioning of the agricultural sector within Oman’s economic diversification plans creates substantial opportunities for continued growth and development. Investment in technology, infrastructure, and human capital development will be essential for maintaining competitive advantages and achieving market expansion goals. The integration of traditional knowledge with modern farming techniques creates unique value propositions that differentiate Omani agricultural products in both domestic and international markets.
Future success will depend on continued innovation, sustainable resource management, and strategic market development that leverages Oman’s strengths while addressing inherent challenges. The Oman agriculture market is well-positioned to achieve significant growth and contribute meaningfully to national economic objectives while maintaining environmental sustainability and cultural heritage preservation.
What is Oman Agriculture?
Oman Agriculture refers to the practices and industries involved in the cultivation of crops and livestock in Oman. This sector plays a crucial role in the country’s economy, providing food security and employment opportunities.
What are the key players in the Oman Agriculture Market?
Key players in the Oman Agriculture Market include Oman Food Investment Holding Company, Al Harthy Agricultural Company, and Dhofar Cattle Feed Company, among others. These companies are involved in various agricultural activities, from crop production to livestock management.
What are the growth factors driving the Oman Agriculture Market?
The Oman Agriculture Market is driven by factors such as increasing demand for local food production, government initiatives to promote sustainable farming, and advancements in agricultural technology. These elements contribute to enhancing productivity and food security in the region.
What challenges does the Oman Agriculture Market face?
The Oman Agriculture Market faces challenges such as water scarcity, limited arable land, and the impact of climate change. These factors can hinder agricultural productivity and sustainability efforts in the country.
What opportunities exist in the Oman Agriculture Market?
Opportunities in the Oman Agriculture Market include the potential for organic farming, investment in agritech solutions, and the development of export markets for local produce. These avenues can enhance the sector’s growth and sustainability.
What trends are shaping the Oman Agriculture Market?
Trends in the Oman Agriculture Market include the adoption of precision farming techniques, increased focus on sustainable practices, and the integration of technology in farming operations. These trends are transforming how agriculture is practiced in Oman.
Oman Agriculture Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
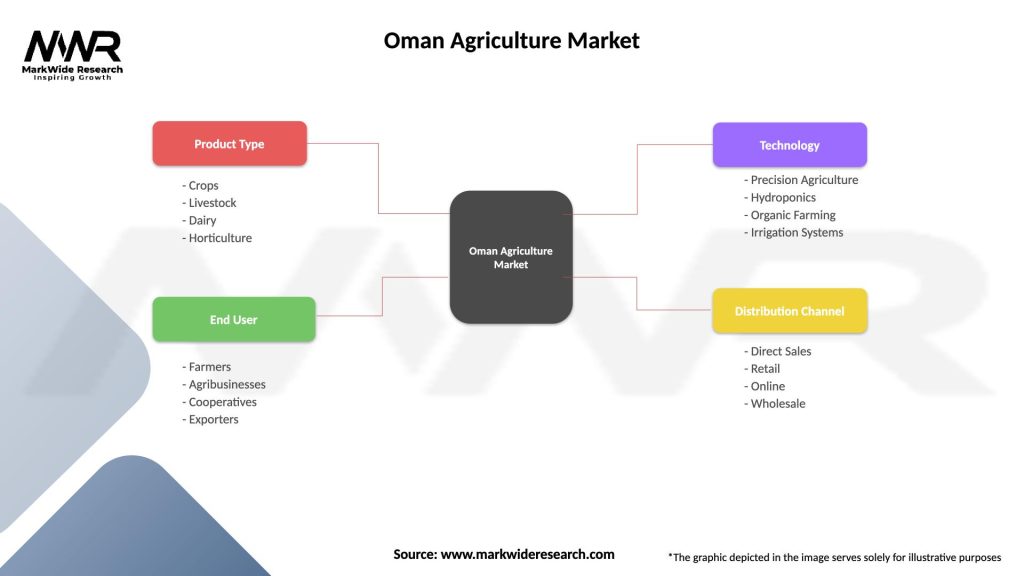
| Product Type | Crops, Livestock, Dairy, Horticulture |
| End User | Farmers, Agribusinesses, Cooperatives, Exporters |
| Technology | Precision Agriculture, Hydroponics, Organic Farming, Irrigation Systems |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Retail, Online, Wholesale |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Oman Agriculture Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at